Содержание
- 2. Warning of Confidentiality The data and information, in its totality or partial expression, contained in this
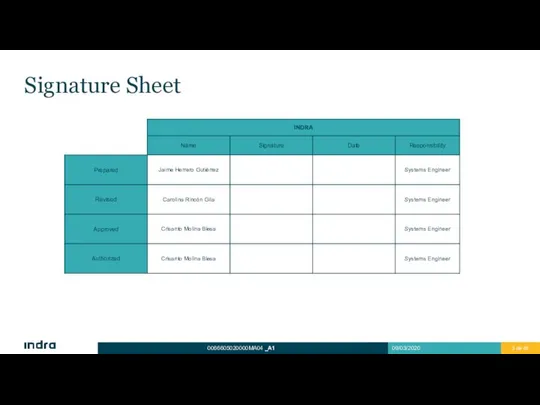
- 3. Signature Sheet
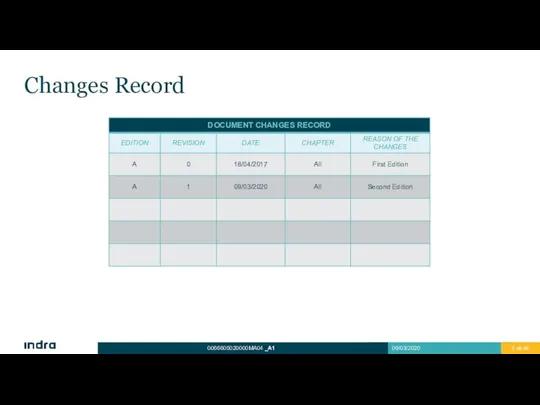
- 4. Changes Record
- 5. Acronyms
- 6. Acronyms
- 7. Index
- 8. Index
- 9. 1 Introduction
- 10. Introduction Functions: RF signal amplification (from 15 dBm to 73 dBm): 58 dB gain. Transmits signal
- 11. Introduction Structure: Solid state amplifiers (10 units). Redundant preamplifier. Low losses splitter and combiner. Class-C output
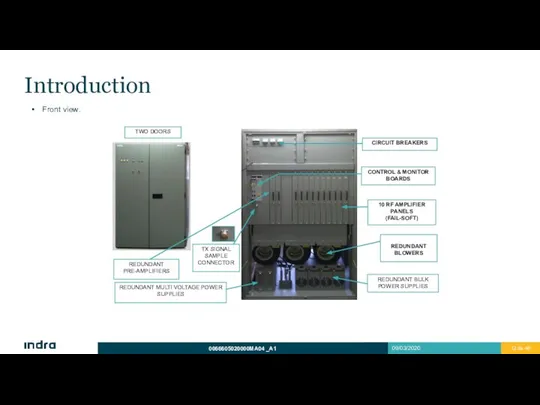
- 12. Introduction Front view.
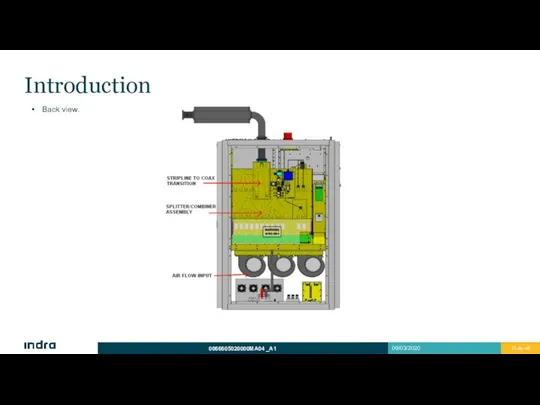
- 13. Introduction Back view.
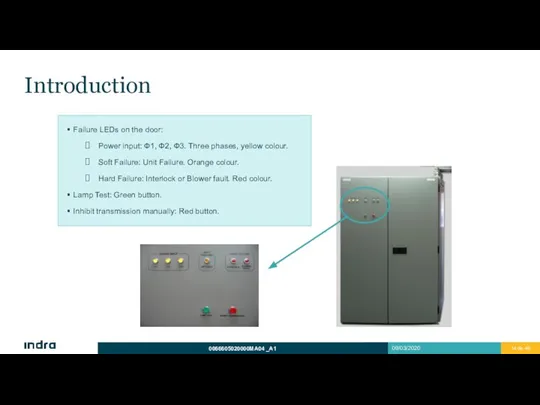
- 14. Introduction Failure LEDs on the door: Power input: Ф1, Ф2, Ф3. Three phases, yellow colour. Soft
- 15. 2 Signal Path Amplification Chain Soft Failure Operation Functional Description
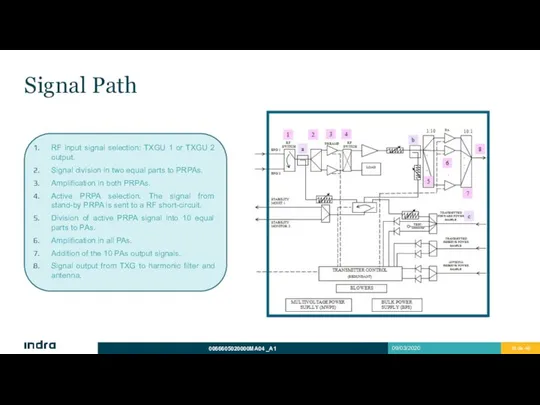
- 16. Signal Path RF input signal selection: TXGU 1 or TXGU 2 output. Signal division in two
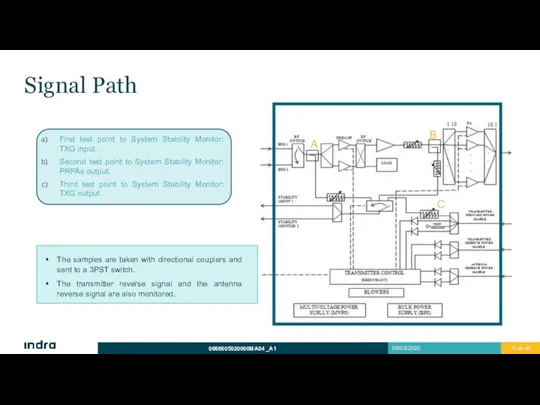
- 17. Signal Path First test point to System Stability Monitor: TXG input. Second test point to System
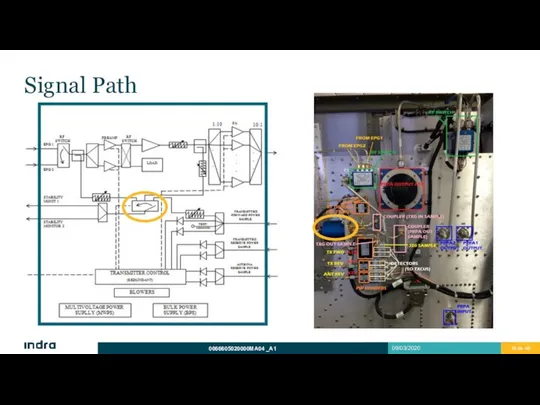
- 18. Signal Path
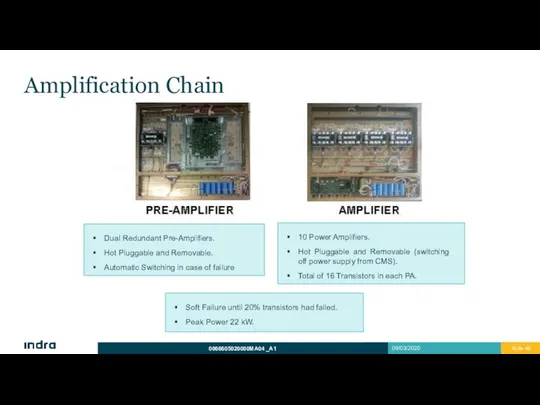
- 19. Amplification Chain Soft Failure until 20% transistors had failed. Peak Power 22 kW. Dual Redundant Pre-Amplifiers.
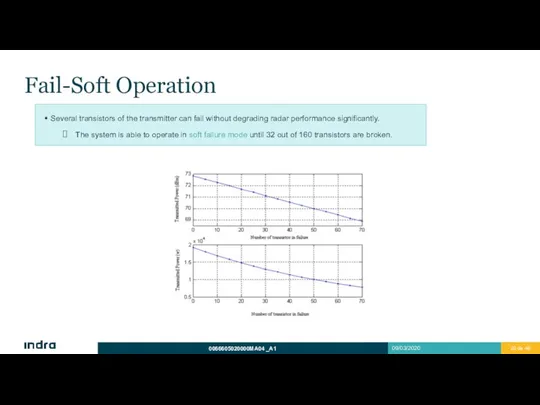
- 20. Fail-Soft Operation Several transistors of the transmitter can fail without degrading radar performance significantly. The system
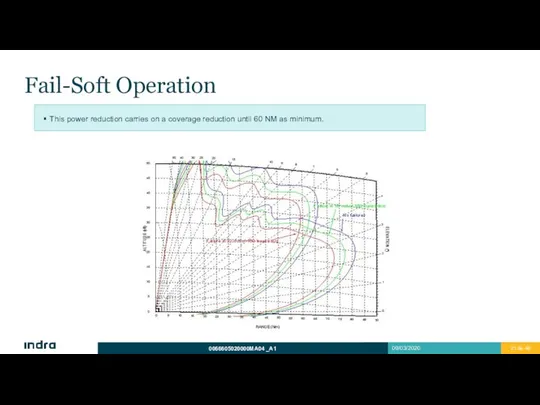
- 21. Fail-Soft Operation This power reduction carries on a coverage reduction until 60 NM as minimum.
- 22. 3 LRU List and Interfaces LRU List Power Distribution Interfaces
- 23. LRU List Transmitter Control Unit, TXCU (2). Power Amplifier, PA (10). Power Preamplifier, PRPA (2). Multivoltage
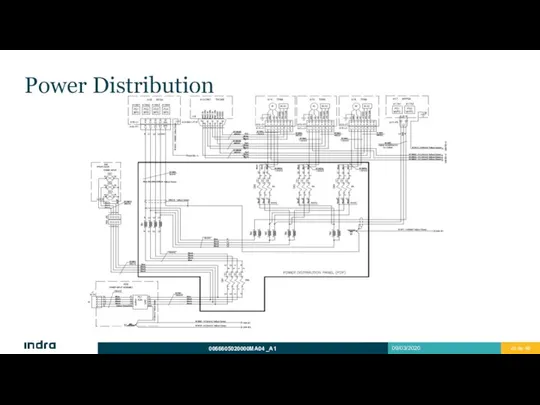
- 24. Power Distribution
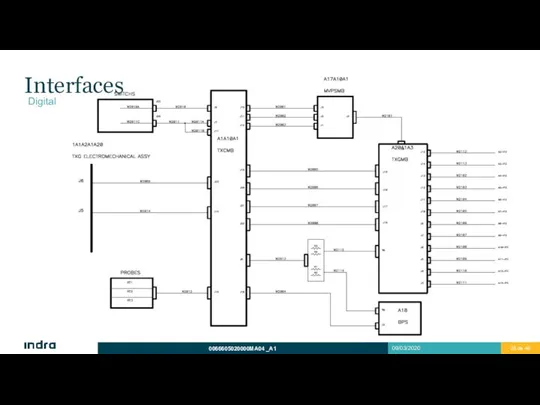
- 25. Interfaces Digital
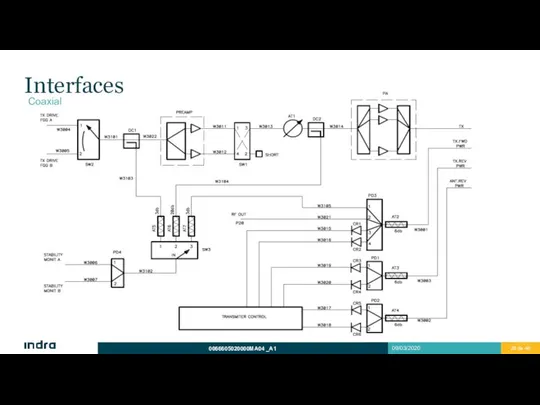
- 26. Interfaces Coaxial
- 27. 4 Subgroup Physical Description General Diagram General Description Transmitter Control Unit (TXCU) Preamplifier Panels (PRPA) Power
- 28. General Description Transmitter subsystems: RF amplification chain: amplifies the signal. It consists of two preamplifiers (redundant)
- 29. General Description Transmitter subsystems: Power supply assembly: consists of two groups, MVPSs and BPSs. One supplies
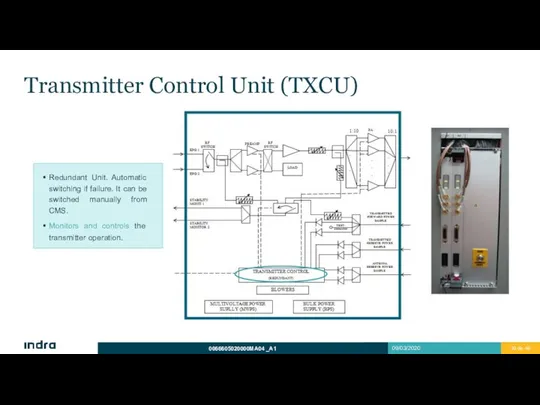
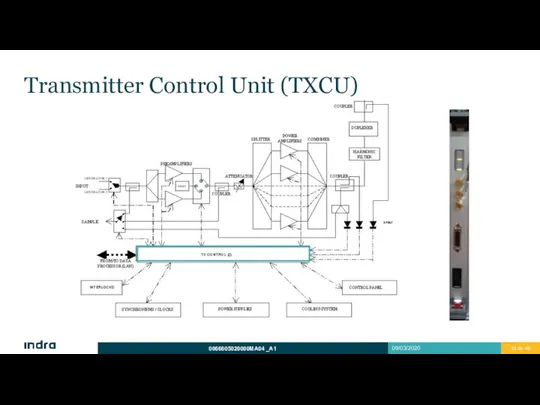
- 30. Transmitter Control Unit (TXCU) Redundant Unit. Automatic switching if failure. It can be switched manually from
- 31. Transmitter Control Unit (TXCU) Monitors and controls the transmitter operation: Acts as an interface between the
- 32. Transmitter Control Unit (TXCU) Monitors and controls the transmitter operation: If a critical failure occurs, TXCU
- 33. Transmitter Control Unit (TXCU)
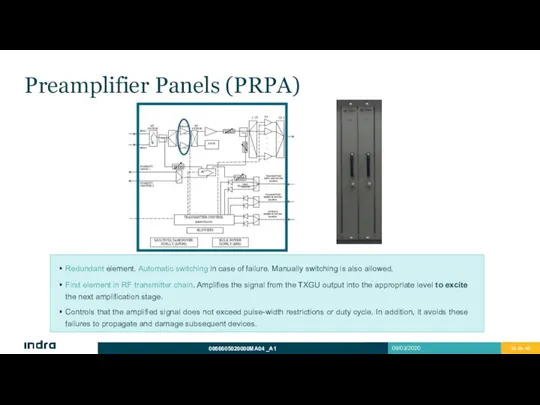
- 34. Preamplifier Panels (PRPA) Redundant element. Automatic switching in case of failure. Manually switching is also allowed.
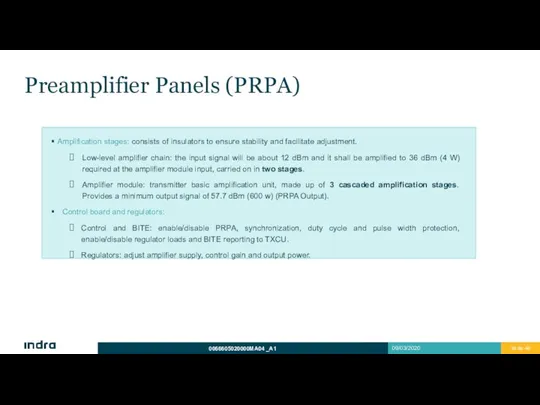
- 35. Preamplifier Panels (PRPA) Amplification stages: consists of insulators to ensure stability and facilitate adjustment. Low-level amplifier
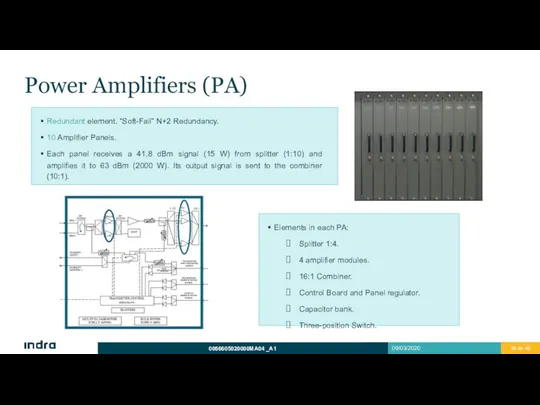
- 36. Power Amplifiers (PA) Redundant element. “Soft-Fail” N+2 Redundancy. 10 Amplifier Panels. Each panel receives a 41.8
- 37. Power Amplifiers (PA) Splitter 1:4: Divides signal to distribute it into four amplifier modules. Amplifier modules:
- 38. Power Amplifiers (PA) Capacitor Bank: 5 parallel capacitors operate as voltage supply filter. Acts as energy
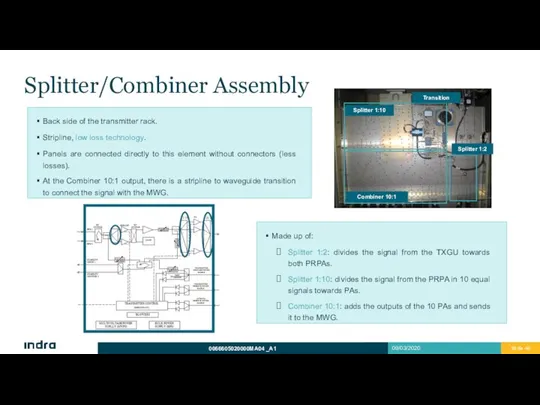
- 39. Splitter/Combiner Assembly Back side of the transmitter rack. Stripline, low loss technology. Panels are connected directly
- 40. Blowers Assembly Redundant Unit. N+1 redundancy, it can operate with 2 out of 3 blowers. The
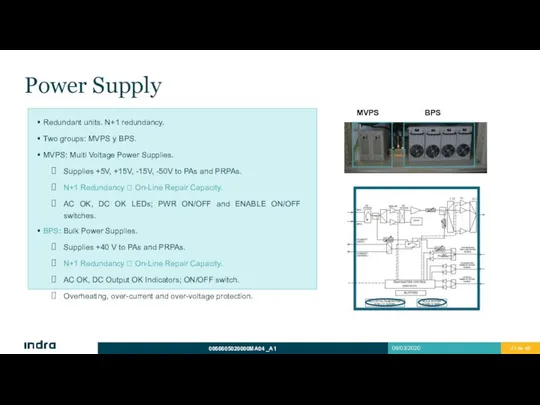
- 41. Power Supply Redundant units. N+1 redundancy. Two groups: MVPS y BPS. MVPS: Multi Voltage Power Supplies.
- 42. Auxiliary Elements Harmonic filter: harmonic level attenuation. Directional output coupler: provides samples of forward and reverse
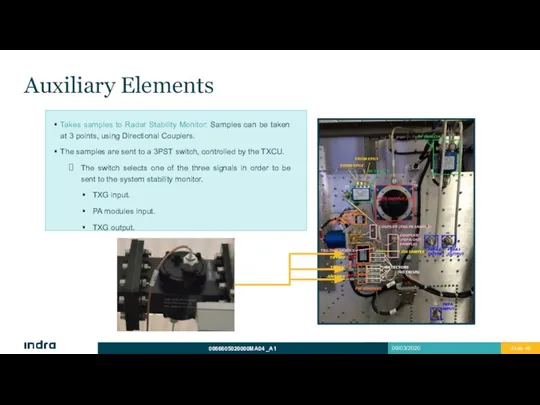
- 43. Auxiliary Elements Takes samples to Radar Stability Monitor: Samples can be taken at 3 points, using
- 45. Скачать презентацию



















 Материалы для дистанционной поддержки учащихся по дополнительной программе
Материалы для дистанционной поддержки учащихся по дополнительной программе Образовательный проект Кинезиология для детей и родителей
Образовательный проект Кинезиология для детей и родителей Мораль
Мораль Деревянные арки и рамы
Деревянные арки и рамы Традиции и новации в русской иконописи
Традиции и новации в русской иконописи Время-деньги,
Время-деньги, Луценко В.Д. презентация 10 б
Луценко В.Д. презентация 10 б Повышение клиентоориентированности многофункционального центра (МФЦ) Владимирской области
Повышение клиентоориентированности многофункционального центра (МФЦ) Владимирской области Carsharing
Carsharing Фоторегистрационные и формные процессы
Фоторегистрационные и формные процессы Гаязов ГТИ
Гаязов ГТИ Thermal processes of processing of petroleum raw materials
Thermal processes of processing of petroleum raw materials Я. Моё имя, его происхождение
Я. Моё имя, его происхождение MaakuntapäivänJulisteOppaat
MaakuntapäivänJulisteOppaat Природо-ресурсный потенциал Болгарии
Природо-ресурсный потенциал Болгарии Производство и применение технических жидкостей и специальных продуктов масляного производства
Производство и применение технических жидкостей и специальных продуктов масляного производства Путь к вершинам (возможности квадрокоптера)
Путь к вершинам (возможности квадрокоптера) Творческий проект Умный дом
Творческий проект Умный дом Разработка бизнес-проекта утилизации отработанных автомобилей и его инженерное обеспечение
Разработка бизнес-проекта утилизации отработанных автомобилей и его инженерное обеспечение Исследование и разработка способа пассивного компостирования птичьего помета в условиях Новгородской области
Исследование и разработка способа пассивного компостирования птичьего помета в условиях Новгородской области Друзья познаются в беде
Друзья познаются в беде Жизнь, посвященная медицине
Жизнь, посвященная медицине Контроллер Logik 9
Контроллер Logik 9 20140616_impressionizm
20140616_impressionizm На одной волне
На одной волне Сопротивление материалов
Сопротивление материалов Global social media plan. Sunshine Format
Global social media plan. Sunshine Format Влияние зарубежных агропромышленных ТНК на развитие российского зернового рынка
Влияние зарубежных агропромышленных ТНК на развитие российского зернового рынка