Содержание
- 2. Constitution of the Russian Federation chapter 7. Judiciary Article 125 4. The constitutional court of the
- 3. Constitution of the Russian Federation chapter 7. Judiciary Article 127 The supreme Arbitration Court of the
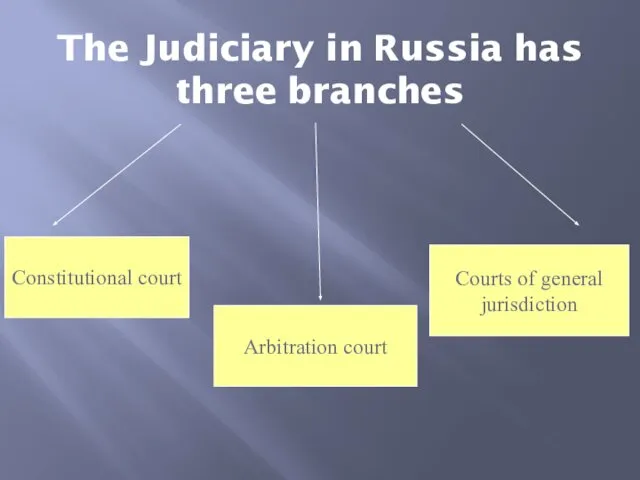
- 4. The Judiciary in Russia has three branches Constitutional court Courts of general jurisdiction Arbitration court
- 5. The category of court cases: 1) Criminal proceedings 2) Property disputes 3) Family matters 4) Labor
- 6. The Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation is entitled to act with a legislative initiative on
- 7. Courts of general jurisdiction: Courts of general jurisdiction or general courts - consider legal matters between
- 8. System of Ships: 1) The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation 2) Mid-level courts (Courts of
- 9. The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation is composed of: 1) Plenum of the Supreme Court
- 10. The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation: Examines cases as a court of first instance, in
- 11. Council of Judges of the Russian Federation A permanent body of the judiciary, elected by the
- 12. Jury trial Conducts the examination of serious and particularly serious criminal cases in the composition of
- 13. Jury trial On February 2, 1999, the Constitutional Court imposed a moratorium on the death penalty,
- 14. World Judges (December 17, 2005) World Judges in the Russian Federation are judges of the general
- 15. The magistrate examines in the first instance: Criminal cases on crimes, for the commission of which
- 16. Arbitration Courts: The Law "On the Arbitration Court" dated July 4, 1991: These are the courts
- 17. The Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation has an official distinctive symbol indicating that it
- 18. Military courts Military (naval) district courts are the courts of the Russian Federation, operating in the
- 19. Military courts consider criminal cases: civil and administrative cases concerning the protection of violated and (or)
- 20. Features of the judiciary: 1) Judicial power is exercised only by the court. 2) Judges are
- 22. Скачать презентацию


















 Інвентаризація активів бюджетної установи
Інвентаризація активів бюджетної установи Вещь как объект права. Классификация вещей и ее значение
Вещь как объект права. Классификация вещей и ее значение Следователь - должностное лицо
Следователь - должностное лицо Классы энергетической эффективности. Нормирование расхода энергоресурсов. Лекция 4
Классы энергетической эффективности. Нормирование расхода энергоресурсов. Лекция 4 Международное воздушное право
Международное воздушное право Временное хранение, декларирование и выпуск товаров (лекция 4)
Временное хранение, декларирование и выпуск товаров (лекция 4) Перемещение предметов в зону транспортной безопасности (ответы)
Перемещение предметов в зону транспортной безопасности (ответы) Современная нормативно-правовая база противодействия терроризму в РФ
Современная нормативно-правовая база противодействия терроризму в РФ День государственного флага ДНР
День государственного флага ДНР Уголовное право
Уголовное право Право в системе социальных норм
Право в системе социальных норм Документы для трудоуйстройства. Узбекистан
Документы для трудоуйстройства. Узбекистан Экспертиза биологических объектов
Экспертиза биологических объектов Понятие алиментного обязательства. Алиментные обязательства родителей и детей
Понятие алиментного обязательства. Алиментные обязательства родителей и детей Организационные и тактические особенности работы специалиста-криминалиста в ходе проведения следственных действий
Организационные и тактические особенности работы специалиста-криминалиста в ходе проведения следственных действий Державна судова адміністрація України
Державна судова адміністрація України Международное частное право. Юриспруденция
Международное частное право. Юриспруденция Отраслевые особенности организации в рыночной экономике
Отраслевые особенности организации в рыночной экономике Конструкторская документация. Правила оформления
Конструкторская документация. Правила оформления Процедуры банкротства
Процедуры банкротства Общая организация борьбы с преступностью
Общая организация борьбы с преступностью Личность, право и государство
Личность, право и государство Система права. Нормы права
Система права. Нормы права Конституция Российской Федерации. Правовой статус личности в РФ
Конституция Российской Федерации. Правовой статус личности в РФ Возбуждение уголовного дела
Возбуждение уголовного дела Изменение трудового договора (ст.72-76 ТК РФ)
Изменение трудового договора (ст.72-76 ТК РФ) Федеральная служба безопасности Российской Федерации
Федеральная служба безопасности Российской Федерации День Государственного флага Российской Федерации
День Государственного флага Российской Федерации