Содержание
- 2. Emergency action plans, or EAPs, describe the actions employees should take to ensure their safety in
- 3. EAP Considerations Any emergency situation that can affect the operation of your facility such as: Tornado
- 4. Mandatory Elements All EAPs must have the following: Procedures for reporting a fire or other emergency
- 5. Mandatory Elements (cont.) Procedures to account for all employees after evacuation Procedures to be followed by
- 6. Important Part of EAP = Means of Egress Any safety issues here? Yes! Exit access obstructed
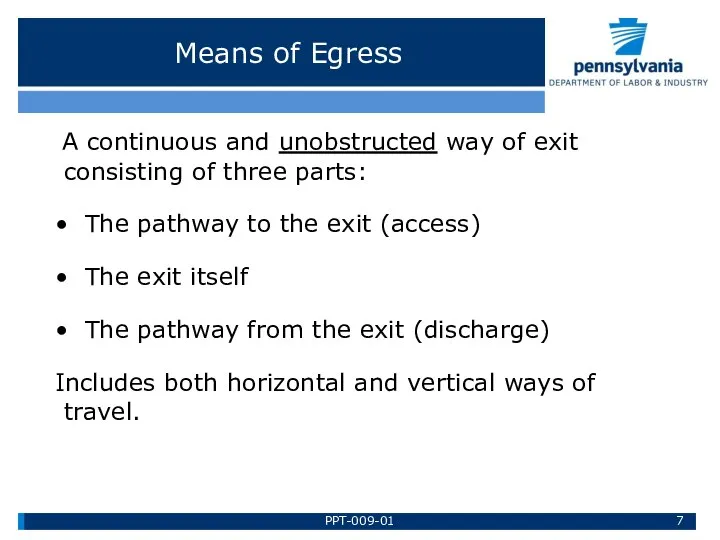
- 7. Means of Egress A continuous and unobstructed way of exit consisting of three parts: • The
- 8. Exits Exits must be marked by a readily-visible sign. Every exit sign must be distinctive and
- 9. Exits (cont.) Exits should not be blocked/obstructed at any time. Exits should not be chained shut,
- 10. Developing an EAP A very simple plan will suffice for offices, small retail shops and small
- 11. Developing an EAP (cont.) More complex plans are required in facilities that: Contain hazardous materials Have
- 12. Developing an EAP (cont.) EAPs must be site specific with respect to: Emergency conditions evaluated Evacuation
- 13. Suggestion for Developing EAP Anticipate the worst, and plan for it! PPT-009-01
- 14. EAP – Planning Process These elements should be addressed: Preferred procedures for reporting emergencies, such as
- 15. EAP – Planning Process (cont.) An evacuation policy, procedure and escape route assignment so employees understand:
- 16. EAPs – Planning Process (cont.) EAP’s should also include: • Procedures for sheltering in place •
- 17. EAP – Planning Process (cont.) EAP’s should also include: • A description of how employees will
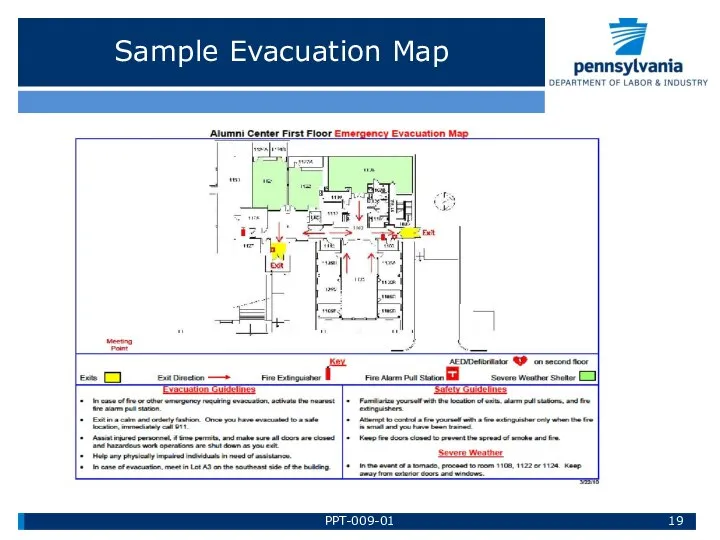
- 18. Evacuation Plans • Recommend posting “evacuation maps” on the wall near the exits and in break
- 19. Sample Evacuation Map PPT-009-01
- 20. Another Important Part of EAP Fire prevention and protection! PPT-009-01
- 21. Fires - Class CLASS A – Ordinary combustibles such as wood, rubber or plastics CLASS B
- 22. Fire Prevention Plan Suggested program elements: List of potential workplace fire hazards Personnel responsible for controlling
- 23. Good EAPs Are practical, functional and understandable Are kept updated and available to all employees (including
- 24. EAPs - Review Must have one for each location Must be communicated to employees Must be
- 26. Скачать презентацию





















 Лесные пожары
Лесные пожары Мета та задачі БЖД. Основні джерела небезпеки. Методи та заходи забезпечення життєдіяльності людини
Мета та задачі БЖД. Основні джерела небезпеки. Методи та заходи забезпечення життєдіяльності людини Выживание в условиях автономного существования в природе
Выживание в условиях автономного существования в природе Аттестационная работа. Уроки здоровья «Формирование культуры здорового и безопасного образа жизни для младших школьников»
Аттестационная работа. Уроки здоровья «Формирование культуры здорового и безопасного образа жизни для младших школьников» Мы против наркотиков!
Мы против наркотиков! Предупреждающие знаки
Предупреждающие знаки ПСО 29, БЖ, теория 1, 30.03.2020
ПСО 29, БЖ, теория 1, 30.03.2020 Безпека при користуванні засобами побутової хімії
Безпека при користуванні засобами побутової хімії Нормативное и правовое регулирование в области защиты от чрезвычайных ситуаций
Нормативное и правовое регулирование в области защиты от чрезвычайных ситуаций Заметьте нас, водители!
Заметьте нас, водители! Требования к защите населения при производственных авариях и стихийных бедствиях. (Тема 2)
Требования к защите населения при производственных авариях и стихийных бедствиях. (Тема 2) Влияние пищевых добавок на организм человека (2)
Влияние пищевых добавок на организм человека (2) Действия населения в районах стихийных бедствий. Безопасность
Действия населения в районах стихийных бедствий. Безопасность Система информации «Человек на пути»
Система информации «Человек на пути» Валеология. Уход за зубами
Валеология. Уход за зубами Если хочешь быть здоров. Викторина
Если хочешь быть здоров. Викторина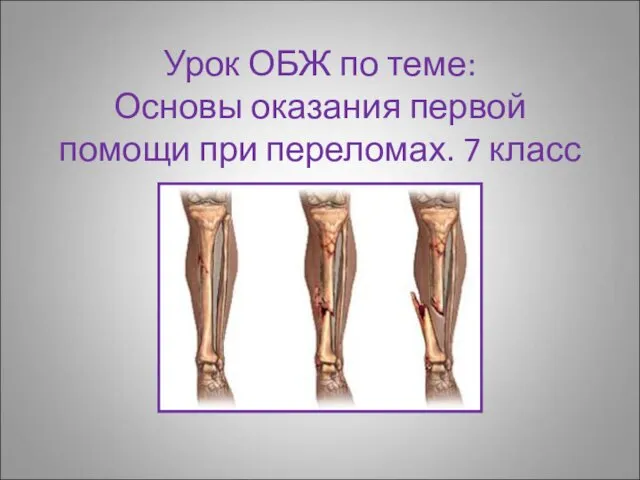 Переломы. Правила оказания первой помощи
Переломы. Правила оказания первой помощи ЧОУ ДПО Забайкальский ЦВВМ. Автошкола
ЧОУ ДПО Забайкальский ЦВВМ. Автошкола Особенности формирования основ безопасности жизнедеятельности у детей
Особенности формирования основ безопасности жизнедеятельности у детей Внимание - клещи! Где можно получить укус?
Внимание - клещи! Где можно получить укус? Методическая разработка Инновационные технологии в работе с детьми по изучению правил дорожного движения
Методическая разработка Инновационные технологии в работе с детьми по изучению правил дорожного движения Меры профилактики сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний
Меры профилактики сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний Пожарная безопасность
Пожарная безопасность Основы безопасности жизнедеятельности
Основы безопасности жизнедеятельности Явления при растекании тока в земле
Явления при растекании тока в земле Литосферные опасности
Литосферные опасности Территория АЗС
Территория АЗС Безопасность аэропортов
Безопасность аэропортов