Содержание
- 2. Foodborn contamination Ensuring the safety of food is the managers most important job. A thorough understanding
- 3. Biological Contamination Microorganisms are small, living beings that can only be seen with a microscope. Helpful
- 4. Bacteria Smallest living celled organisms Found in Food, Water, Soil, Humans, Insects They can reproduce every
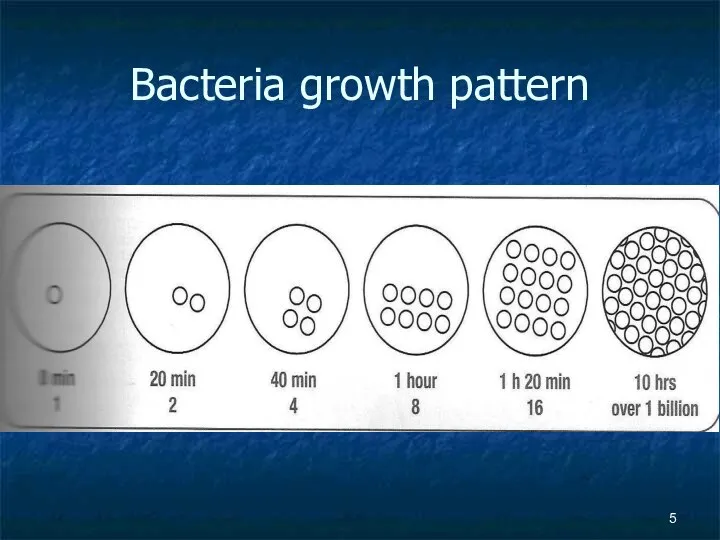
- 5. Bacteria growth pattern
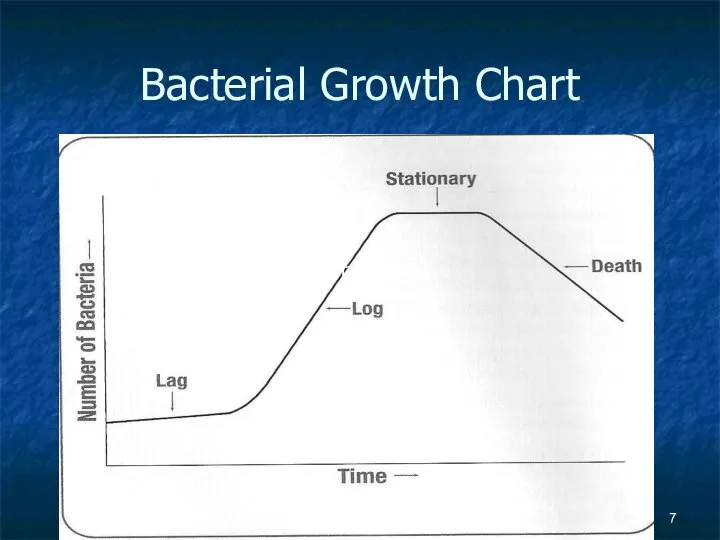
- 6. Bacterial Growth continued There are 4 phases that bacteria go through Lag phase… Starting to adjust
- 7. Bacterial Growth Chart Bacterial Growth
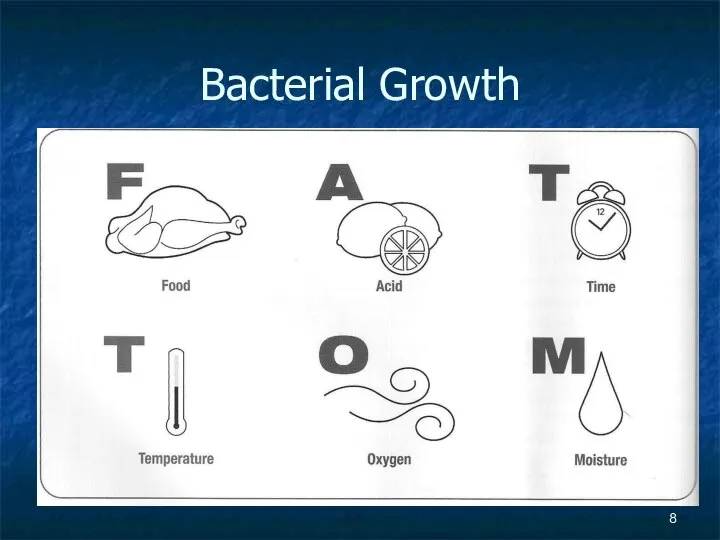
- 8. Bacterial Growth
- 9. FOOD All food is susceptible to microorganisms, however they grow best in foods that are high
- 10. Acidity (pH) This is a measurement of the degree of Acidity or Alkalinity. The scale is
- 11. TEMPERATURE Bacteria grow best between the temperature of 5 degrees c and 60 degrees c (Temperature
- 12. MOISTURE There must be adequate moisture for bacteria to grow. The amount of moisture available is
- 13. CONTROLING THE GROWTH OF MICROORGANISMS Adding lactic or citric acid (Vinegar/ Lemon) pH Adding sugar or
- 14. VIRUSES Viruses are the smallest of the microbial contaminants. They consist of genetic material wrapped with
- 15. BASIC CARACTERISTICS OF VIRUSES Unlike bacteria they rely on a living cell to reproduce They are
- 16. PARASITES Parasites need a live host to survive Person, Animal or Plant Cattle, Poultry, Pigs and
- 17. MOULDS Individual mould cells can usually be seen only with a microscope, however fuzzy or slimy
- 18. MOULDS continued Moulds are responsible for the spoilage of food, that results in discoloration and the
- 19. MOULDS continued Some moulds produce toxins that can cause allergic reaction, nervous system disorders and kidney
- 20. BASIC CHARACTERISTICS OF FOODBORN MOULDS continued Trim back or throw away moldy food unless the mould
- 21. YEASTS Yeast is best known for producing bread and beer, however Yeast can spoil food by
- 22. BIOLOGICAL TOXINS Ciguatera poisoning… reef fish Paralytic poisoning… shell fish Scombroid poisoning… spoiled fish Some plants
- 23. CHEMICAL CONTAMINATION Chemical contaminants are responsible for many cases of foodborne illness, they may come from
- 24. TOXIC METALS Utensils and equipment that contain toxic metals such as Lead, Copper, Brass, Zinc, can
- 25. CHEMICALS AND PESTICIDES Chemicals such as cleaning products, polishes, lubricants and sanitizers can contaminate food Always
- 26. PHYSICAL CONTAMINATION Physical contamination can occur when foreign objects are accidentally introduced into food Examples;- Natural
- 28. Скачать презентацию






















 Понятие и общая классификация чрезвычайных ситуаций
Понятие и общая классификация чрезвычайных ситуаций Пожарная безопасность. Экспертиза промышленных объектов
Пожарная безопасность. Экспертиза промышленных объектов Предупреждение заболеваний сердца и сосудов
Предупреждение заболеваний сердца и сосудов День солидарности в борьбе с терроризмом
День солидарности в борьбе с терроризмом Перша допомога. Вступ до теми, визначення понять, принципи виклику невідкладної допомоги, ICE. Мальтійська служба
Перша допомога. Вступ до теми, визначення понять, принципи виклику невідкладної допомоги, ICE. Мальтійська служба Средства индивидуальной и коллективной защиты населения и работников организаций. Средства коллективной защиты
Средства индивидуальной и коллективной защиты населения и работников организаций. Средства коллективной защиты Прогнозирование ЧС, цели и задачи
Прогнозирование ЧС, цели и задачи Охрана труда. (Тема 1.11)
Охрана труда. (Тема 1.11) Здоровому все здорово
Здоровому все здорово Правила дорожного движения. Интерактивная игра для детей дошкольного возраста
Правила дорожного движения. Интерактивная игра для детей дошкольного возраста Основные понятия охраны труда. Законодательство в области охраны труда
Основные понятия охраны труда. Законодательство в области охраны труда Правила поведения на улицах и дорогах
Правила поведения на улицах и дорогах Свобода мысли и слова
Свобода мысли и слова Принципы радиационной защиты населения
Принципы радиационной защиты населения Нашақорлық патофизиологиялық негіздері
Нашақорлық патофизиологиялық негіздері Пожарная безопасность
Пожарная безопасность 1 марта- Международный день борьбы с наркоманией и наркобизнесом
1 марта- Международный день борьбы с наркоманией и наркобизнесом Кто нас защищает. (3 класс)
Кто нас защищает. (3 класс) Гигиена труда женщин и подростков
Гигиена труда женщин и подростков Ребенок и незнакомец
Ребенок и незнакомец Какие машины могут ехать на красный свет?
Какие машины могут ехать на красный свет? Табак -твой враг
Табак -твой враг Безопасность жизнедеятельности. Вводная лекция
Безопасность жизнедеятельности. Вводная лекция Основы пожарной безопасности. (Лекция 1)
Основы пожарной безопасности. (Лекция 1) Интерактивная игра для детей 5-7 лет Незнайка.в большом городе
Интерактивная игра для детей 5-7 лет Незнайка.в большом городе Основы обеспечения безопасности технологических процессов
Основы обеспечения безопасности технологических процессов Типовое положение о службе охраны труда
Типовое положение о службе охраны труда Ответственность родителей за несоблюдениие детьми ПДД
Ответственность родителей за несоблюдениие детьми ПДД