Содержание
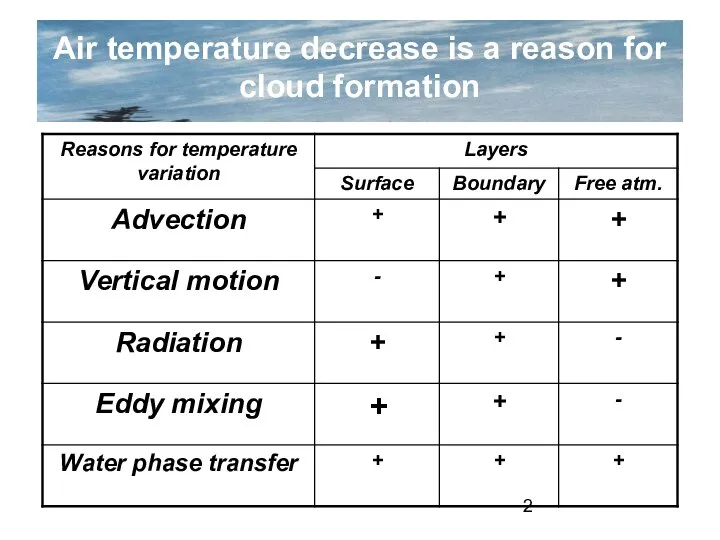
- 2. Air temperature decrease is a reason for cloud formation
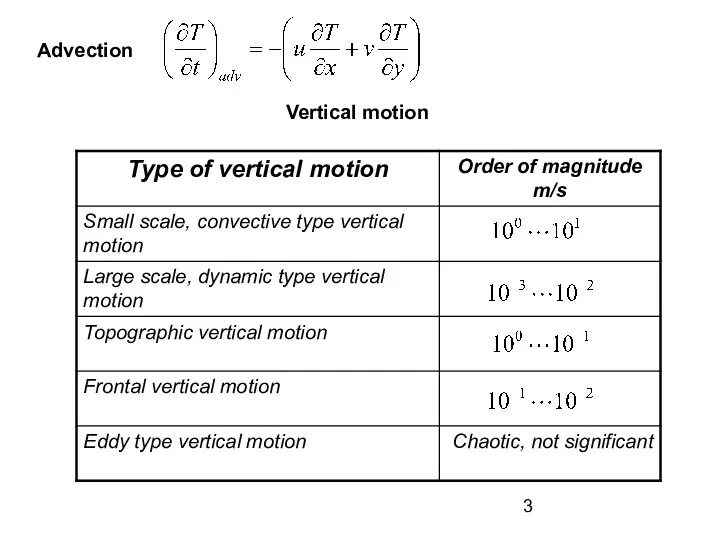
- 3. Advection Vertical motion
- 4. Water vapor content variation Eddy mixing Advection Divergence These factors act in case there is a
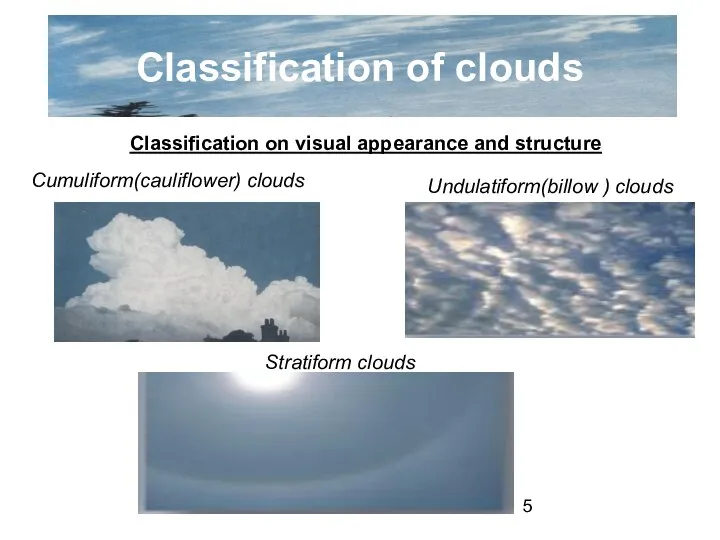
- 5. Classification of clouds Classification on visual appearance and structure Cumuliform(cauliflower) clouds Undulatiform(billow ) clouds Stratiform clouds
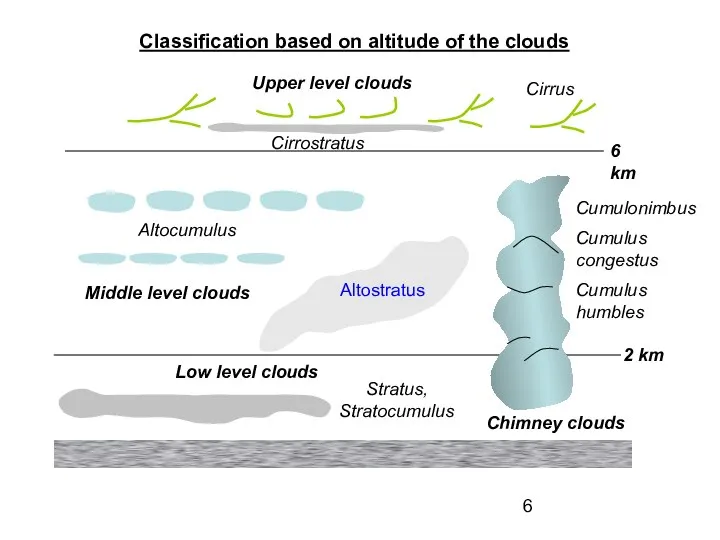
- 6. Classification based on altitude of the clouds 2 km 6 km Low level clouds Stratus, Stratocumulus
- 7. Cirrus felosus
- 8. Cirrus uncinus
- 9. Cirrostratus
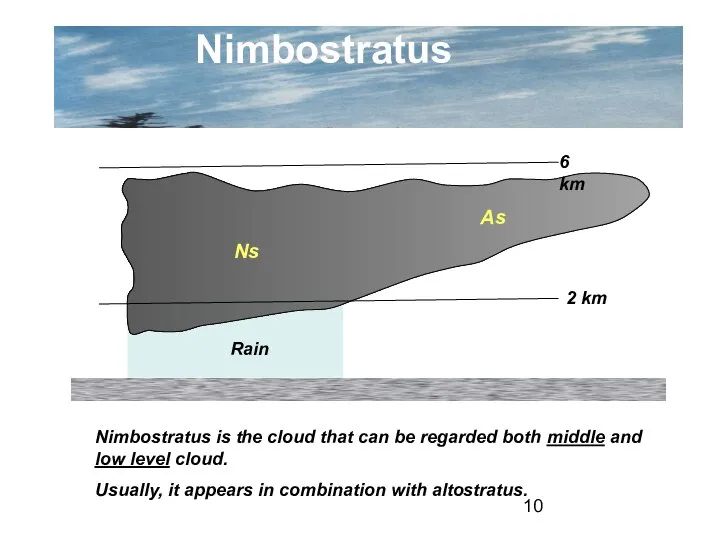
- 10. Nimbostratus 2 km 6 km Ns As Rain Nimbostratus is the cloud that can be regarded
- 11. Altostratus
- 12. Nimbostratus
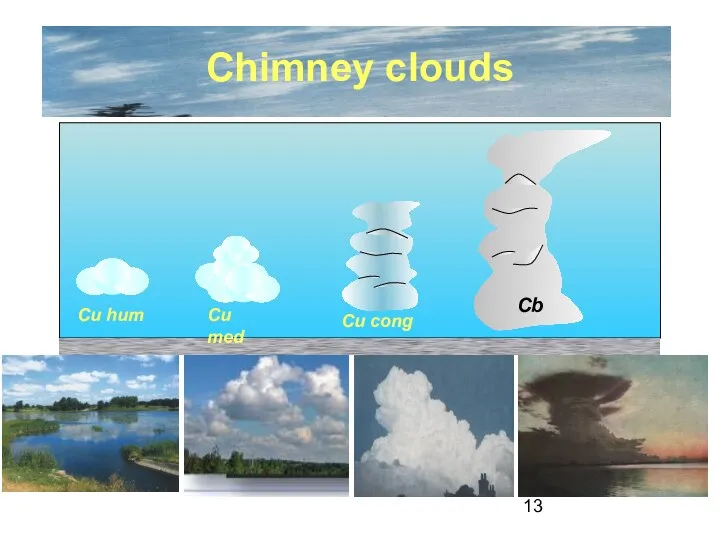
- 13. Chimney clouds Cu hum Cu med Cu cong Cb
- 14. Meso – scale convective complexes (MCC)
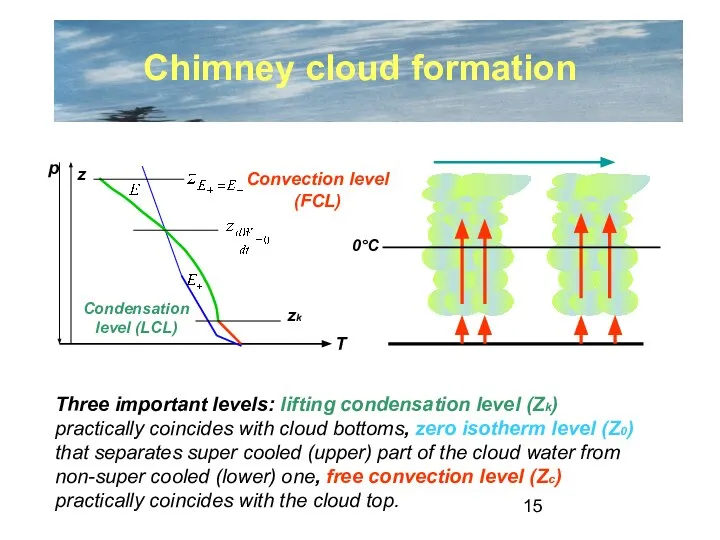
- 15. Chimney cloud formation Condensation level (LCL) zk Convection level (FCL) Three important levels: lifting condensation level
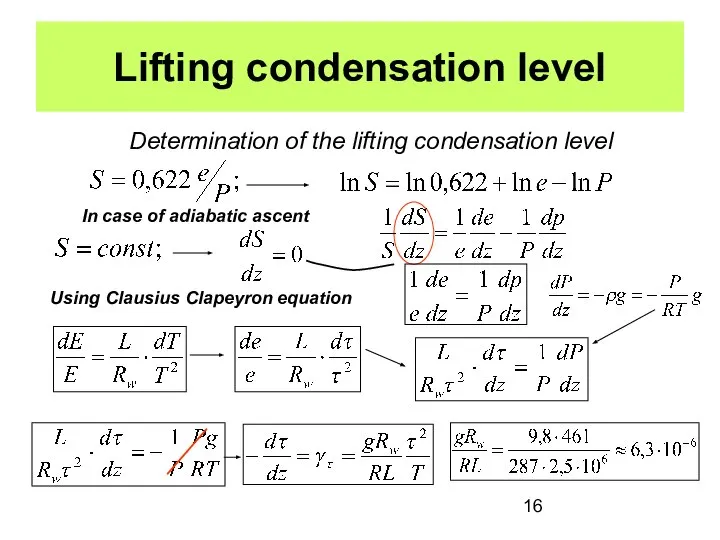
- 16. Lifting condensation level Determination of the lifting condensation level In case of adiabatic ascent Using Clausius
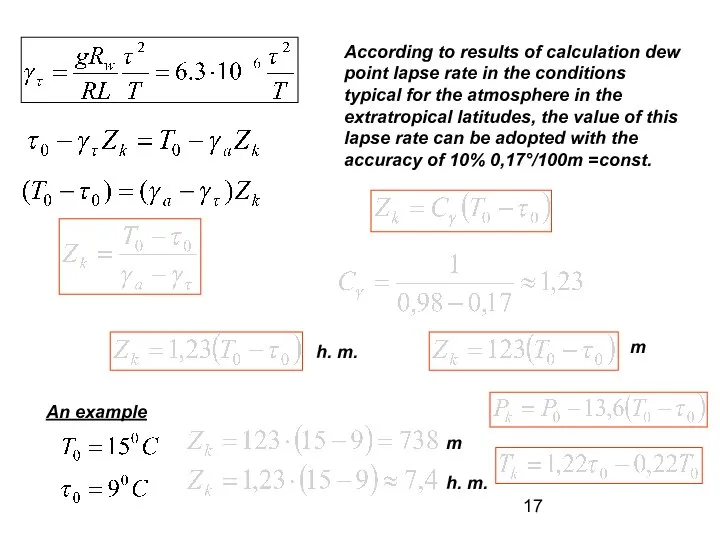
- 17. According to results of calculation dew point lapse rate in the conditions typical for the atmosphere
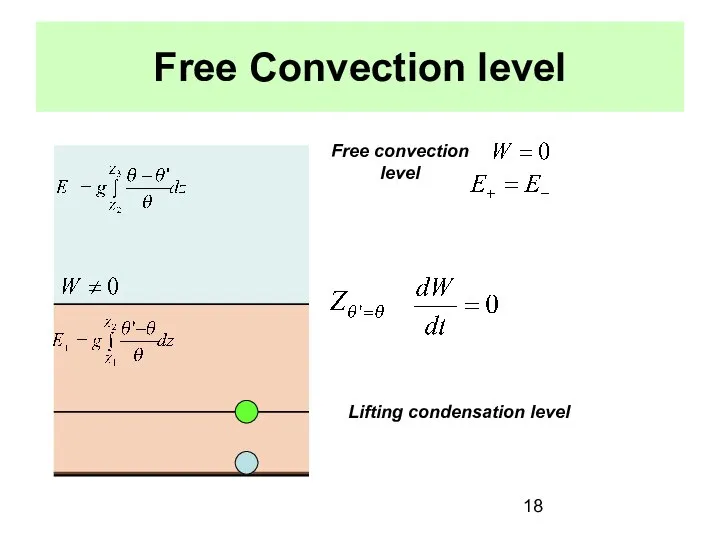
- 18. Free Convection level Lifting condensation level Free convection level
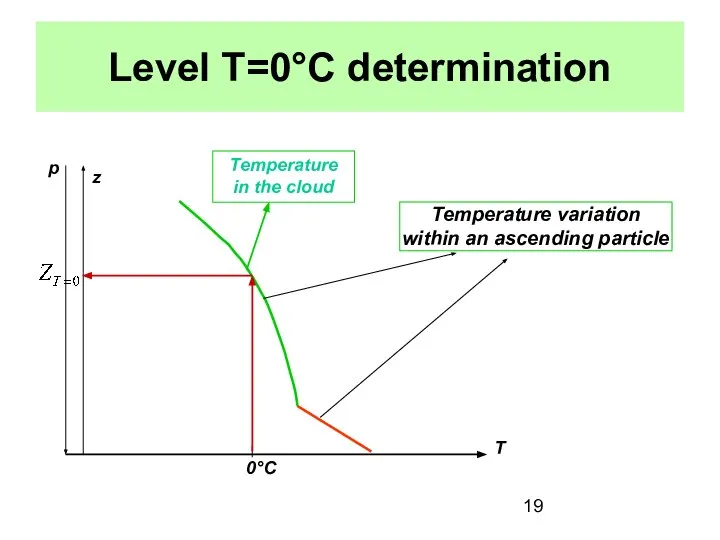
- 19. Level T=0°C determination Temperature variation within an ascending particle Temperature in the cloud 0°C
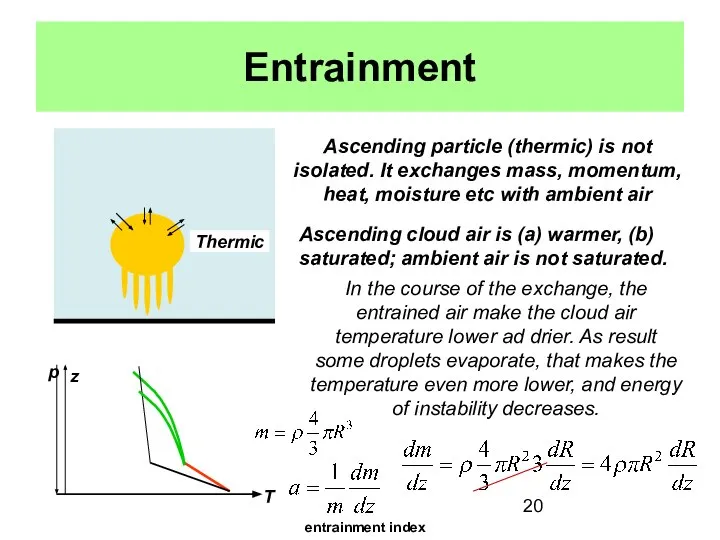
- 20. Entrainment Ascending particle (thermic) is not isolated. It exchanges mass, momentum, heat, moisture etc with ambient
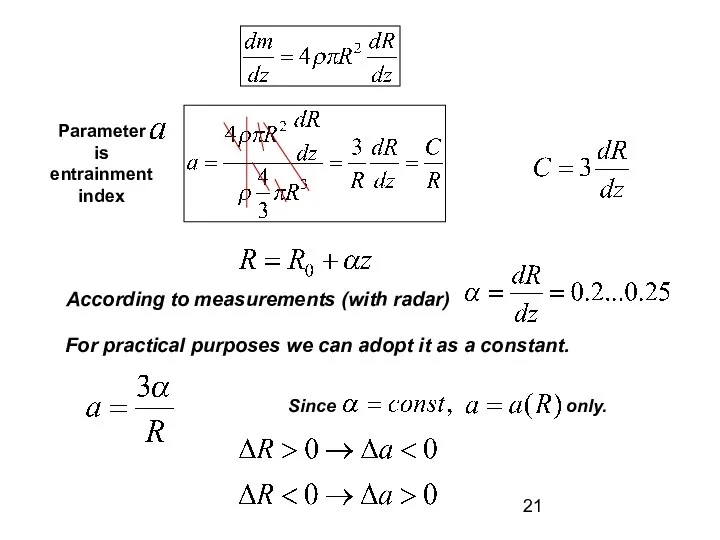
- 21. According to measurements (with radar) For practical purposes we can adopt it as a constant. Parameter
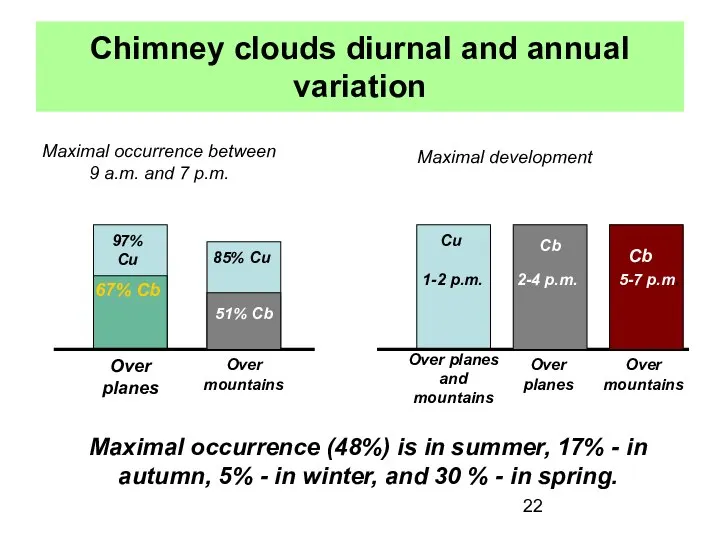
- 22. Chimney clouds diurnal and annual variation Maximal occurrence between 9 a.m. and 7 p.m. Cu Cb
- 24. Скачать презентацию






 Отчет о выполнении работ по благоустройству общественной территории. Вельский район деревня Никифорово
Отчет о выполнении работ по благоустройству общественной территории. Вельский район деревня Никифорово Политический режим
Политический режим Презентация Рынок недвижимости (РОССТАТ)
Презентация Рынок недвижимости (РОССТАТ)  Волгоградский Государственный Медицинский Университет Кафедра анатомии человека Общая артрология. Частная анатомия суст
Волгоградский Государственный Медицинский Университет Кафедра анатомии человека Общая артрология. Частная анатомия суст ХиТРРЭ.pptx
ХиТРРЭ.pptx Pneumatic devices
Pneumatic devices The Executive Branch
The Executive Branch  Группы риска макет
Группы риска макет Сахарный диабет 2 типа
Сахарный диабет 2 типа  Мой Петербург
Мой Петербург Массивы в Pascal. Одномерные массивы
Массивы в Pascal. Одномерные массивы Детско-юношеский отдых в регионах Татарстана. Лениногорский район
Детско-юношеский отдых в регионах Татарстана. Лениногорский район Инфекции, передаваемые половым путем
Инфекции, передаваемые половым путем Неоднозначность факторного решения
Неоднозначность факторного решения Курбан-байрам - праздник жертвоприношения
Курбан-байрам - праздник жертвоприношения Презентация на тему "Современный УМК как средство опережающего развития школьников в условиях обновления содержания образован
Презентация на тему "Современный УМК как средство опережающего развития школьников в условиях обновления содержания образован Информационно-исследовательский проект по музыке: «Влияние колокольного искусства на духовное возрождение общества в современны
Информационно-исследовательский проект по музыке: «Влияние колокольного искусства на духовное возрождение общества в современны Модификатор зеркало и создание разрезов
Модификатор зеркало и создание разрезов Проект на тему «Система работы с родителями в образовательном учреждении»
Проект на тему «Система работы с родителями в образовательном учреждении» Критика и самокритика
Критика и самокритика Общественное мнение и средства массовой информации
Общественное мнение и средства массовой информации Movie Industry in America
Movie Industry in America Административное право РК
Административное право РК Докторските студии -трет циклус во високото образование на РМ Проф. Д-р Марика Башеска – Ѓорѓиеска УКЛО, Економски факултет-Приле
Докторските студии -трет циклус во високото образование на РМ Проф. Д-р Марика Башеска – Ѓорѓиеска УКЛО, Економски факултет-Приле Работа в группа сентябрьх
Работа в группа сентябрьх Переход права собственности на жилое помещение в порядке договора купли продажи
Переход права собственности на жилое помещение в порядке договора купли продажи  Как свести к нулю количество конфликтов между проектной командой и командами поддержки или I believe in love. - презентация
Как свести к нулю количество конфликтов между проектной командой и командами поддержки или I believe in love. - презентация Буклет менеджера. Всероссийский форум breakpoint
Буклет менеджера. Всероссийский форум breakpoint