Формирование критического мышления обучающихся на уроках английского языка через применение денотантной карты
Содержание
- 2. Цель обучения иностранному языку в СПО – развитие и формирование общей коммуникативной компетенции профессионально-коммуникативной компетенции. Важное
- 3. Преподавателю необходимо помочь студенту научить выражать свою мысль чужим языком, не боясь ошибаться.
- 4. Технология развития критического мышления – это набор особых приёмов и стратегий, которые способствуют освоению нового способа
- 5. 3 стадии: Стадия вызова (выдвижение версий, связанных с развитием сюжета); Стадия осмысления (сопоставление версии с новым
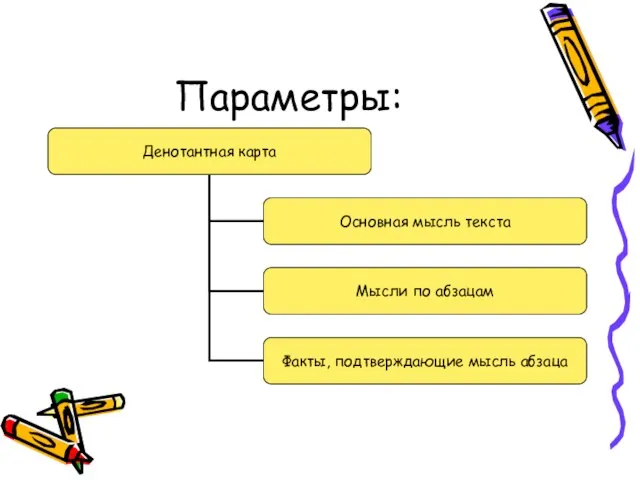
- 6. Денотантная карта – один из приёмов работы с текстовой информацией, который позволяет обучающимся не только извлекать
- 7. Параметры:
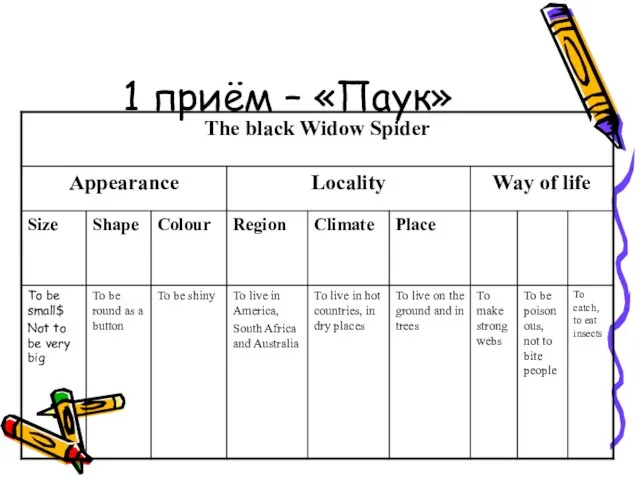
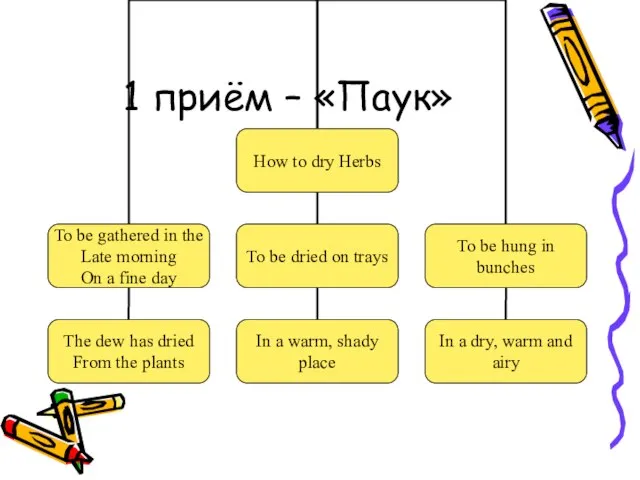
- 8. 1 приём – «Паук»
- 9. 1 приём – «Паук»
- 10. 2 приём – «Шкала времени»
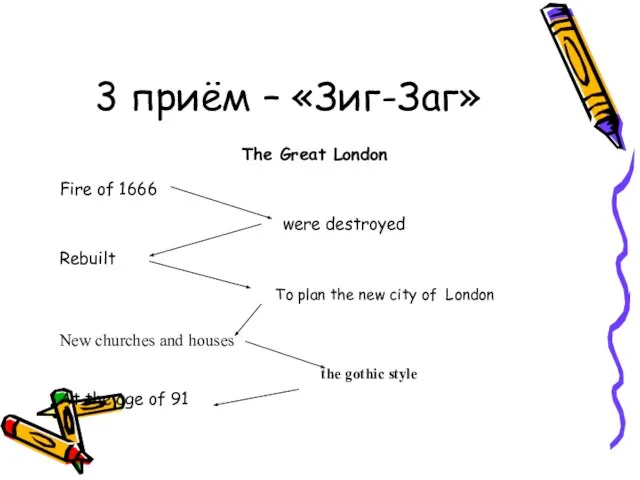
- 11. 3 приём – «Зиг-Заг» The Great London Fire of 1666 were destroyed Rebuilt To plan the
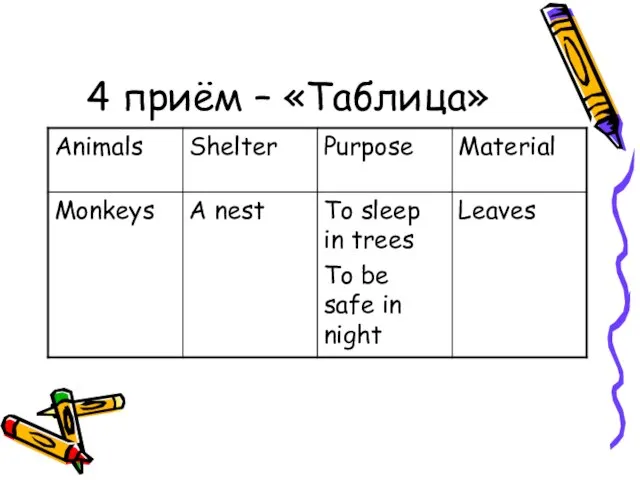
- 12. 4 приём – «Таблица»
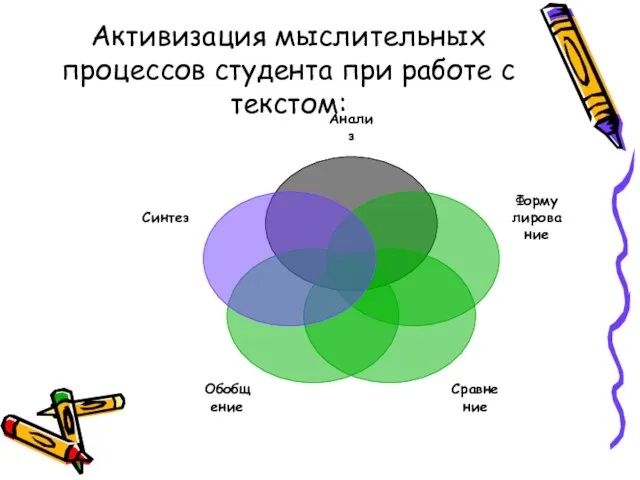
- 13. Активизация мыслительных процессов студента при работе с текстом:
- 14. Перспективы студента при работе с текстом на стадии осмысления и рефлексии: Сопоставление своей точки зрения с
- 16. Computer operations Much of the processing computers can be divided into two general . Arithmetic operations
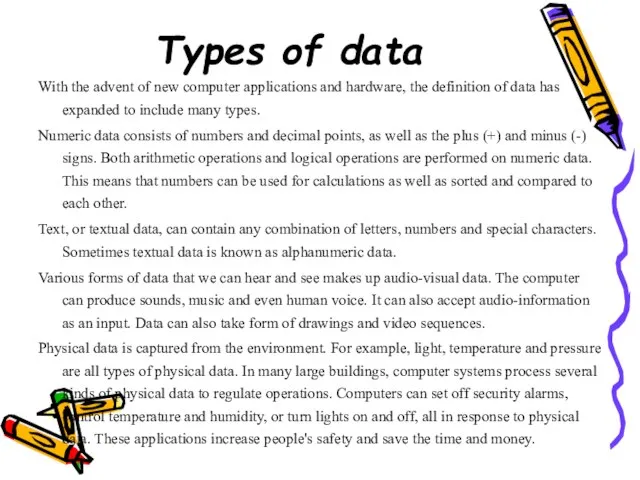
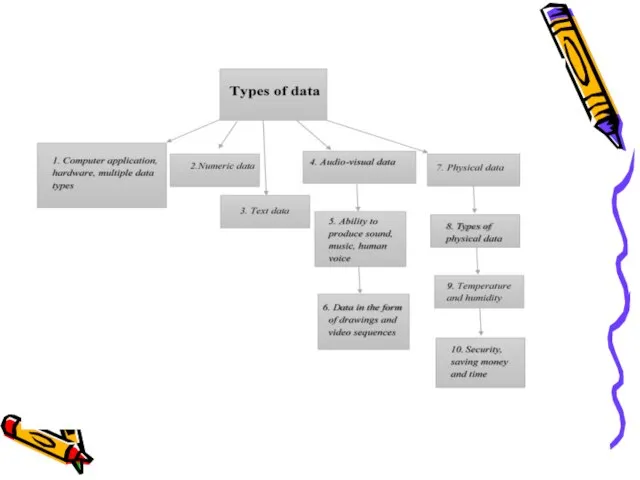
- 18. Types of data With the advent of new computer applications and hardware, the definition of data
- 21. Скачать презентацию










 Управление инфраструктурой городского хозяйства
Управление инфраструктурой городского хозяйства 20170124_milyutinskaya_shkola_v_gody_velikoy_otechestvennoy_voyny
20170124_milyutinskaya_shkola_v_gody_velikoy_otechestvennoy_voyny Заметки о морском рынке перевозок
Заметки о морском рынке перевозок 20140114_unizhennye_i_oskorblyonnye_-2_lyubov_i_eyo_variatsii
20140114_unizhennye_i_oskorblyonnye_-2_lyubov_i_eyo_variatsii Водомерное стекло
Водомерное стекло Автомобиль будущего: каким он будет
Автомобиль будущего: каким он будет Духовное Христианство
Духовное Христианство Игра в Игре с Лопшо Педунем
Игра в Игре с Лопшо Педунем Ремонт блоку живлення LCD телевізора LG19MN43D
Ремонт блоку живлення LCD телевізора LG19MN43D Игра Внутри, снаружи
Игра Внутри, снаружи Педагогическое общение
Педагогическое общение Первый лист презентации
Первый лист презентации Ящик для гвоздей
Ящик для гвоздей Джек Лондон
Джек Лондон Isollat (objects of application)
Isollat (objects of application) ISLOM KARIMOV
ISLOM KARIMOV Prezentatsia_Railya_Gimadieva
Prezentatsia_Railya_Gimadieva Требования к участию в научной работе, к выбору тематики и подготовке выпускных квалификационных работ
Требования к участию в научной работе, к выбору тематики и подготовке выпускных квалификационных работ Оборудование для эксплуатации фонтанных скважин
Оборудование для эксплуатации фонтанных скважин Сортировка и фильтрация даных в электронной таблице
Сортировка и фильтрация даных в электронной таблице Электромеханические системы (электропривод). Механическая часть электропривода
Электромеханические системы (электропривод). Механическая часть электропривода The second coming
The second coming Наш дружный 4 В класс
Наш дружный 4 В класс Растим таланты
Растим таланты Процесс образования однониточного цепного стежка
Процесс образования однониточного цепного стежка Русский язык. Задание 13
Русский язык. Задание 13 Онлайн-корпоратив
Онлайн-корпоратив фолк-фест Папоротник
фолк-фест Папоротник