Содержание
- 3. Emergency procedures Where is our nearest exit? Where do we go if we have to evacuate?
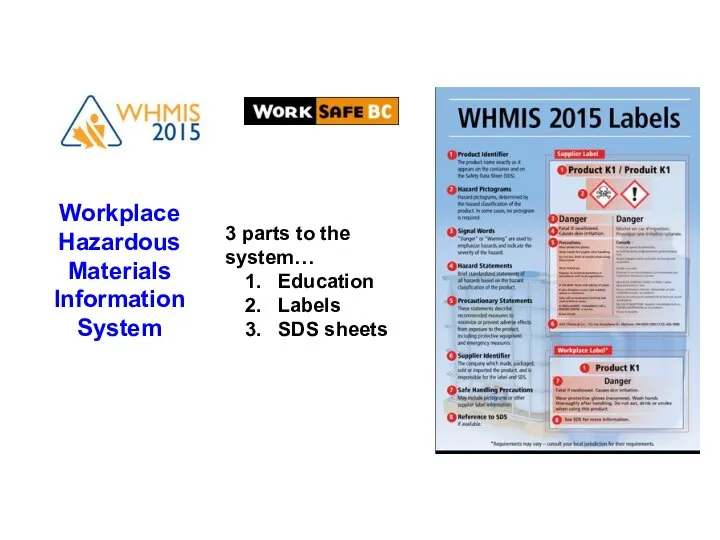
- 4. Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System 3 parts to the system… Education Labels SDS sheets
- 5. In regular lab activities, students are responsible for: Reading labels in the lab Identifying the hazards
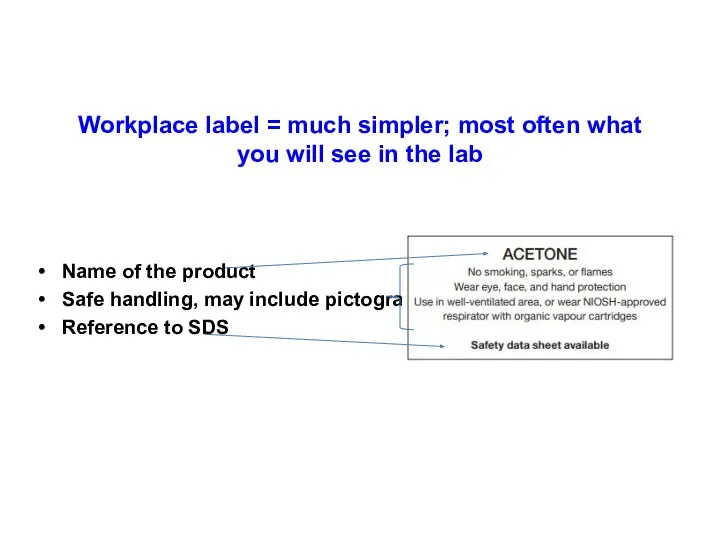
- 6. Workplace label = much simpler; most often what you will see in the lab Name of
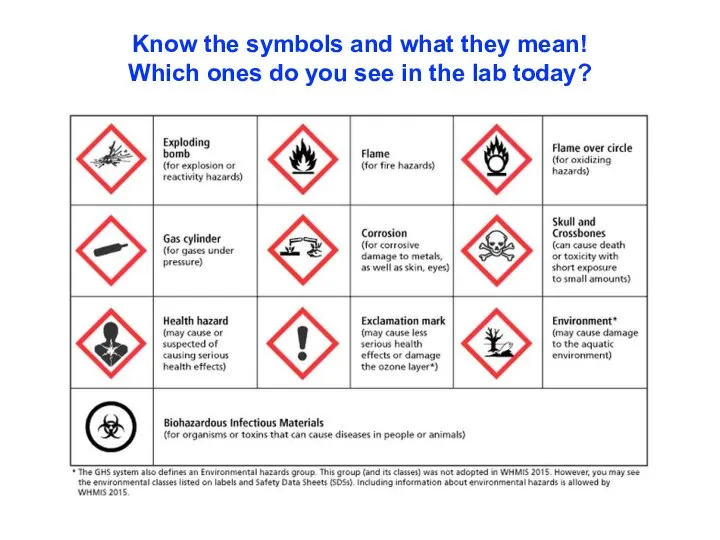
- 7. Know the symbols and what they mean! Which ones do you see in the lab today?
- 8. Introduction to Microscopes BIOL 104: Lab 1
- 9. Goals for today: Compare longitudinal and cross sections Compare four types of microscopes Demonstrate correct use
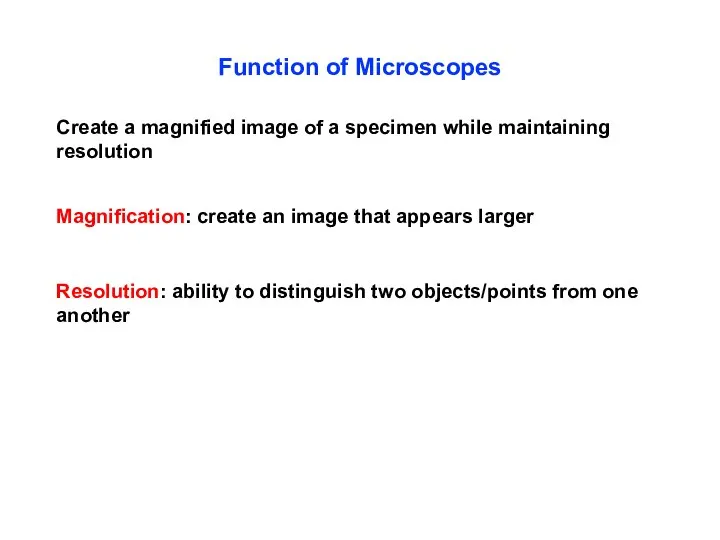
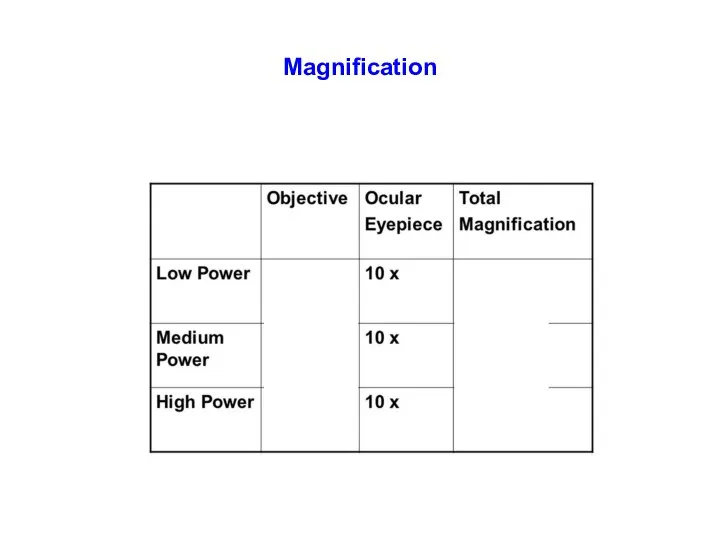
- 10. Function of Microscopes Create a magnified image of a specimen while maintaining resolution Magnification: create an
- 11. Increased magnification with no change in resolution Increased magnification with increased resolution
- 12. Electron Microscopes Use electron beam to create image Advantages High magnification High resolution Drawbacks Expensive Require
- 13. Transmission EM 2D image Specimen has to be sectioned (=sliced very thin) Scanning EM Can view
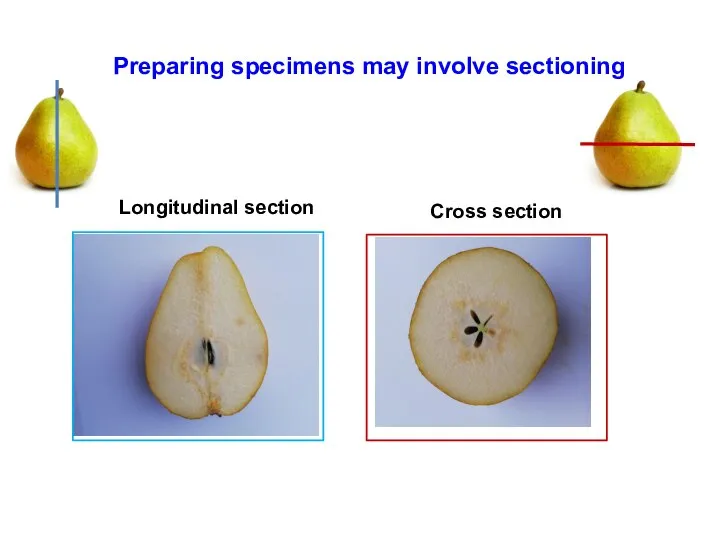
- 14. Preparing specimens may involve sectioning Longitudinal section Cross section
- 15. Light microscopes Compound Microscope Stereo Microscope Specimen goes here Specimen goes here
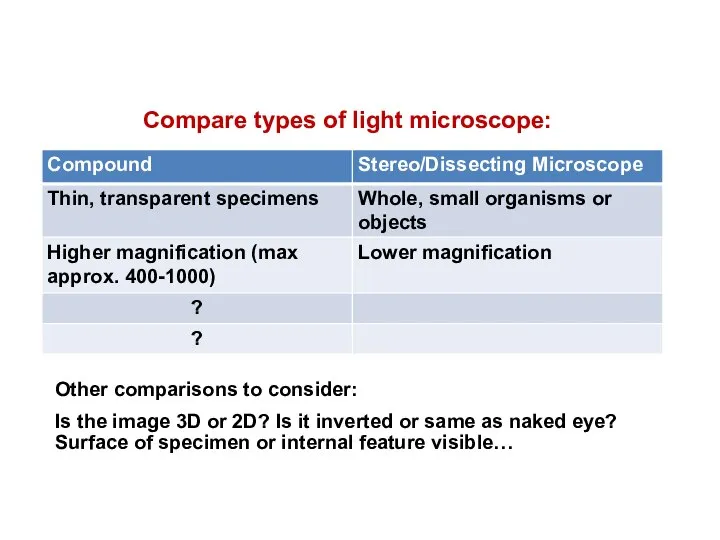
- 16. Compare types of light microscope: Other comparisons to consider: Is the image 3D or 2D? Is
- 17. COMPOUND MICROSCOPES
- 18. Scanning Low High Magnification
- 19. Working Distance: Space between specimen and magnifying lens ALWAYS START AT LOWEST MAGNIFICATION As you increase
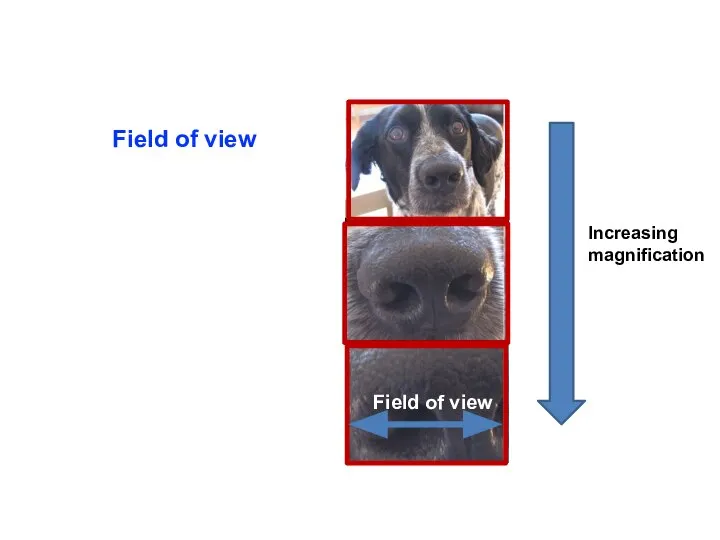
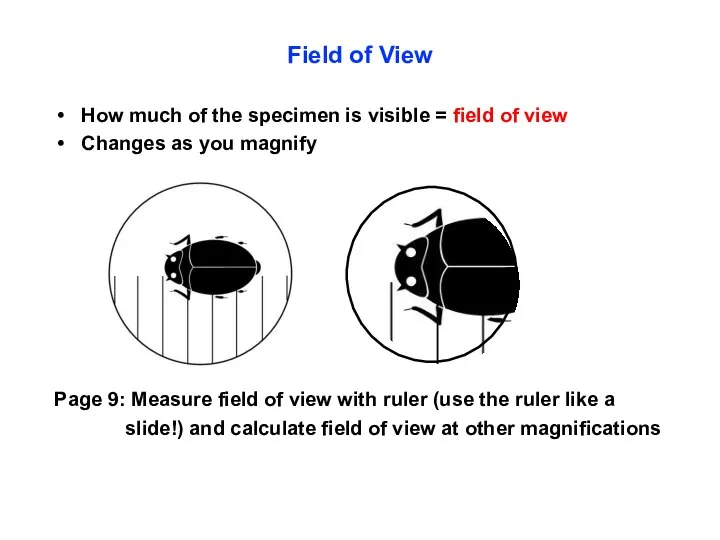
- 20. Increasing magnification Field of view Field of view
- 21. Field of View How much of the specimen is visible = field of view Changes as
- 22. Depth of field Compound microscope gives 2D image Need to refocus to see top and bottom
- 23. Today’s to do list: Complete all activities in the “Microscopy” lab in your lab manual You
- 25. Скачать презентацию













 Пожаро- и взрывобезопасность в электроустановках
Пожаро- и взрывобезопасность в электроустановках Презентация Оказание первой медицинской помощи при тепловом и солнечном ударе, обморожении и ожоге
Презентация Оказание первой медицинской помощи при тепловом и солнечном ударе, обморожении и ожоге  Подготовка к конкурсу «Безопасное колесо»
Подготовка к конкурсу «Безопасное колесо» Формирование здорового образа жизни
Формирование здорового образа жизни Организация совместной деятельности с детьми дошкольного возраста по профилактике детского дорожно-транспортного травматизма
Организация совместной деятельности с детьми дошкольного возраста по профилактике детского дорожно-транспортного травматизма Электромагнитные волны и здоровье человека
Электромагнитные волны и здоровье человека Алкоголь и наркотики - яд
Алкоголь и наркотики - яд Дом, который может стать ловушкой
Дом, который может стать ловушкой Алкоголь и его влияние на здоровье человека
Алкоголь и его влияние на здоровье человека Оповещения населения при природных ЧС
Оповещения населения при природных ЧС Определение ЧС природного и техногенного характера. Причина возникновения чрезвычайной ситуации
Определение ЧС природного и техногенного характера. Причина возникновения чрезвычайной ситуации Управление МЧС России по Красноярскому краю
Управление МЧС России по Красноярскому краю Световое загрязнение
Световое загрязнение Азбука безопасности
Азбука безопасности OHS line managers meeting
OHS line managers meeting Презентация «Я против наркотиков!»
Презентация «Я против наркотиков!» Оздоровление воздушной среды
Оздоровление воздушной среды Здоровый образ жизни
Здоровый образ жизни Короткое замыкание. Предохранители. Электробезопасность
Короткое замыкание. Предохранители. Электробезопасность Организация санитарно-противоэпидемического обеспечения в чрезвычайных ситуациях
Организация санитарно-противоэпидемического обеспечения в чрезвычайных ситуациях Формирование у дошкольников основ безопасности жизнедеятельности
Формирование у дошкольников основ безопасности жизнедеятельности Самый умный пешеход - интерактивная игра для младших школьников
Самый умный пешеход - интерактивная игра для младших школьников Министерство по делам гражданской обороны и чрезвычайным ситуациям
Министерство по делам гражданской обороны и чрезвычайным ситуациям Здоровьесберегающие технологии
Здоровьесберегающие технологии Безопасное колесо. Знатоки правил дорожного движения. Тренинг 2
Безопасное колесо. Знатоки правил дорожного движения. Тренинг 2 Безопасные летние каникулы
Безопасные летние каникулы Моё безопасное лето
Моё безопасное лето Случайные опасности
Случайные опасности