Содержание
- 2. PLAN Introduction 1.Types of emissions 2.Emissions control Conclusion References
- 3. Introduction Combustion, metal machining, chemical processes, material handling – the number of pollutants occurring in connection
- 4. Characteristic features: * possibility of measurement visualization within any time horizon, * archiving of data and
- 5. 1.Types of emissions Emissions of many air pollutants have been shown to have variety of negative
- 6. Carbon monoxide (CO) - A product of incomplete combustion, inhaled carbon monoxide reduces the blood's ability
- 7. Sulfur oxide (SOx) - A general term for oxides of sulfur, which are emitted from motor
- 8. 2.Emissions control Engine efficiency has been steadily improved with improved engine design, more precise ignition timing
- 11. Conclusion Emissions control is the attempt to control, limit, reduce or even completely remove the pollutants
- 13. Скачать презентацию







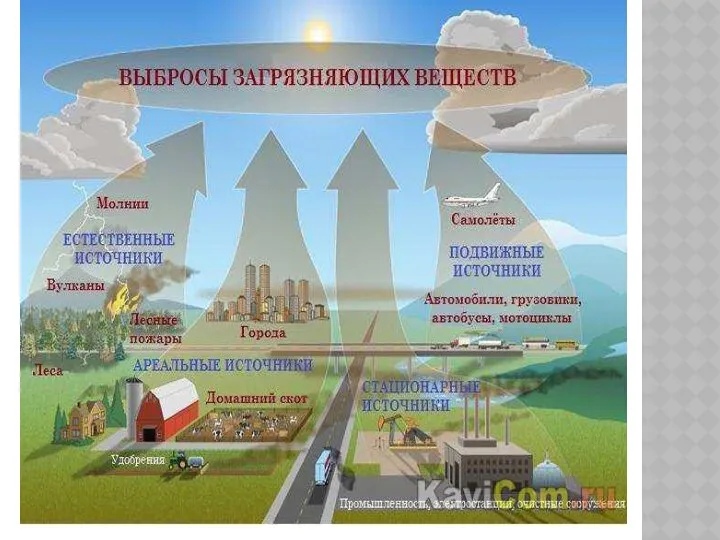


 Особенности взаимодействия общества и природы
Особенности взаимодействия общества и природы Предмет и задачи дисциплины. Региональные антропогенные изменения экосферы
Предмет и задачи дисциплины. Региональные антропогенные изменения экосферы Рекомендации Римского клуба о развитии человечества
Рекомендации Римского клуба о развитии человечества Физикалық әсердің қоршаған ортаға тигізетін әсері
Физикалық әсердің қоршаған ортаға тигізетін әсері Всероссийский экологический урок «Сделаем вместе»
Всероссийский экологический урок «Сделаем вместе» Сніжний барс
Сніжний барс Презентация Правила поведения в магазине
Презентация Правила поведения в магазине  Экологическое ассорти
Экологическое ассорти Экология как научная основа природопользования
Экология как научная основа природопользования Окружающая среда и здоровье человека
Окружающая среда и здоровье человека Презентация Праздник осени 1 сентября
Презентация Праздник осени 1 сентября  Экскурсии по экологической тропе
Экскурсии по экологической тропе Презентация на тему РАЗНЫЕ ПОРОДЫ СОБАК
Презентация на тему РАЗНЫЕ ПОРОДЫ СОБАК Среда обитания человека. Естественная и искусственная среда обитания
Среда обитания человека. Естественная и искусственная среда обитания Проблема загрязнения окружающей среды
Проблема загрязнения окружающей среды Канівський природний заповідник
Канівський природний заповідник Учение о биосфере
Учение о биосфере Экология в Татарстане. Загрязнение воздуха
Экология в Татарстане. Загрязнение воздуха Акция «Чистый лес»
Акция «Чистый лес» Экология. Green Peace - Гринпис
Экология. Green Peace - Гринпис Презентация на тему ПОЛЯРНАЯ ЗВЕЗДА
Презентация на тему ПОЛЯРНАЯ ЗВЕЗДА  Экологическое образование дошкольников: проблемы и перспективы
Экологическое образование дошкольников: проблемы и перспективы Экологическое проектирование в урбанизированной среде. Рекультивация
Экологическое проектирование в урбанизированной среде. Рекультивация Загрязнение и изменения литосферы
Загрязнение и изменения литосферы Экологический аудит «Заглянем в мусорное ведро»
Экологический аудит «Заглянем в мусорное ведро» Река Сырдарья
Река Сырдарья Деревья эко-сквера
Деревья эко-сквера Экологическая роль живых существ
Экологическая роль живых существ