Содержание
- 2. 1. The head of the state
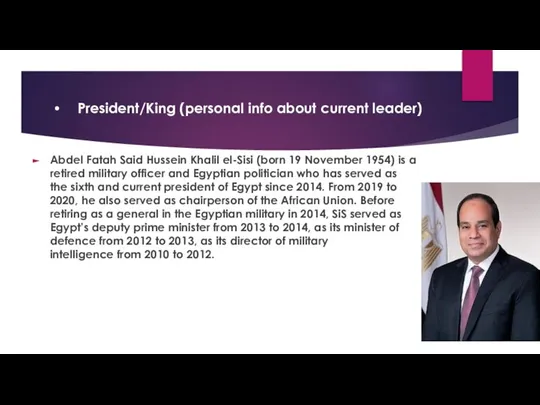
- 3. President/King (personal info about current leader) Abdel Fatah Said Hussein Khalil el-Sisi (born 19 November 1954)
- 4. Qualifications for the candidate in Egypt Requirements to hold office: The president of the republic should:
- 5. Manner of election, term of office Elections in Egypt are held for the President and a
- 6. Function of the president in Egypt The president represents Egypt in foreign relations and has the
- 7. Termination of his office After four continuous years of extension, President Abdel Fatah Al-Sisi announced the
- 8. 2. Legislative power
- 9. Parliament The Parliament is located in Cairo, Egypt's capital. Under the country's 2014 constitution, as the
- 10. Qualifications for the candidates in Egypt To be an Egyptian, enjoying the Egyptian nationality alone.To be
- 11. Manner of formation/election A statement that includes the candidate’s curriculum vitae, in particular his scientific and
- 12. Functions of parliament in Egypt The 2014 constitution describes the roles and function of the parliament
- 13. 3. Executive power
- 14. Government The politics of Egypt are based on republicanism, with a semi presidential-system of government. The
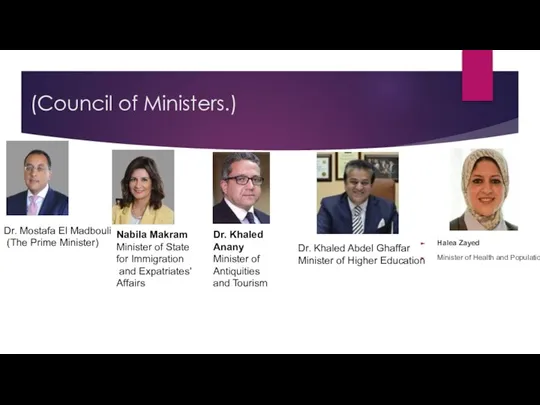
- 15. (Council of Ministers.) Halea Zayed Minister of Health and Population Nabila Makram Minister of State for
- 16. Functions The main role of the executive branch is to enforce the nation's laws. It also
- 17. 4. Judicial power
- 19. Скачать презентацию














 Римское право. Юридические лица в римском частном праве
Римское право. Юридические лица в римском частном праве Теория государства и права
Теория государства и права Избирательное право граждан РФ
Избирательное право граждан РФ Система организационно-правовой документации
Система организационно-правовой документации Научно-методическое обеспечение проверки развернутых ответов выпускников по обществознанию в ЕГЭ
Научно-методическое обеспечение проверки развернутых ответов выпускников по обществознанию в ЕГЭ Гражданство Российской Федерации
Гражданство Российской Федерации Основные правовые системы современности
Основные правовые системы современности Правовая система О.А.Э
Правовая система О.А.Э Проект Обязательная маркировка товара
Проект Обязательная маркировка товара Права ребенка в России
Права ребенка в России Юридическое делопроизводство. Процедурные правила
Юридическое делопроизводство. Процедурные правила Комплексный экзамен гуманитарный блок
Комплексный экзамен гуманитарный блок Понятие, общая характеристика и сфера использования справочных правовых систем
Понятие, общая характеристика и сфера использования справочных правовых систем Защита бездомных животных: в России и за рубежом (США, Турции, Германии и Китае)
Защита бездомных животных: в России и за рубежом (США, Турции, Германии и Китае) Гражданское право как отрасль российского права. Источники гражданского права
Гражданское право как отрасль российского права. Источники гражданского права Отмена ЕНВД с 2021 года. Альтернативные системы налогообложения
Отмена ЕНВД с 2021 года. Альтернативные системы налогообложения Деловые письма на китайском
Деловые письма на китайском Нормативно-правовое обеспечение процесса продажи алкогольной продукции
Нормативно-правовое обеспечение процесса продажи алкогольной продукции Страхование от несчастного случая
Страхование от несчастного случая Уголовно-правовые отношения
Уголовно-правовые отношения Анализ рисков и экономическая безопасность
Анализ рисков и экономическая безопасность Норма права
Норма права Кафедра гражданского права и процесса 2
Кафедра гражданского права и процесса 2 Регламенты палат парламента
Регламенты палат парламента Інформаційна безпека особистості
Інформаційна безпека особистості Особенности регулирования труда отдельных категорий работников
Особенности регулирования труда отдельных категорий работников Гражданское правоотношение. Основание возникновения, изменения и прекращения гражданских правоотношений
Гражданское правоотношение. Основание возникновения, изменения и прекращения гражданских правоотношений Вещь как объект права. Классификация вещей и ее значение
Вещь как объект права. Классификация вещей и ее значение