Содержание
- 2. Key focus in this background lecture: The strategic context of CSR: vision, mission, strategy and tactics
- 3. vision, mission, strategy and tactics example: a food bank Vision: Mission: Strategy: Tactics:
- 4. Constraints and the need for a strategic lens: CSR filter Organizational constraints . . . Policy
- 5. Vision, mission, strategy and tactics are limited by these restraints, for example Organizational constraints Environmental constraints
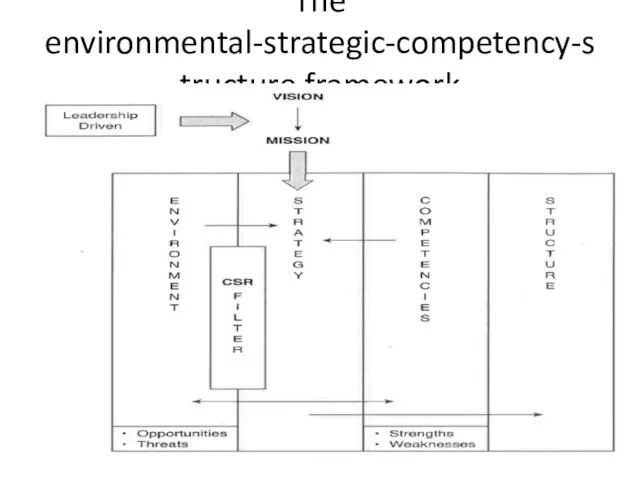
- 6. The environmental-strategic-competency-structure framework
- 7. CSR filter
- 8. CSR filter, back to the IKEA example: The basic thinking behind all IKEA products is that
- 9. The development of business ethics: the example of North America – 5 stages
- 10. The development of business ethics: Start with the 1920’s in the USA: focus on: living wage;
- 11. The development of business ethics: Example Sarbanes Oxley Act SOX: aspects: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
- 13. Скачать презентацию









 Белорусское производство автомобилей
Белорусское производство автомобилей Масло жизни из зародышей пшеницы
Масло жизни из зародышей пшеницы Открытки с 1 сентября
Открытки с 1 сентября Новые бизнес. Возможности работы в интернете
Новые бизнес. Возможности работы в интернете Особливості реклами в Фінляндії
Особливості реклами в Фінляндії Комерческое предложение к деловому сотрудничеству. Агрохолдинг ЗАО Алтайская крупа
Комерческое предложение к деловому сотрудничеству. Агрохолдинг ЗАО Алтайская крупа Маркетинг. Маркетинговая стратегия 4P+STP
Маркетинг. Маркетинговая стратегия 4P+STP Операционный стандарт по послепродажному обслуживанию. Проверка качества выполненных работ пере выдачей автомобиля
Операционный стандарт по послепродажному обслуживанию. Проверка качества выполненных работ пере выдачей автомобиля Личный кабинет. Теле 2
Личный кабинет. Теле 2 SMM Adept. Продвижение бренда в социальных сетях
SMM Adept. Продвижение бренда в социальных сетях Новогоднее оформление торговых центров
Новогоднее оформление торговых центров Продается дом в г. Сочи
Продается дом в г. Сочи Network of flower shops Gentle Lotus
Network of flower shops Gentle Lotus Группа компаний ИнструмСнаб
Группа компаний ИнструмСнаб Стоковая фотография. Микростоки – интернет-магазины фотографий
Стоковая фотография. Микростоки – интернет-магазины фотографий Демонстрационная стойка. Терминал
Демонстрационная стойка. Терминал Потребительские методы органолептической оценки продуктов питания
Потребительские методы органолептической оценки продуктов питания Продажа нежилого здания с земельным участком в Малопургинском районе, село Бураново
Продажа нежилого здания с земельным участком в Малопургинском районе, село Бураново Детальніше про новинки. Новорічний талісман
Детальніше про новинки. Новорічний талісман Молодежный туризм в Европе
Молодежный туризм в Европе Фасадные панели NORDSIDE
Фасадные панели NORDSIDE Оконечное абонентское оборудование мониторинга
Оконечное абонентское оборудование мониторинга Автоматизация работы салона красоты Арника
Автоматизация работы салона красоты Арника Медицинские компрессоры серии F REMEZA 2016
Медицинские компрессоры серии F REMEZA 2016 Штамп-эмоция. Из чего состоит хороший заголовок
Штамп-эмоция. Из чего состоит хороший заголовок Создание и модернизация предприятий под ключ
Создание и модернизация предприятий под ключ Creative. Event end entertainment
Creative. Event end entertainment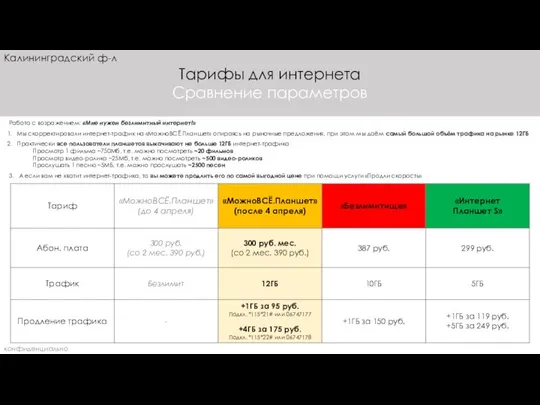 Интернет-тарифы. Калининград
Интернет-тарифы. Калининград