Содержание
- 2. Agenda for Week Three
- 3. Current Events
- 4. Theoretical Approaches
- 6. Overview of Previous Theories Anarchy › self-help States are positional actors Relative gains Balance of power
- 7. Constructivism Response to neorealism and neoliberal institutionalism Late 1980s, early 1990s Alexander Wendt, John Ruggie, Nicolas
- 8. Constructivism Social facts are very real (ex: institutions, language, norms etc.) They are products of the
- 9. Constructivism Global affairs are laden with social facts: Anarchy During Cold War After Cold War Ex:
- 10. Constructivism Ideas and norms matter Thus, we need to pay attention to the intersubjective structure of
- 11. Constructivism Norms assign meaning to material facts Change in ideas can change behaviour Ideas and Norms
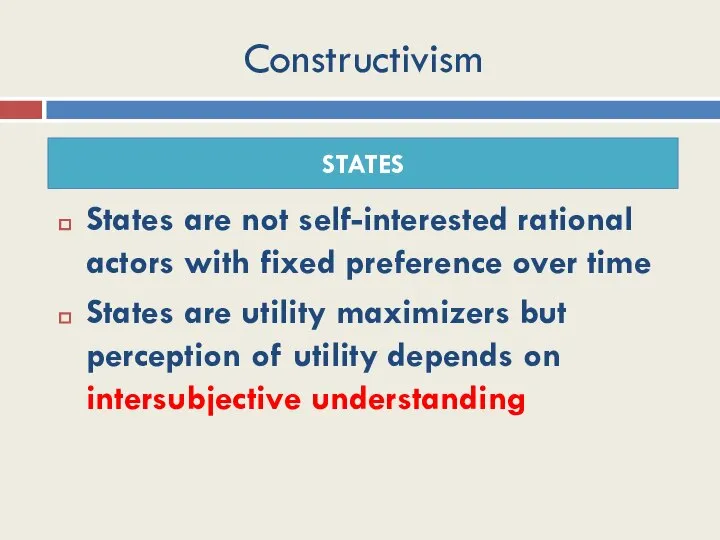
- 12. Constructivism States are not self-interested rational actors with fixed preference over time States are utility maximizers
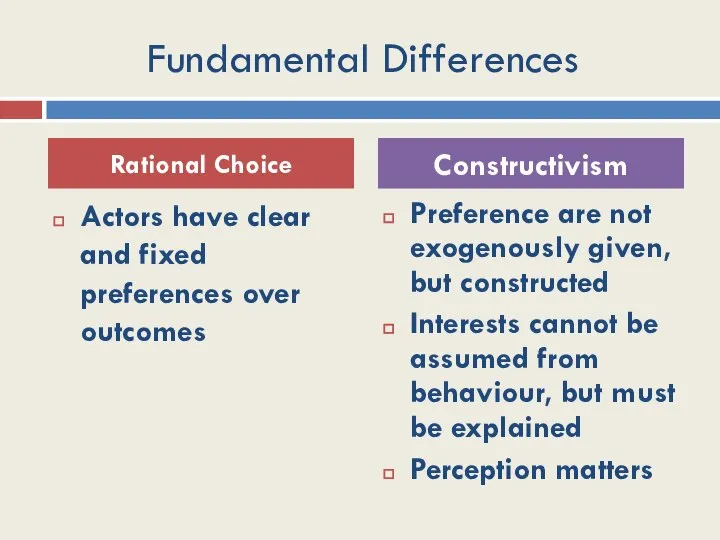
- 13. Fundamental Differences Actors have clear and fixed preferences over outcomes Preference are not exogenously given, but
- 14. Constructivism Anarchy is what states make of it Logic of appropriateness not of consequences Identity is
- 15. Constructivism Interactions influences preference Ex. Trade negotiations: persuasive argumentation not just coercive bargaining Interactions
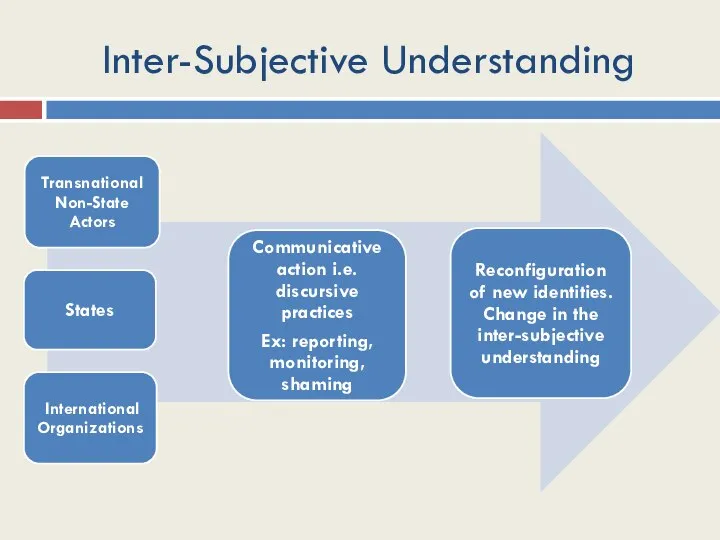
- 16. Inter-Subjective Understanding
- 17. Case Study: US Grand Strategy Towards Russia How would neorealists and neoliberal institutionalists explain the rising
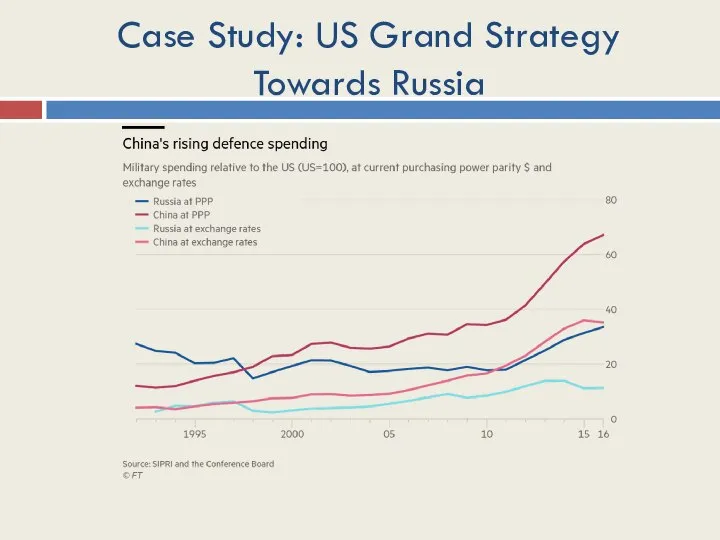
- 18. Case Study: US Grand Strategy Towards Russia
- 19. Case Study: US Grand Strategy Towards Russia What would constructivists say about the US withdrawal from
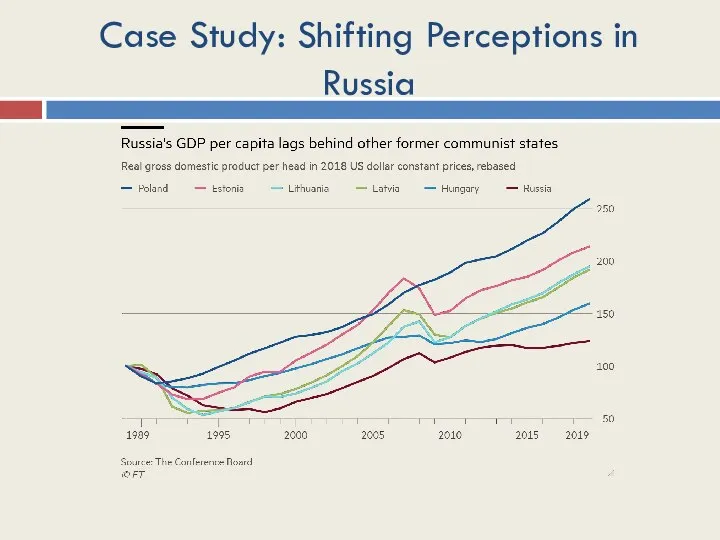
- 20. Case Study: Shifting Perceptions in Russia
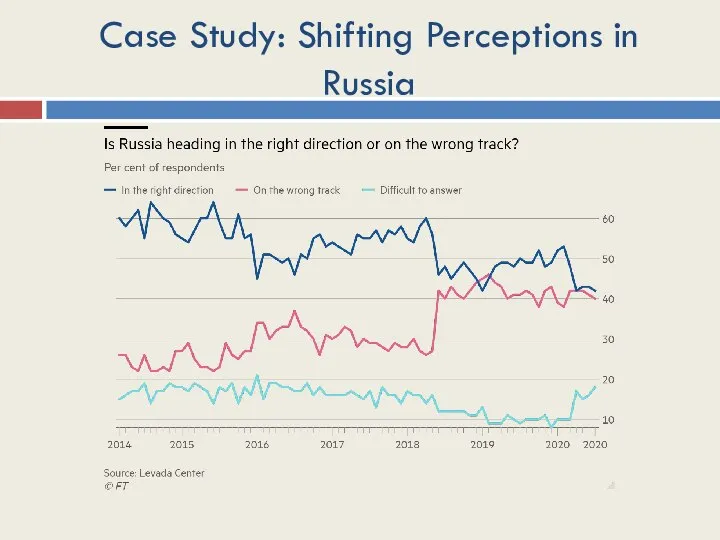
- 21. Case Study: Shifting Perceptions in Russia
- 22. Agenda for Week Three
- 23. Current Events
- 24. Feminist Approaches Feminist political theory Aftermath of Cold War J. Ann Tickner Samanta Power Cynthia Enloe
- 25. Feminist Approaches Set of socially constructed characterises that vary across time and places: Woman – Man
- 26. Feminist Approaches World is organized according to gendered categories: Masculinity Femininity These categories operate in a
- 27. Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JgaOK74HqiA
- 28. Feminist Approaches Women underrepresentation in politics IR
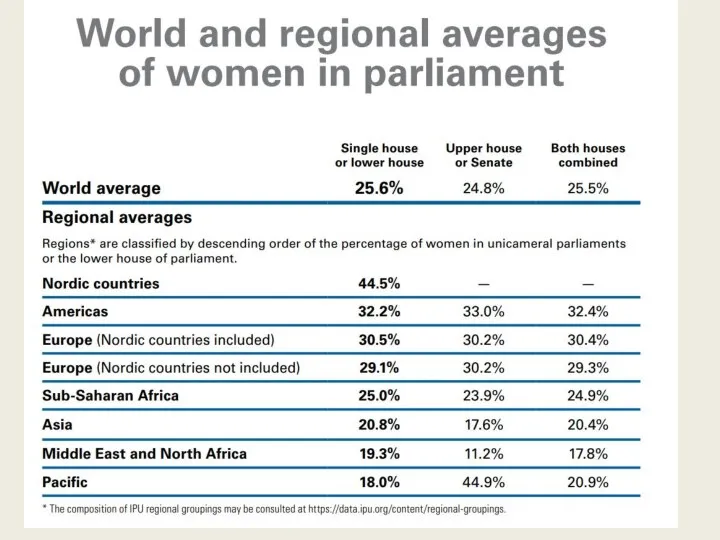
- 29. Women underrepresentation IPU’s data for 2021 9 women heads of states 13 women heads of government
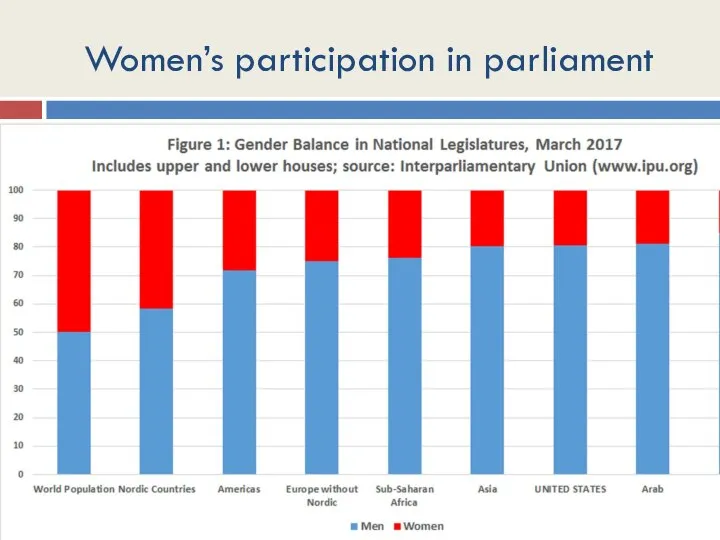
- 35. Women’s participation in parliament
- 36. Exercise How can we end gender discrimination? Legal means: Quotas Bans on discrimination Other means
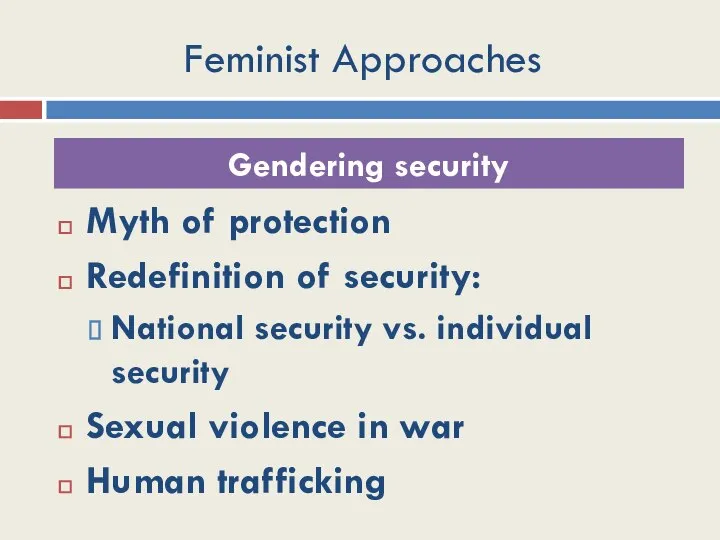
- 38. Feminist Approaches Gendering Security Gendering the Economy
- 39. Feminist Approaches Myth of protection Redefinition of security: National security vs. individual security Sexual violence in
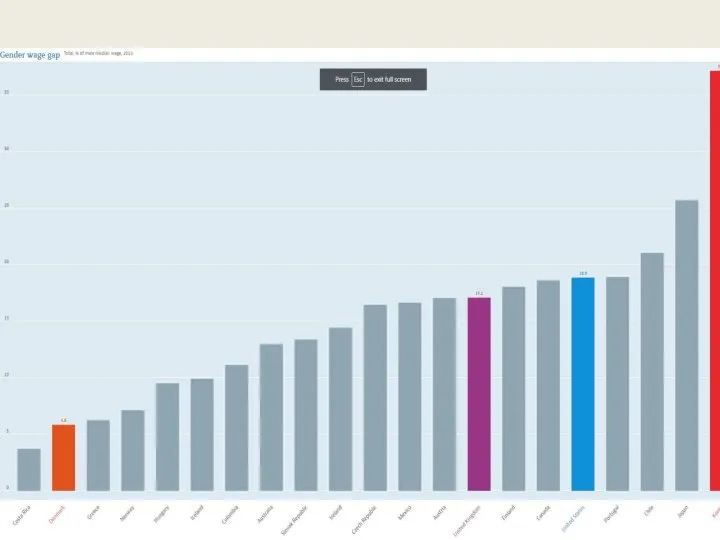
- 40. Feminist Approaches Gendered division of labour Non-remunerated work Pay gap Gendering the economy
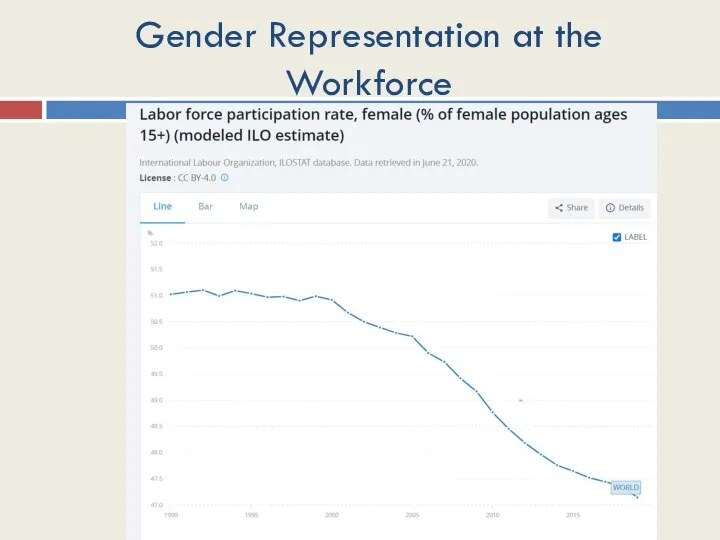
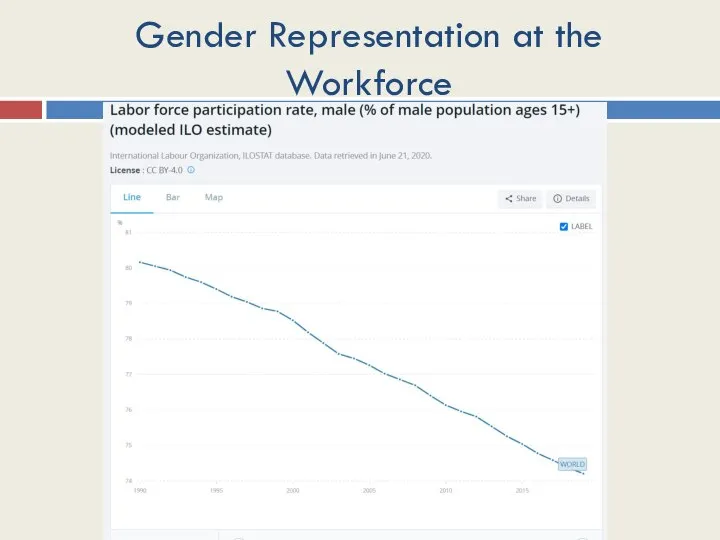
- 41. Gender Representation at the Workforce
- 42. Gender Representation at the Workforce
- 46. Скачать презентацию




























 469df1b7b121b272a758b813060a1b74
469df1b7b121b272a758b813060a1b74 Жил_такой_парень
Жил_такой_парень 20150402_9_maja2
20150402_9_maja2 Устройство и принцип действия электрического фена для сушки волос
Устройство и принцип действия электрического фена для сушки волос Сова из туалетной втулки
Сова из туалетной втулки Классификация свойств строительных материалов
Классификация свойств строительных материалов Машины и оборудование для свайных работ
Машины и оборудование для свайных работ Снижение времени простоя подвижного состава под разгрузкой в торговых точках обслуживаемых ОАО” Форнакс”
Снижение времени простоя подвижного состава под разгрузкой в торговых точках обслуживаемых ОАО” Форнакс” 8.Что такое предложение
8.Что такое предложение Технология изготовления труб
Технология изготовления труб Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation
Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation Команда%20ЯДС%20слёт%20молодёжи%20ЦСС%202022
Команда%20ЯДС%20слёт%20молодёжи%20ЦСС%202022 Применение современных передовых решений и технологий на контактных сетях электротранспорта г. Санкт-Петербург
Применение современных передовых решений и технологий на контактных сетях электротранспорта г. Санкт-Петербург Профилактика COVID-19 для студентов
Профилактика COVID-19 для студентов Презентация по программированию_SiCam
Презентация по программированию_SiCam ТОО Институт высоких технологий. Повышение эффективности добычи урана через научные исследования
ТОО Институт высоких технологий. Повышение эффективности добычи урана через научные исследования Контроль за параметрами бурения в процессе строительства скважин
Контроль за параметрами бурения в процессе строительства скважин Дизайн - проект и ландшафтный дизайн набережной
Дизайн - проект и ландшафтный дизайн набережной 38536-samyj-opasnyj-prazdnik-v-mire-sovet-turistam
38536-samyj-opasnyj-prazdnik-v-mire-sovet-turistam itinerant
itinerant Формирование критического мышления обучающихся на уроках английского языка через применение денотантной карты
Формирование критического мышления обучающихся на уроках английского языка через применение денотантной карты Kinetics melting and electrode metal transfer features in electric-arc welding flux cord wire in shielding gases
Kinetics melting and electrode metal transfer features in electric-arc welding flux cord wire in shielding gases 20141214_interesnye_mesta_v_gorode_pavlovo
20141214_interesnye_mesta_v_gorode_pavlovo Буровые технологические жидкости. Экологизация и оптимизация качества буровых промывочных и тампонажных растворов. (Лекция 15)
Буровые технологические жидкости. Экологизация и оптимизация качества буровых промывочных и тампонажных растворов. (Лекция 15) Чем и как работает художник
Чем и как работает художник Projekt kanalizacji
Projekt kanalizacji 20150413_tanets
20150413_tanets istoriya-fotoapparata
istoriya-fotoapparata