Содержание
- 2. Infections Toxoplasmosis Rubella Varicella Parvovirus CMV HIV Syphilis
- 3. Introduction 3% of the perinatal mortalities are related to (fetal infection) Fetus can be affected at
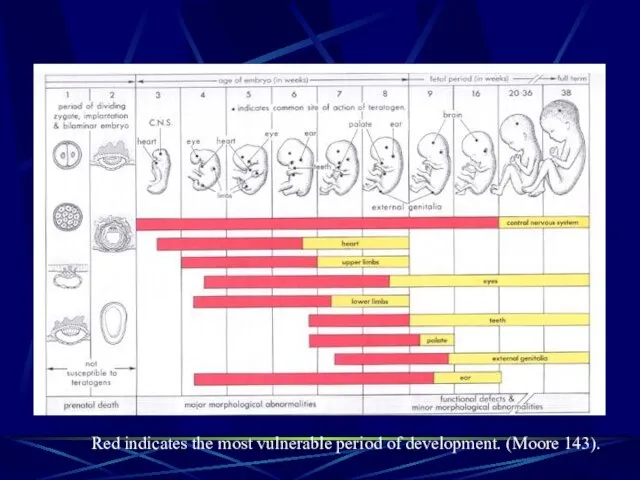
- 4. Red indicates the most vulnerable period of development. (Moore 143).
- 5. First Trimester Organogenesis Growth restriction Second and Third Trimester Neuological Impairment Growth restriction
- 6. Think of fetal infection I.U.G.R Hepatic Calcification Intracrainal Calcification Hydrocephally, Microcephally Ascits Pericardial,Pleural Effusion Non Immune
- 13. Toxoplasmosis - Toxoplasmon gondii (intracellular parasite) Trans-placental affect the placenta fetus Transmission Rate - 10 –15%
- 15. Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis - Incidence of congenital toxoplasmosis - 0.07 – 0.5 : 1000 London - 2
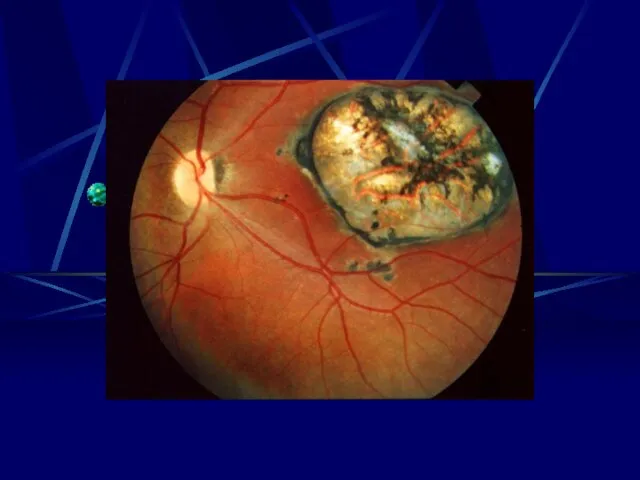
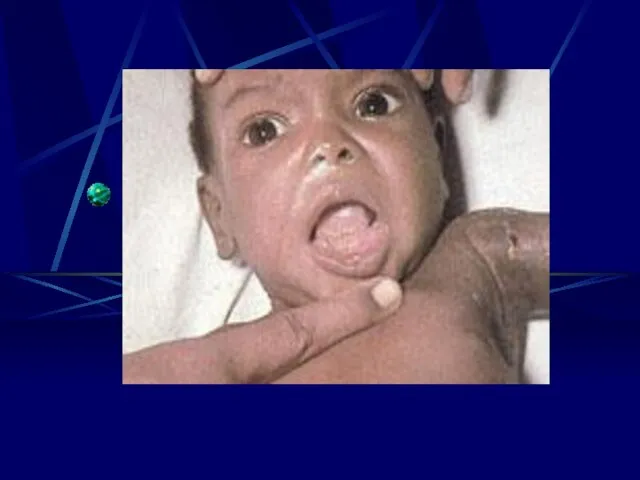
- 16. Risks to the Fetus 1st Trimester - 55 – 85% will show sequilie - Chrioretinitis severe
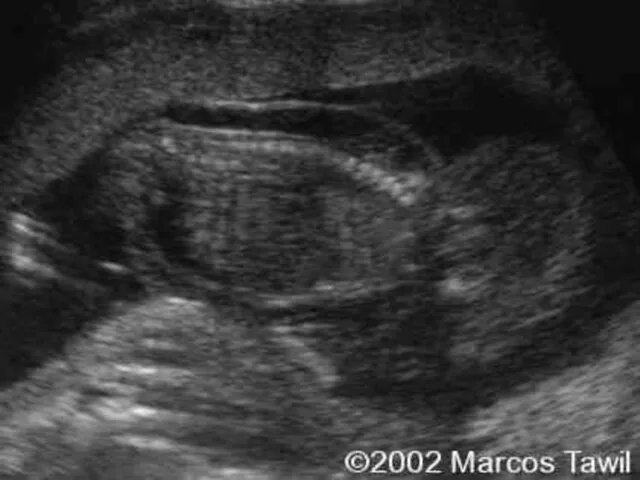
- 17. Toxoplasmonsis Ultra Sound - Intracranial, hepatic, calcification - Ascitis - Hepatosplenomegally - Microcephally - I.U.G.R Diagnosis
- 18. Toxoplasmosis Treatment - Reduce risk of transmission Spiramycin - If fetal infection documented - Pyrimethamine -
- 19. Pyron F, Wallonlion C, Goner P, Cochrane Database Review January 2005 Objective To assess whether treatment
- 20. Look, outcome of the children 3332 Papers identified
- 21. NO Trial fulfill the criteria
- 22. Conclusion We do not know whether antibiotics Treatment reduces the congenital transmission or not. Screening is
- 23. Toxoplasmosis Prevention to Toxoplasmosis: Advice to Pregnant Women whose Serological Tests are Negative. Cook meat at
- 24. Cont.. Prevention of Toxoplasmosis Carefully wash hands after handling raw meat, dirt, or vegetables soiled by
- 32. Rubella German Measles Rubella - 3rd Disease RNA Virus - Respiratory secretions - 2 – 3
- 33. Rubella - 0.5 – 2% Non Immune - 0.2 – 0.5 Congenital Rubella Syndrome Risk of
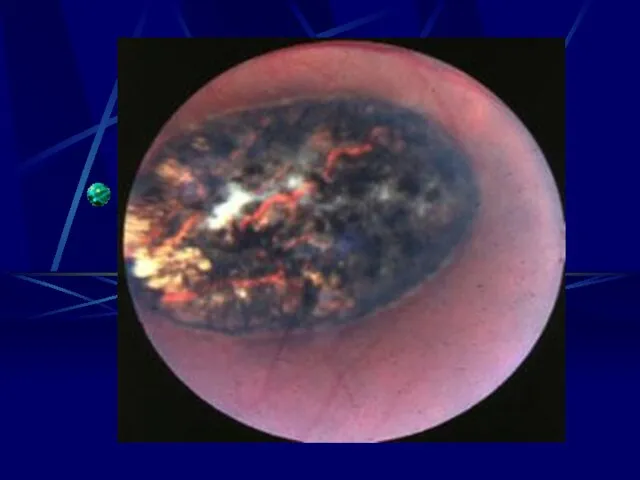
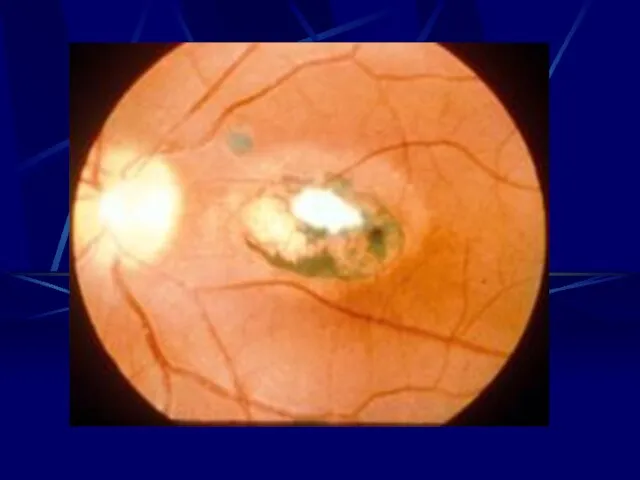
- 34. Rubella Ultra Sound - I.U.G.R. - Hepto-splenomegally Congenital Rubella syndrome - Eye Cataract, Retinopathy Microphthalmia, glaucoma
- 35. Rubella Diagnosis IgM
- 36. RUBELLA Prevention Active immunization by vaccination is the only efficient way of preventing congenital rubella.
- 39. Varicella Zoster Virus DNA Herpes - Chickenpox - Herpes Zoster - Incidence in pregnancy 0.4 –
- 40. Varicella Neonatal Infection Increase in Mortality - 5 days before delivery – 48 hours post partum
- 41. Diagnosis Viral Culture - PCR Presence of infection does not predicate the severity of the disease
- 42. VARICELLA Prevention Passive immunization is currently available and should be administered within 24-72 hours to sero-negative
- 43. Varicella Treatment - Oral cyclovir to improve sysmatic I.V. to treat pneumonia - Safe in Pregnancy
- 44. Varicella Screening - Not Recommended
- 47. Parvovirus B.19 the fifth disease Infectious period 5 – 10 days after exposure Mode of transmission
- 48. Intrauterine fetal infection Fetal effect of B19 : - A symptomatic - IUGR - Congenital anomalies
- 49. Diagnosis Parpovirus - ELISA -Western blot test IGM Diagnosis of Primary Infection Elect Microscopy - Direct
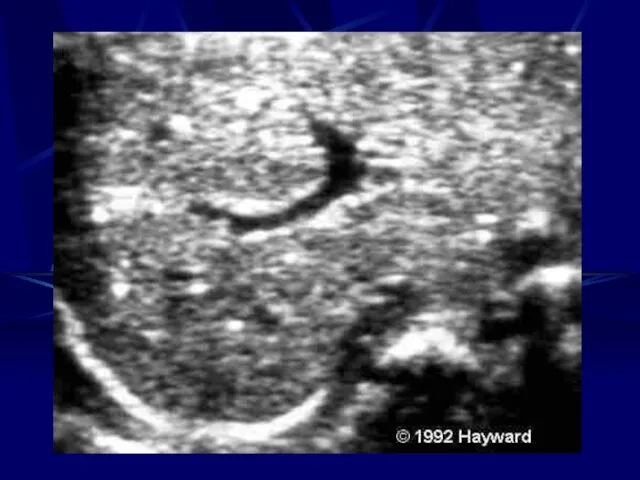
- 50. Parvovirus Fetal Diagnosis PCR in A.F., Placenta & Blood Ultra Sound Hydropy Fetalis
- 51. Parvovirus Prognosis and therapy Survivor recovers normal Fetal Therapy Intravascualr Intrauterine Blood Transfusion
- 55. CMV DNA Herpes Virus Most common perinatal infection 0.2 – 2% of all newborns Leading cause
- 56. CMV I.P 28 – 60 days Viremia 2 – 3 weeks Maternal effect – Asympathic, mild
- 57. Epidimulogical Facts Primary Infection -Risk of Transmission 30 – 40% -10% Seguilie of the infected -30%
- 58. Recurrent Infection Transmission 0.1 – 2% Mostly a symptomatic most of the sequilie occurs as hearing
- 59. Diagnosis CMV Diagnosis Culture or PCR – blood, urine & salvia IgG Serial Measurements 3 –
- 60. IGM is not reliable as it may be negative even in the right phase and may
- 61. Diagnosis Fetal Diagnosis Ultra Sound System - Intracrainal or hepatic calcification - Echogenic bowel - Ascits
- 62. CMV Treatment - Not available - Neonatal therapy ganciclovir may decrease neonatal infections Vaccine - May
- 67. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Infection This is the major cause of congenital infection in the developing
- 68. Mother ? child in utero at birth breast milk Organ/tissue donation Semen Kidneys Skin, bone marrow,
- 69. TO SCREEN OR NOT TO SCREEN? The best defense is a strong offense. The American Academy
- 70. PRE-TEST COUNSELING Risks of transmission (including Mode) Risks of perinatal transmission Potential social and psychological implication
- 71. Timing of Perinatal HIV Transmission Cases documented intrauterine, intrapartum, and postpartum by breastfeeding In utero -
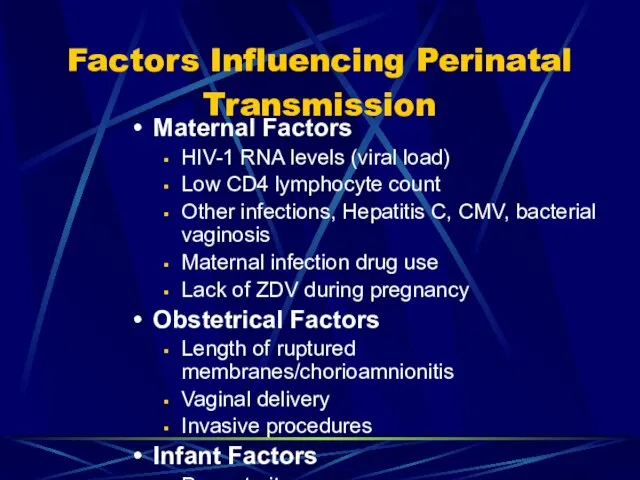
- 72. Factors Influencing Perinatal Transmission Maternal Factors HIV-1 RNA levels (viral load) Low CD4 lymphocyte count Other
- 73. Reducing HIV Transmission with Suboptimal Regimens Partial ZDV regimens: ( New York cohort) Transmission rates 6.1%
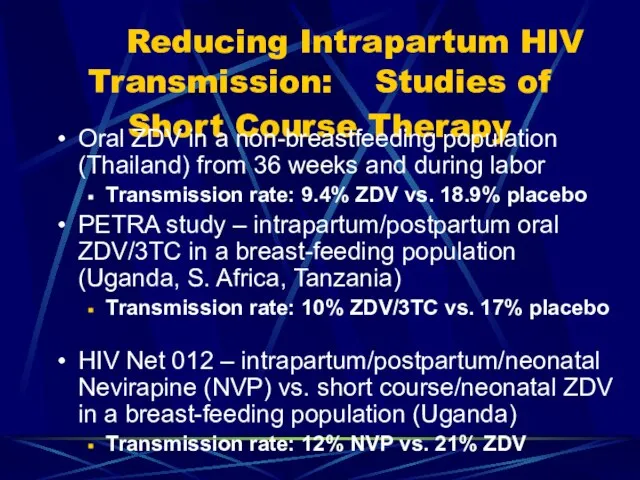
- 74. Reducing Intrapartum HIV Transmission: Studies of Short Course Therapy Oral ZDV in a non-breastfeeding population (Thailand)
- 75. Treatment with zidovudine appears to be safe in pregnancy. Elective caesarean section may decrease mother-to-child transmission.
- 76. HIV Chochrane Database 2002 Objective to assess what intervention will decrease the risk of mother to
- 77. AZT 4 trials decrease 1585 patients Neviropine compared AZT 626 decrease transmission C/S one trial 436
- 78. Conclusion Zidoridine, Nevirpine C/S decreases the transmission significantly.
- 79. Syphilis - T.P. - Increase HIV Transmission all through
- 80. Manifestation Ultra Sound Thick Placenta Hydrops fetalis I.U.G.R Hydroamnios – Hepato-splenomegaly …… Risk of Transmission 90%
- 81. Diagnosis Screening Non Specific VDAL RPR Specific TPHA F.T.A. becomes ….. 3 – 4 weeks
- 82. Treatment - Penicillin - Benzathin Penicillin 2.4 million unit - Erythpromycine
- 90. Скачать презентацию














































































 Заглянем в кладовые Земли
Заглянем в кладовые Земли Обход города Кемерово
Обход города Кемерово Основы религиозных культур и светской этики
Основы религиозных культур и светской этики Порядок действий по закреплению подвижного состава на железнодорожном транспорте в случае усиления ветра
Порядок действий по закреплению подвижного состава на железнодорожном транспорте в случае усиления ветра Б-П
Б-П Путешествие в страну здоровья
Путешествие в страну здоровья Computer memory
Computer memory Техническое обслуживание и ремонт тормозной системы автомобиля Renault Logan
Техническое обслуживание и ремонт тормозной системы автомобиля Renault Logan Занятие мои помощники правила
Занятие мои помощники правила вспоминая парад
вспоминая парад Komplexnyi_774__Informatika
Komplexnyi_774__Informatika 20180224_vospitatel_goda
20180224_vospitatel_goda Русские академисты
Русские академисты Тема занятия: Разгадывание ребусов
Тема занятия: Разгадывание ребусов Запорная арматура
Запорная арматура Обладнання для камерного сушіння пиломатеріалів
Обладнання для камерного сушіння пиломатеріалів Механические свойства строительных материалов
Механические свойства строительных материалов Кристиан Диор
Кристиан Диор Давайте подготовим наши сердца в молитве
Давайте подготовим наши сердца в молитве Религиозный терроризм
Религиозный терроризм Обследование структуры МАРХИ
Обследование структуры МАРХИ Машины постоянного тока
Машины постоянного тока Комфортність робочого місця водія та салону
Комфортність робочого місця водія та салону Модули тренинга по процессу экструзии
Модули тренинга по процессу экструзии Information and communication technologies
Information and communication technologies Соответствие детских площадок МО Оккервиль современным стандартам ГОСТов
Соответствие детских площадок МО Оккервиль современным стандартам ГОСТов класс чист
класс чист Инструменты и приспособления для малярных работ
Инструменты и приспособления для малярных работ