Содержание
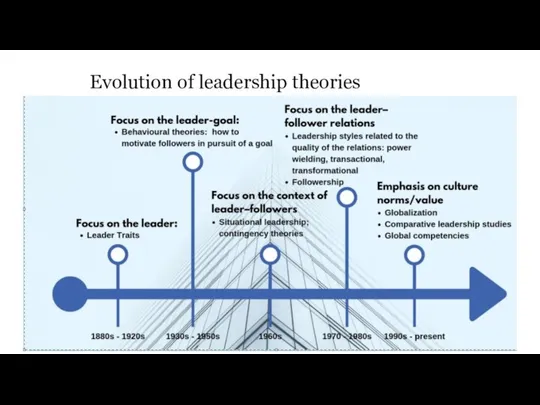
- 2. Evolution of leadership theories
- 3. Basics Transactional leadership theory was first described by Max Weber and developed by M. Bass in
- 4. Transactional leadership style follows these basic steps
- 5. Transactional leadership focuses on results conforms to the existing structure of an organization and measures success
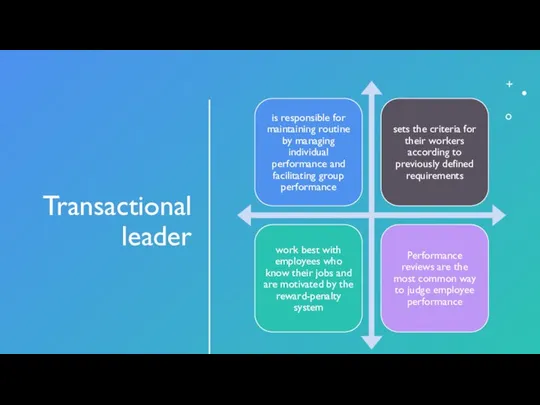
- 6. Transactional leader
- 7. Dimensions of transactional leadership
- 8. Contingent Reward It focuses on achieving results. Humans receive concrete, tangible, material rewards in exchange of
- 9. Management by Exception (Active) Leaders expect their workers to perform the job to a satisfactory standard.
- 10. Management by Exception (Passive) Leaders avoid specifying agreement, and fail to provide goals and standards to
- 11. Pros of Transactional Leadership
- 12. Cons of Transactional Leadership Rewards the worker on a practical level only, such as money or
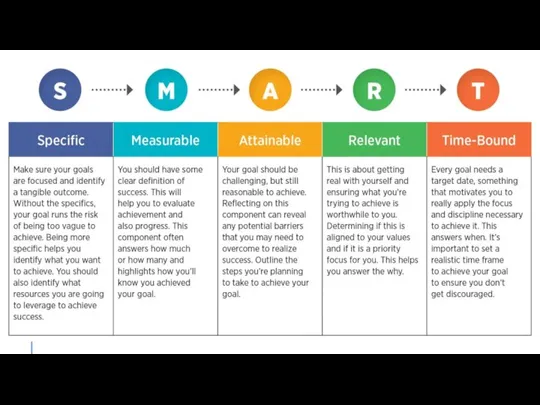
- 13. GOAL SETTING
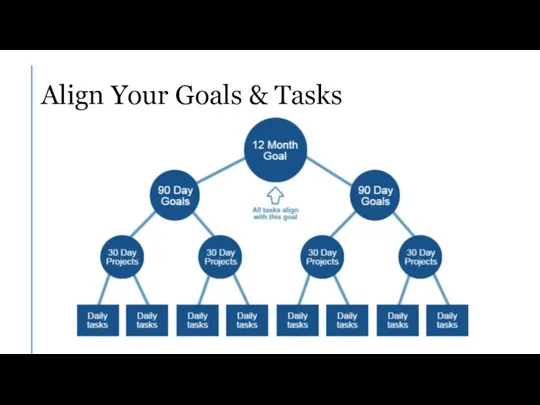
- 15. Align Your Goals & Tasks
- 16. FEEDBACK & PERFORMANCE REVIEWS
- 17. High-Quality feedback
- 18. High-Quality feedback
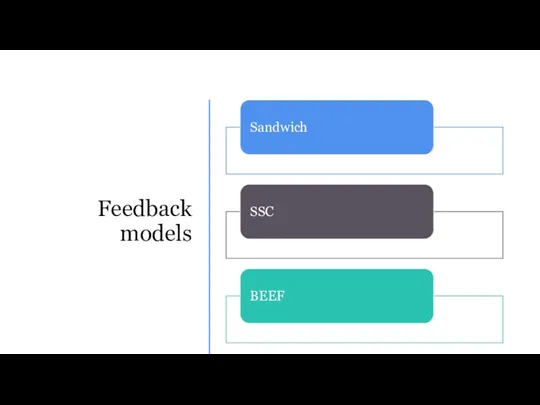
- 19. Feedback models
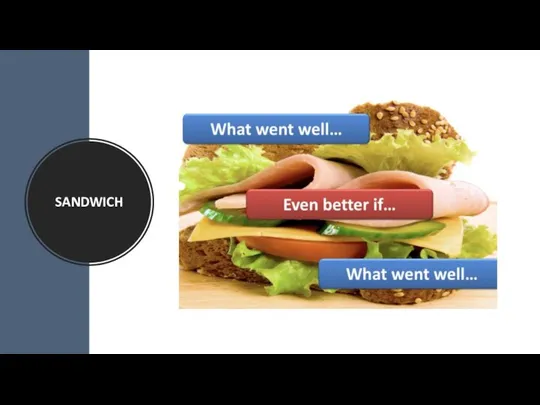
- 20. SANDWICH
- 21. STOP-START-CONTINUE
- 22. BEEF
- 23. Exercise Scenarios of a work situation
- 24. Dealing with reactions – H.E.A.R. model
- 26. Скачать презентацию

















 Сервисы для повышения конверсии. Онлайн-консультант
Сервисы для повышения конверсии. Онлайн-консультант Theatreslides
Theatreslides Samsung Galaxy A7 (2016)
Samsung Galaxy A7 (2016) Матрица направленной политики компании Шелл
Матрица направленной политики компании Шелл Магазин мобильной связи In the network
Магазин мобильной связи In the network SEO-практик: 10 шагов к результату
SEO-практик: 10 шагов к результату г. Витебск, Бешенковичское шоссе (арочная конструкция)
г. Витебск, Бешенковичское шоссе (арочная конструкция) Интернет-маркетинг. Базовый практико-ориентированный курс
Интернет-маркетинг. Базовый практико-ориентированный курс История витрин. Первые витрины XVIII – XIV веков
История витрин. Первые витрины XVIII – XIV веков Брендбук
Брендбук Lecture 01. Introduction to the role of market research
Lecture 01. Introduction to the role of market research Ведущий Анатолий Товпенец
Ведущий Анатолий Товпенец LangHack
LangHack Классическая модель повседневных прозрачных эластичных колготок с шортиками
Классическая модель повседневных прозрачных эластичных колготок с шортиками Анализ рациональности и конкурентоспособности ассортимента игрушек
Анализ рациональности и конкурентоспособности ассортимента игрушек План схема а5
План схема а5 Международные чтения. Восприятие творчества Ф.М. Достоевского в современном мире
Международные чтения. Восприятие творчества Ф.М. Достоевского в современном мире Размещение маркетинговых материалов при высадке банка Открытие в офисах Росгосстраха
Размещение маркетинговых материалов при высадке банка Открытие в офисах Росгосстраха Производственно-преддипломная практика в организации ТОО Барыс 2007
Производственно-преддипломная практика в организации ТОО Барыс 2007 Маркетинг в сфере информационных услуг
Маркетинг в сфере информационных услуг Магазин Пятая передача Волгодонск
Магазин Пятая передача Волгодонск Мастер класс-тренажер. План продвижения бизнеса в Instagram
Мастер класс-тренажер. План продвижения бизнеса в Instagram Автобусные туры в Грузию 2018 от Сэвэн Трэвел
Автобусные туры в Грузию 2018 от Сэвэн Трэвел Организация корпоративного нового года
Организация корпоративного нового года Львівська майстерня шоколаду
Львівська майстерня шоколаду Магазин открыток Dream Shop
Магазин открыток Dream Shop Браслеты и Фенечки
Браслеты и Фенечки О журнале Телепрограмма
О журнале Телепрограмма