Содержание
- 2. Outlines Introduction Classification of health care agencies: 1- classification by length of stay 2- classification by
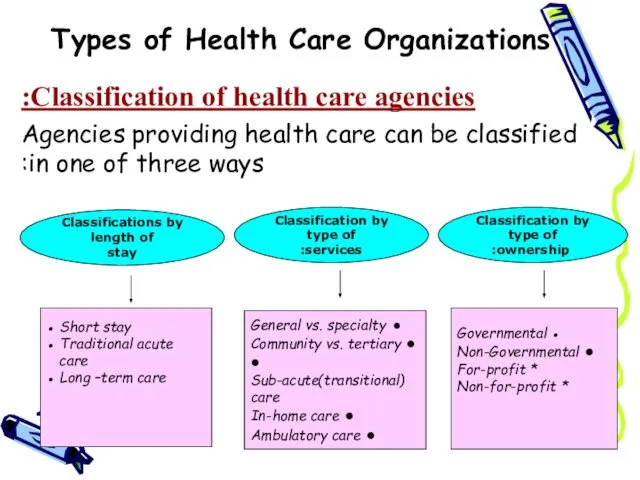
- 3. Types of Health Care Organizations Classification of health care agencies: Agencies providing health care can be
- 4. Types of Health Care Organizations Classification according to length of stay: 1) Sort-stay facilities: ● Which
- 5. Types of Health Care Organizations 2) Traditional acute care: ● It takes place in the hospital.
- 6. Types of Health Care Organizations Classification by type of service: 1) General hospital: ● Which offers
- 7. Types of Health Care Organizations 2) Specialty hospital: ● Which offers only a particular type of
- 8. Types of Health Care Organizations 3) Community hospital: ● Which provides those services provided in the
- 9. Types of Health Care Organizations 4) Sub-acute care (transitional care): ● It is a growing type
- 10. Types of Health Care Organizations 6) In-home services: ●Which are provided in the community health care
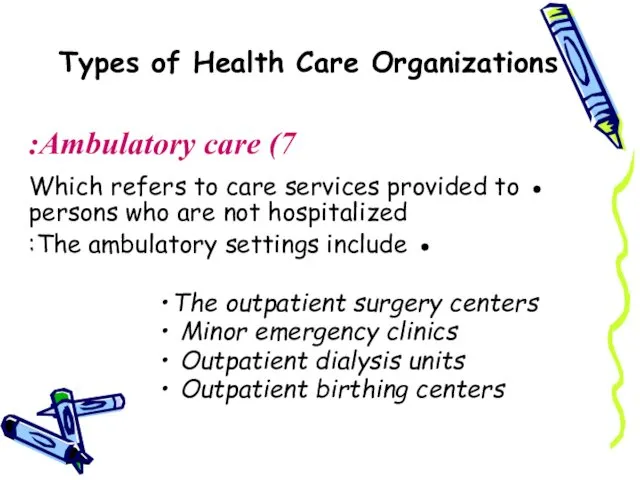
- 11. Types of Health Care Organizations 7) Ambulatory care: ● Which refers to care services provided to
- 12. Types of Health Care Organizations Classification by ownership Governmental Organizations: Owned, administered, and controlled by government
- 13. Types of Health Care Organizations The governmental hospital are owned by: a- The Ministry of Health
- 14. Types of Health Care Organizations 2) Non-Governmental Organizations: For-profit agencies (PRIVATE): owned, operated, and controlled by
- 15. Types of Health Care Organizations Non-for-profit agencies (Voluntary health agencies): ● Owned and operated by non-profit
- 16. The essential difference between the health care system in Kazakhstan is to maintain a high degree
- 17. Each division has established a mandatory procedure for the staff and patients of the internal rules
- 18. Emergency room or emergency department are in every hospital where there are inpatient units for treatment
- 19. Practical skills, which must hold a nurse working in the emergency department In the case of
- 21. Скачать презентацию
















 Регионарная анестезия
Регионарная анестезия Типичные травмы и заболевания в единоборствах. Методика массажа
Типичные травмы и заболевания в единоборствах. Методика массажа Грибковые заболевания кожи и волос
Грибковые заболевания кожи и волос Ферменты как маркеры заболеваний зубочелюстной системы
Ферменты как маркеры заболеваний зубочелюстной системы Эмоции тревоги и страха: сравнительная характеристика
Эмоции тревоги и страха: сравнительная характеристика Синдром острого повреждения легких
Синдром острого повреждения легких 1. مقدمة في قضايا في صحة المرأة
1. مقدمة في قضايا في صحة المرأة Даруя кровь – спасаешь жизнь
Даруя кровь – спасаешь жизнь Актуальность проблемы антибиотикорезистентности при лечении бактериальных респираторных инфекций и причины ее возникновения
Актуальность проблемы антибиотикорезистентности при лечении бактериальных респираторных инфекций и причины ее возникновения Опухоли ЦНС у детей
Опухоли ЦНС у детей Ботулизм. МКБ диагностика
Ботулизм. МКБ диагностика Инструментальная диагностика варикозной болезни вен нижних конечностей. Техника поведения функциональных проб
Инструментальная диагностика варикозной болезни вен нижних конечностей. Техника поведения функциональных проб Менингит
Менингит Нефроптаз. Причины развития нефроптоза
Нефроптаз. Причины развития нефроптоза Твердые лекарственные формы. Порошки. Нормативные документы
Твердые лекарственные формы. Порошки. Нормативные документы Интенсивния терапия инсультов
Интенсивния терапия инсультов Психофизиологические основы учебно-трудовой деятельности
Психофизиологические основы учебно-трудовой деятельности Кишечный шов. Виды, техника. Операция ушивания колотой и резанной раны кишки. Межкишечные анастомозы, виды, техника
Кишечный шов. Виды, техника. Операция ушивания колотой и резанной раны кишки. Межкишечные анастомозы, виды, техника Болезни слизистой полости рта
Болезни слизистой полости рта Генетические аспекты кариеса
Генетические аспекты кариеса Дифузія у медицині
Дифузія у медицині Интенсивная терапия инфекционно-токсического (септического) шока у детей
Интенсивная терапия инфекционно-токсического (септического) шока у детей Хірургічні методи лікування
Хірургічні методи лікування Новые санитарные правила и нормативы
Новые санитарные правила и нормативы Exanthema
Exanthema Эндокринная офтальмопатия
Эндокринная офтальмопатия Стандартизация и сертификация парфюмерно-косметических средств в Украине. (Лекция 2)
Стандартизация и сертификация парфюмерно-косметических средств в Украине. (Лекция 2) Антигены и антитела. (Лекция 2)
Антигены и антитела. (Лекция 2)