Содержание
- 2. NEW IN CLASS? Send me an email to the following address: susanne.saral@okan.edu.tr DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL
- 3. Activation of piazza.com account Enter your first and last name Select : Undergraduate Select : Economy
- 4. Organizing categorical data Categorical data produce values that are names, words or codes, but not real
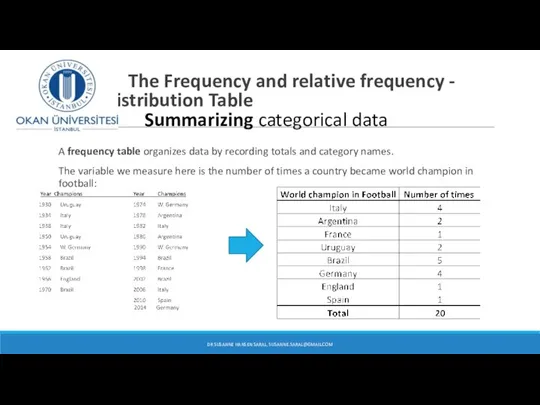
- 5. The Frequency and relative frequency - Distribution Table Summarizing categorical data A frequency table organizes data
- 6. Contingency table another type of frequency table Contingency tables list the number of observations for every
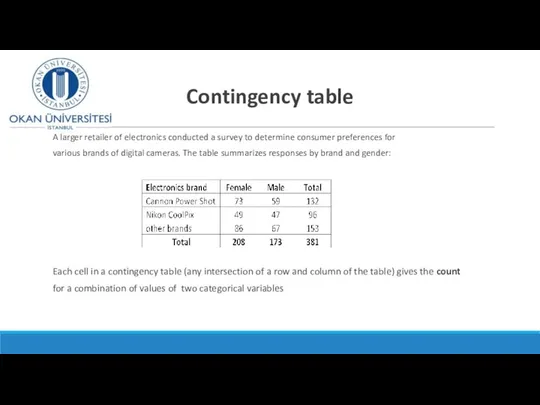
- 7. Contingency table A larger retailer of electronics conducted a survey to determine consumer preferences for various
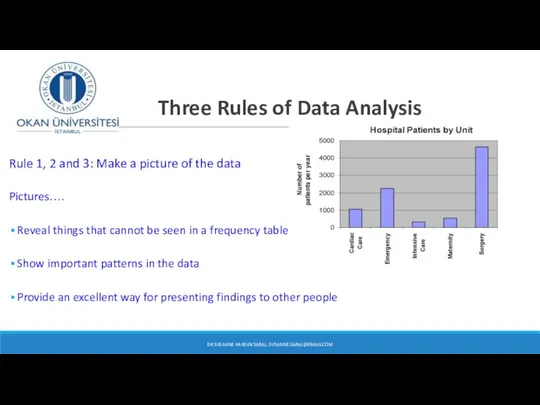
- 8. Three Rules of Data Analysis Rule 1, 2 and 3: Make a picture of the data
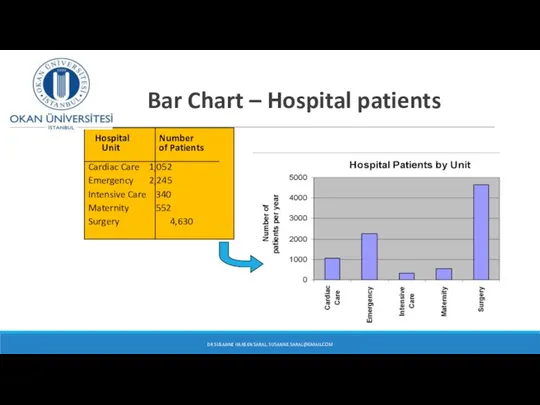
- 9. Bar Chart – Hospital patients DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL, SUSANNE.SARAL@GMAIL.COM Hospital Number Unit of Patients Cardiac
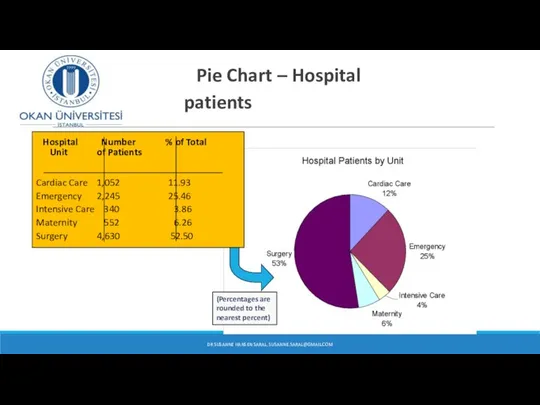
- 10. Pie Chart – Hospital patients DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL, SUSANNE.SARAL@GMAIL.COM (Percentages are rounded to the nearest
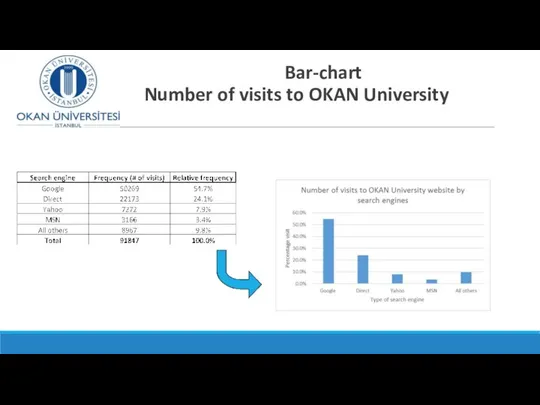
- 11. Bar-chart Number of visits to OKAN University website
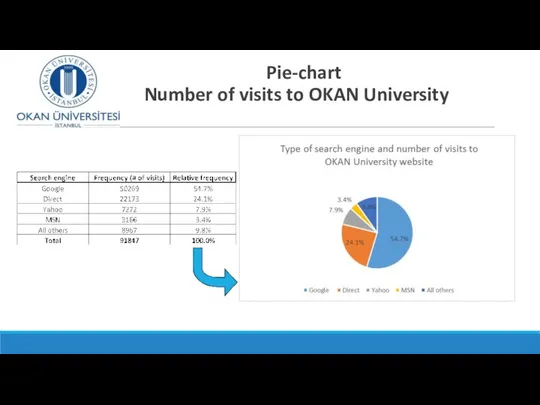
- 12. Pie-chart Number of visits to OKAN University website
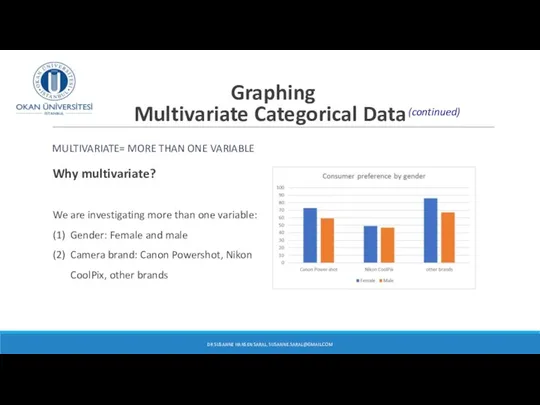
- 13. Graphing Multivariate Categorical Data MULTIVARIATE= MORE THAN ONE VARIABLE Why multivariate? We are investigating more than
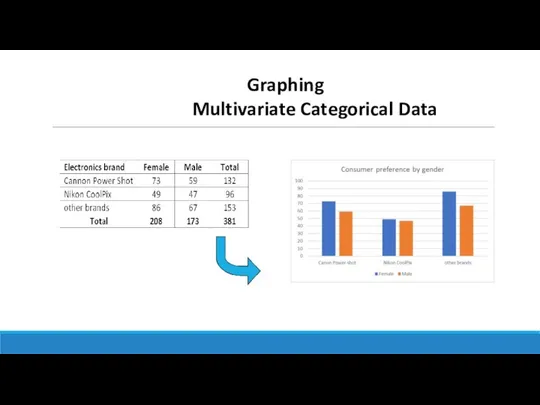
- 14. Graphing Multivariate Categorical Data
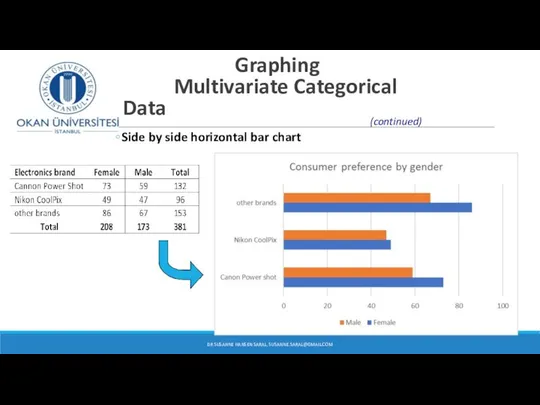
- 15. Graphing Multivariate Categorical Data Side by side horizontal bar chart DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL, SUSANNE.SARAL@GMAIL.COM (continued)
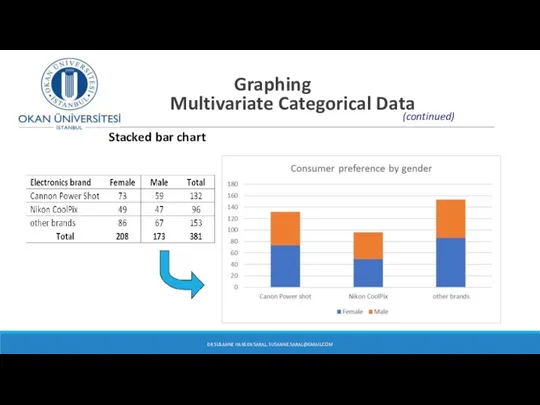
- 16. Graphing Multivariate Categorical Data Stacked bar chart DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL, SUSANNE.SARAL@GMAIL.COM (continued)
- 17. Class exercise The following raw data show responses to the question “What is your primary source
- 18. Class exercise A cable company surveyed its customers and asked how likely they were to bundle
- 19. Week 2 (2) How to organize and illustrate numerical data DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL EMAIL: SUSANNE.SARAL@OKAN.EDU.TR
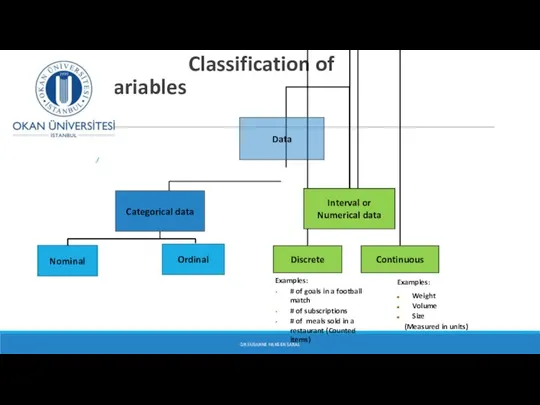
- 20. Classification of Variables DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL Examples: # of goals in a football match #
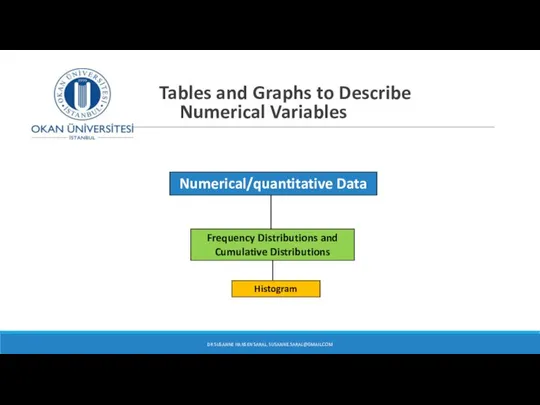
- 21. Numerical/quantitative Data Histogram Frequency Distributions and Cumulative Distributions Tables and Graphs to Describe Numerical Variables DR
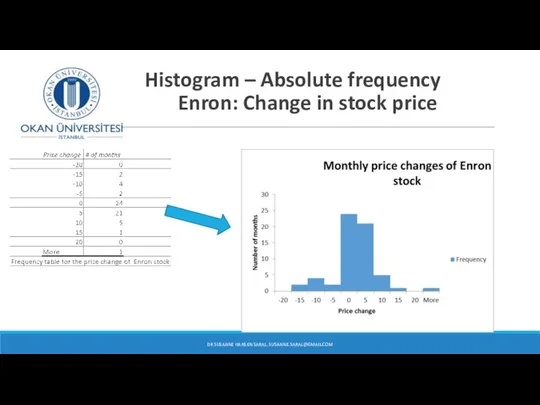
- 22. Enron Corporation - energy trading company Energy trading company from 1985 – 2001 (then went bankrupt):
- 23. Enron Corporation - energy trading company Energy trading company from 1985 – 2001: Were there any
- 24. Enron Corporation - energy trading company Energy trading company from 1985 – 2001: Were there any
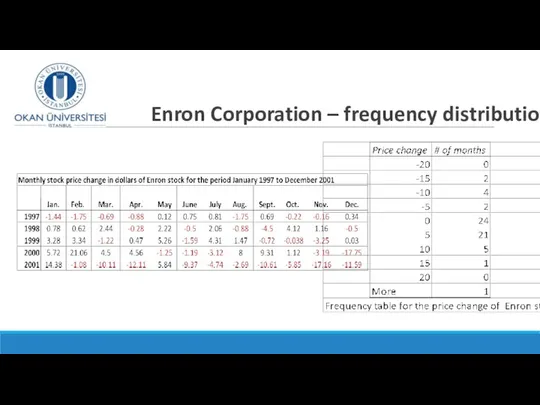
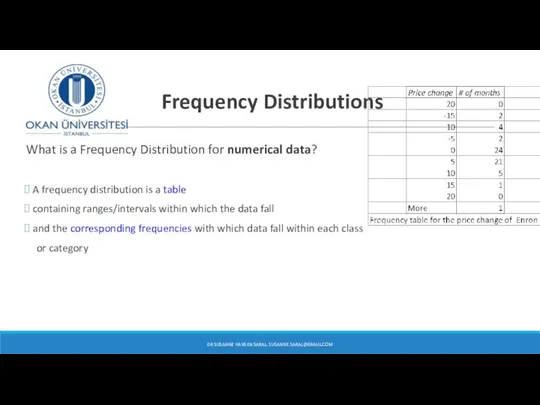
- 26. Enron Corporation – frequency distribution
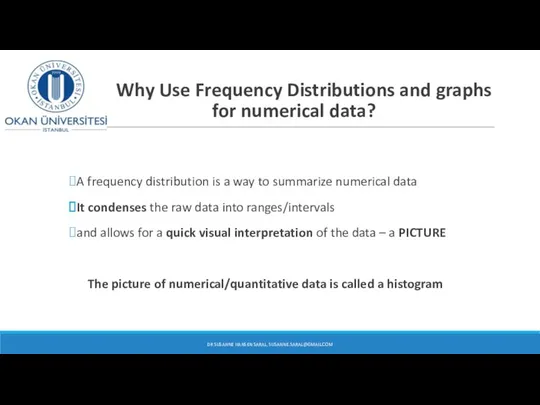
- 28. Why Use Frequency Distributions and graphs for numerical data? A frequency distribution is a way to
- 29. Frequency Distributions What is a Frequency Distribution for numerical data? A frequency distribution is a table
- 30. Frequency Distributions for numerical data Intervals for numerical data are not as easy to identify as
- 31. Raw data (sample of 110 employees in a production plant) Completion Times of a particular task
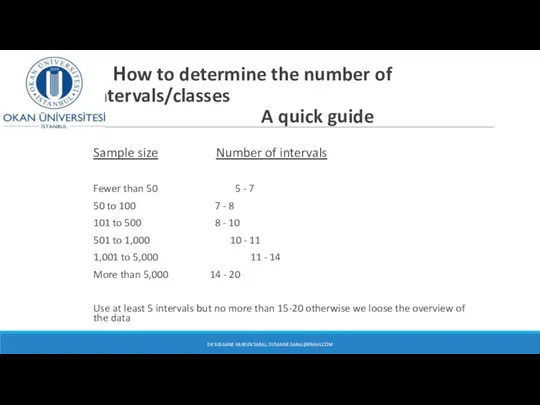
- 32. How to determine the number of intervals/classes A quick guide Sample size Number of intervals Fewer
- 33. How to determine the interval width Each class/interval grouping has to have the same width Determine
- 34. Employee completion time 110 employees’ time have been recorded and the plant supervisor needs to report
- 35. Employee completion time DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL, SUSANNE.SARAL@GMAIL.COM
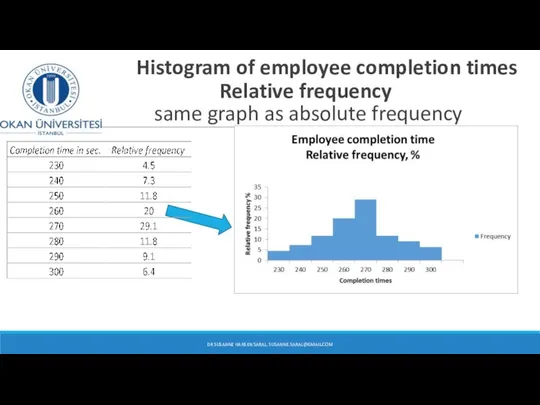
- 36. Employee completion time Completion time (in seconds) Frequency Relative frequency % 220 – 229 5 4.5
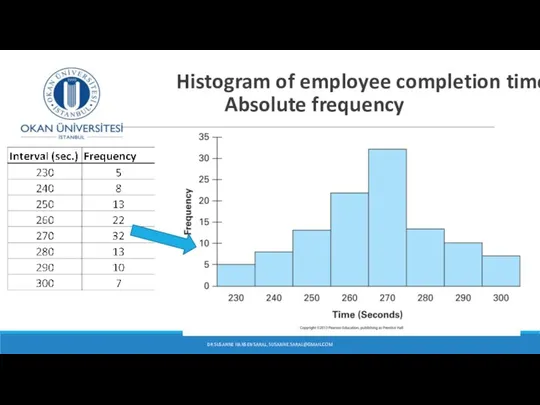
- 37. Histogram of employee completion times Absolute frequency DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL, SUSANNE.SARAL@GMAIL.COM
- 38. Histogram of employee completion times Relative frequency same graph as absolute frequency DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL,
- 39. Employee completion time Cumulative frequency DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL, SUSANNE.SARAL@GMAIL.COM
- 40. Histogram – Absolute frequency Enron: Change in stock price DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL, SUSANNE.SARAL@GMAIL.COM
- 42. Скачать презентацию

















 Кодирование факторов
Кодирование факторов Нижние оценки
Нижние оценки Начертательная геометрия. Положение прямой относительно плоскости проекций. (Лекция 2)
Начертательная геометрия. Положение прямой относительно плоскости проекций. (Лекция 2) Признаки делимости на 3 и 9 (записываем № вопроса и выбранное число или слово)
Признаки делимости на 3 и 9 (записываем № вопроса и выбранное число или слово) Объём прямоугольного параллелепипеда
Объём прямоугольного параллелепипеда Математика в изобразительном искусстве
Математика в изобразительном искусстве Урок 2. Новое из истории развития математики
Урок 2. Новое из истории развития математики Симметрия в пространстве
Симметрия в пространстве Презентация на тему СЛОЖЕНИЕ И ВЫЧИТАНИЕ ДВУЗНАЧНЫХ ЧИСЕЛ Урок математики во 2 классе
Презентация на тему СЛОЖЕНИЕ И ВЫЧИТАНИЕ ДВУЗНАЧНЫХ ЧИСЕЛ Урок математики во 2 классе Умножение десятичных дробей
Умножение десятичных дробей Составление комбинаторных и учебно-практических задач разными способами
Составление комбинаторных и учебно-практических задач разными способами Свойства функций, непрерывных на отрезке
Свойства функций, непрерывных на отрезке Презентация по математике "Путешествие в город Математинск" - скачать
Презентация по математике "Путешествие в город Математинск" - скачать  Предварительная обработка экспериментальных данных
Предварительная обработка экспериментальных данных Suboptimal control in the stochastic nonlinear dynamic systems
Suboptimal control in the stochastic nonlinear dynamic systems Статистические группировки
Статистические группировки Qeyri stasionar qaz dinamikasi. Tənliyinin riyazi modelinin. Qurulmasi
Qeyri stasionar qaz dinamikasi. Tənliyinin riyazi modelinin. Qurulmasi Кути трикутника
Кути трикутника Нахождение наибольшего и наименьшего элемента линейного массива
Нахождение наибольшего и наименьшего элемента линейного массива Магические квадраты
Магические квадраты Решение задачи по теореме Пифагора
Решение задачи по теореме Пифагора Общее и различие в свойствах четырехугольников
Общее и различие в свойствах четырехугольников Геометрия в начальной школе
Геометрия в начальной школе Презентация по математике "Интеллектуальная игра на тему «Площади плоских фигур»" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация по математике "Интеллектуальная игра на тему «Площади плоских фигур»" - скачать бесплатно Математика вокруг нас. Проект
Математика вокруг нас. Проект Презентация на тему Выражения с переменными
Презентация на тему Выражения с переменными  Исследование функции и построение графика
Исследование функции и построение графика Разложение многочленов на множители
Разложение многочленов на множители