Содержание
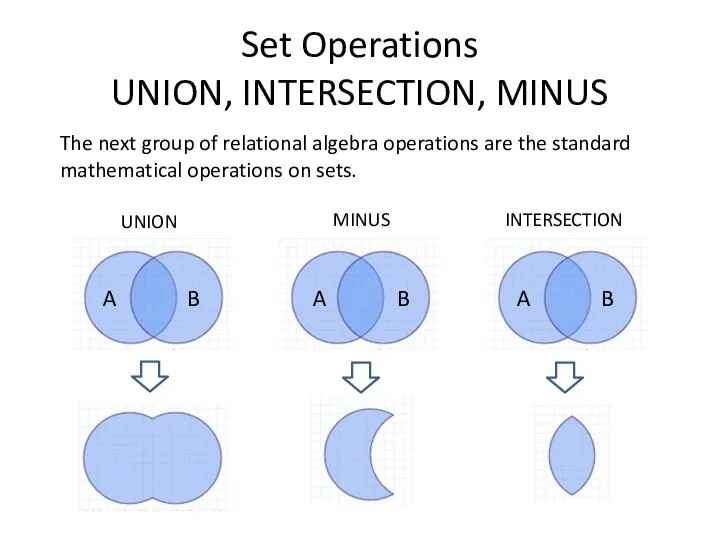
- 2. A B A B A B UNION MINUS INTERSECTION Set Operations UNION, INTERSECTION, MINUS The next
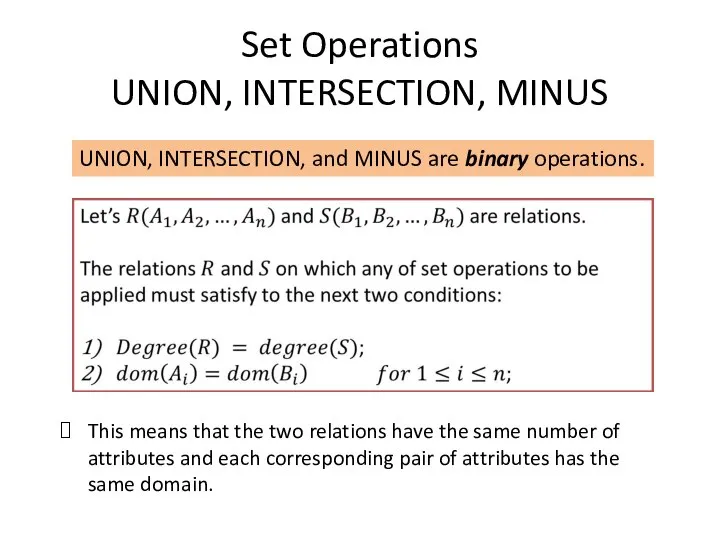
- 3. Set Operations UNION, INTERSECTION, MINUS UNION, INTERSECTION, and MINUS are binary operations. This means that the
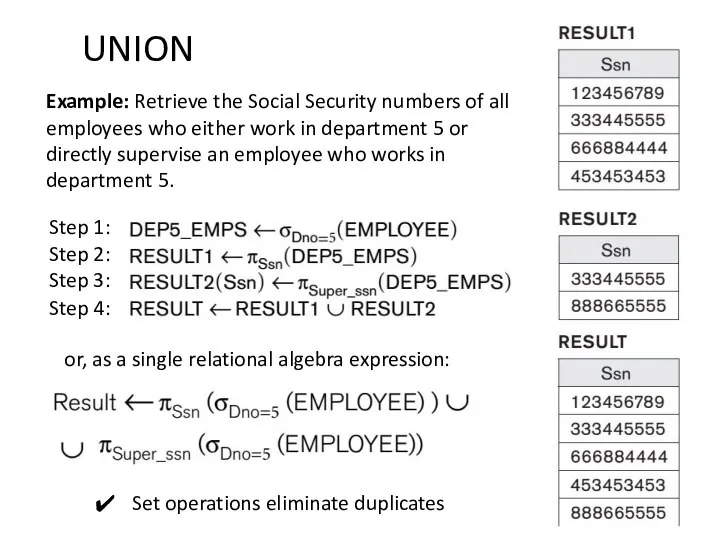
- 4. UNION Example: Retrieve the Social Security numbers of all employees who either work in department 5
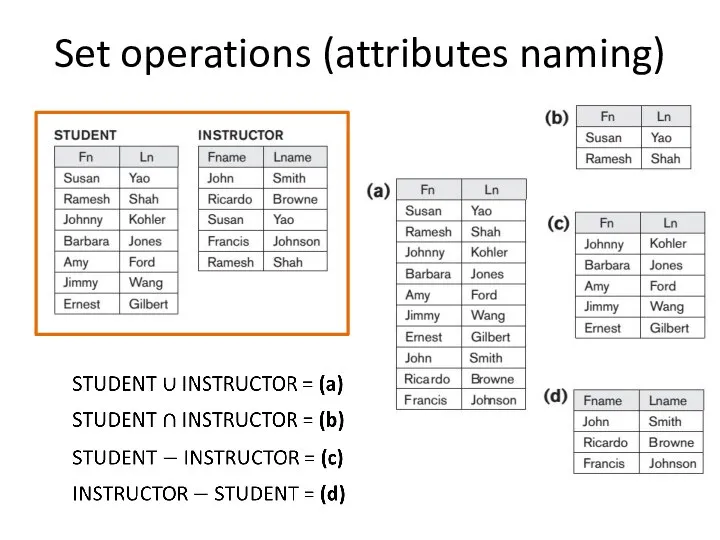
- 5. Set operations (attributes naming)
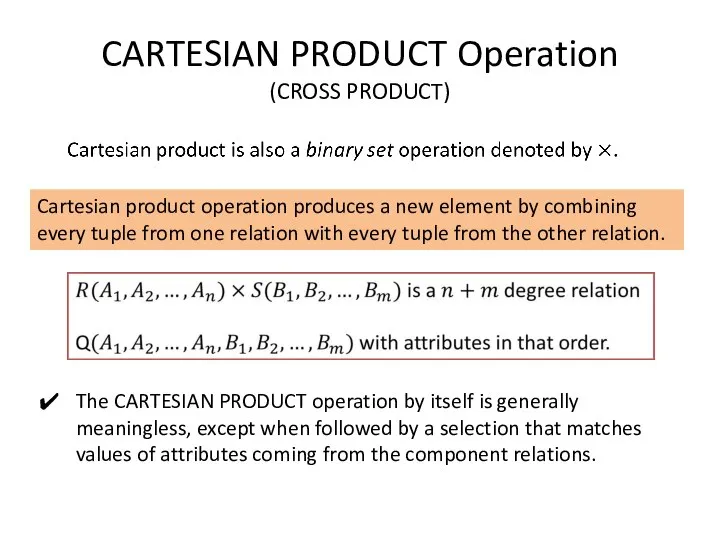
- 6. CARTESIAN PRODUCT Operation (CROSS PRODUCT) Cartesian product operation produces a new element by combining every tuple
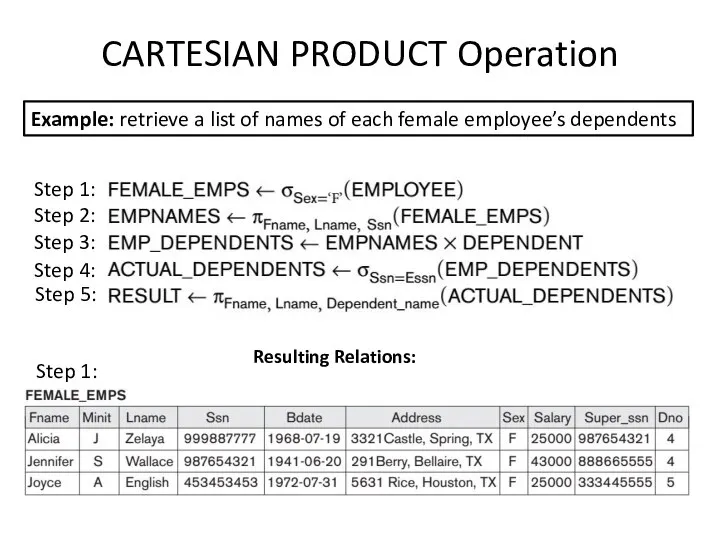
- 7. CARTESIAN PRODUCT Operation Example: retrieve a list of names of each female employee’s dependents Step 1:
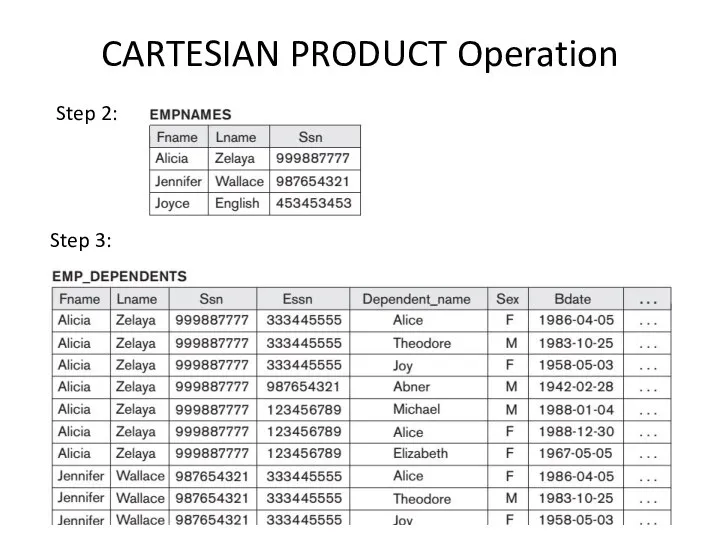
- 8. CARTESIAN PRODUCT Operation Step 2: Step 3:
- 9. CARTESIAN PRODUCT Operation Step 4: Step 5: Because this sequence of CARTESIAN PRODUCT followed by SELECT
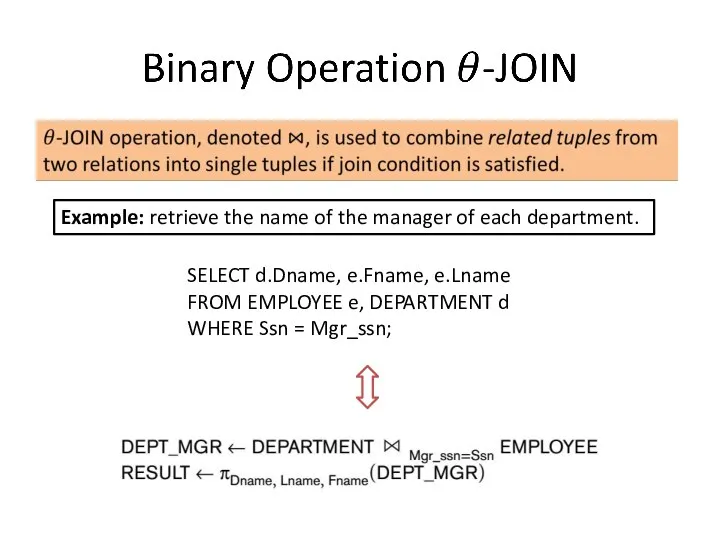
- 10. Example: retrieve the name of the manager of each department. SELECT d.Dname, e.Fname, e.Lname FROM EMPLOYEE
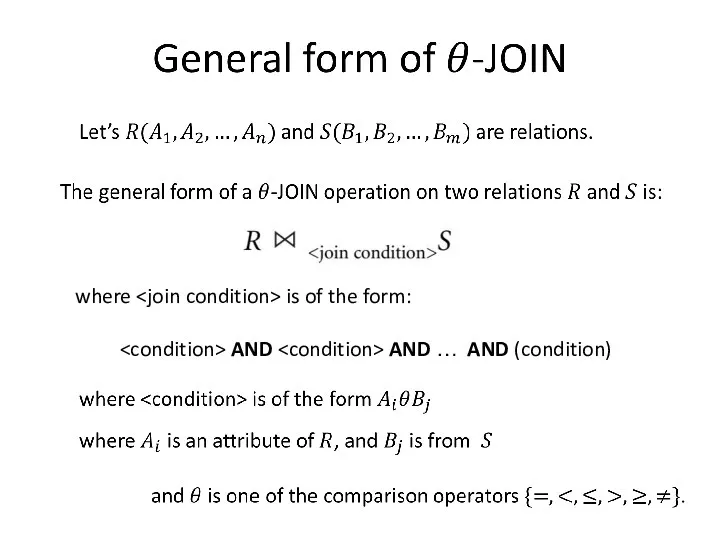
- 11. where is of the form: AND AND … AND (condition)
- 13. Скачать презентацию

 Ордера в архитектуре
Ордера в архитектуре Выявление следов рук
Выявление следов рук Подготовка технического задания для электронных курсов
Подготовка технического задания для электронных курсов Общевоинские уставы, их основные требования и содержание
Общевоинские уставы, их основные требования и содержание Понятие измерительного сигнала и его преобразование
Понятие измерительного сигнала и его преобразование ШЕДЕВРЫ АРХИТЕКТУРЫ ИНДИИ
ШЕДЕВРЫ АРХИТЕКТУРЫ ИНДИИ Гензель и Гретель Художник Сергий Елена
Гензель и Гретель Художник Сергий Елена  Искусство анимации как средство развития речи детей младшего школьного возраста Формирующий эксперимент «ВОРОНА» ГОУ СОШ №
Искусство анимации как средство развития речи детей младшего школьного возраста Формирующий эксперимент «ВОРОНА» ГОУ СОШ № Материнство и заработная плата: почему женщины с детьми зарабатывают меньше?
Материнство и заработная плата: почему женщины с детьми зарабатывают меньше? Получение наноструктурированных пленок Al2O3 из золь-гель пленок
Получение наноструктурированных пленок Al2O3 из золь-гель пленок Фридрих Вильгельм Ницше
Фридрих Вильгельм Ницше Банковские услуги для малого и среднего бизнеса: современное состояние и потребительские предпочтения Результаты исследования
Банковские услуги для малого и среднего бизнеса: современное состояние и потребительские предпочтения Результаты исследования Символічне значення одягу священнослужителів. Символіка кольорів
Символічне значення одягу священнослужителів. Символіка кольорів В лесу - презентация для начальной школы_
В лесу - презентация для начальной школы_ Классный час «Творчество Сурикова Василия Ивановича»
Классный час «Творчество Сурикова Василия Ивановича» Спортплощадка
Спортплощадка Язык программирования Java
Язык программирования Java do does игра
do does игра Описание картины осенней тематики - презентация для начальной школы_
Описание картины осенней тематики - презентация для начальной школы_ Мы показываем кукол, а куклы показывают нам мир. Презентация учащихся 4-го класса спецшколы – интерната № 21 г. Петрозаводска
Мы показываем кукол, а куклы показывают нам мир. Презентация учащихся 4-го класса спецшколы – интерната № 21 г. Петрозаводска Подготовительные и вспомогательные процессы при выполнении земляных работ
Подготовительные и вспомогательные процессы при выполнении земляных работ Тұрғындарға фармацевтикалық көмекті ұйымдастырудың заңнамалық базасы. Дәрілік заттар айналымы саласындағы халықаралық сапа
Тұрғындарға фармацевтикалық көмекті ұйымдастырудың заңнамалық базасы. Дәрілік заттар айналымы саласындағы халықаралық сапа Florence Nightingale - Pioneer of nursing
Florence Nightingale - Pioneer of nursing Функция менеджмента «Контроль» КОНТРОЛЬ – СИСТЕМА НАБЛЮДЕНИЯ ЗА ДЕЯТЕЛЬНОСТЬЮ ФИРМЫ.
Функция менеджмента «Контроль» КОНТРОЛЬ – СИСТЕМА НАБЛЮДЕНИЯ ЗА ДЕЯТЕЛЬНОСТЬЮ ФИРМЫ. Презентация Черный квадрат
Презентация Черный квадрат Массивы в Java
Массивы в Java Школа футбольного арбитра. Правило 5. Арбитр
Школа футбольного арбитра. Правило 5. Арбитр Презентация "Сказочные узоры. Городецкая роспись" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Сказочные узоры. Городецкая роспись" - скачать презентации по МХК