Содержание
- 2. G 3. Construction Contracts Types of contracts Recognition methods : Presentation :
- 3. IAS 11 (International Accounting Standards) Construction Contracts provides requirements on the allocation of contract revenue and
- 4. History of IAS 11 — Construction Contracts
- 5. TYPES OF CONSTRUCTION CONTRACTS Two broad categories: Price Given in Advance Contracts (Priced-based Contracts) Cost Reimbursement
- 6. TYPES OF CONSTRUCTION CONTRACTS 1. Lump Sum Contact 2. Contract based on a Bill of Quantities
- 7. 1. Lump Sum Contact Main Aspects 1. Payment may be staged at intervals of time. 2.
- 8. 1. Lump Sum Contact Advantages The final price is known The contractor has more incentive to
- 9. 2. Contract based on a Bill of Quantities Sometimes called Unit Price Contract Main Aspects Items
- 10. 2. Contract based on a Bill of Quantities Sometimes called Unit Price Contract Advantages 1. Saving
- 11. 3. Schedule of Rates Contract Main Aspects 1. A Schedule of the work items without quantities.
- 12. 3. Schedule of Rates Contract Advantages 1. Work can be commenced earlier than if a full
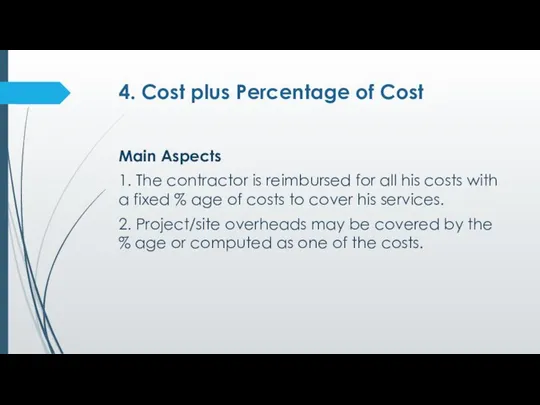
- 13. 4. Cost plus Percentage of Cost Main Aspects 1. The contractor is reimbursed for all his
- 14. 4. Cost plus Percentage of Cost Advantages 1. Construction can start before design is completed. 2.
- 15. 5. Cost plus Fixed Fee Main Aspects 1. The owner pays all costs of construction with
- 16. 6. Target Cost with Variable Fees Contract Main Aspects 1. The contractor and owner agree to
- 17. 6. Target Cost with Variable Fees Contract Advantages 1. There is an incentive to carry out
- 18. 7. Guaranteed Maximum Price Contract (GMP) 1. The contractor guarantees that he will construct the project
- 19. Recognition methods Stage of Completion (Percentage of Completion) Value Based Methods Cost Based Method - See
- 21. Скачать презентацию

















 Михаил Юриевич Лермонтов Живот и творчество в картини Разр а ботил : М. Илиева. - презентация
Михаил Юриевич Лермонтов Живот и творчество в картини Разр а ботил : М. Илиева. - презентация Пересечение поверхности плоскостью
Пересечение поверхности плоскостью Тенденции современной моды
Тенденции современной моды Доклад Сентябрь-время учиться
Доклад Сентябрь-время учиться Методы решения квадратных уравнений - презентация по Алгебре
Методы решения квадратных уравнений - презентация по Алгебре Статические характеристики средств измерений
Статические характеристики средств измерений Организация транспортного обслуживания международных экономических связей
Организация транспортного обслуживания международных экономических связей К.А.Григорьева кафедра зарубежной литературы и журналистики Саратовский госуниверситет Американский Уголок в Саратове К
К.А.Григорьева кафедра зарубежной литературы и журналистики Саратовский госуниверситет Американский Уголок в Саратове К Боевые свойства и поражающие факторы химического оружия
Боевые свойства и поражающие факторы химического оружия  Буддизм. Буддистские монахи
Буддизм. Буддистские монахи Федеральная служба по финансовому мониторингу (Росфинмониторинг)
Федеральная служба по финансовому мониторингу (Росфинмониторинг) Пунктуация для малышей - презентация для начальной школы_
Пунктуация для малышей - презентация для начальной школы_ Презентация на тему "Сетевые педагогические сообщества как форма самообразования и повышения квалификации учителей" - скача
Презентация на тему "Сетевые педагогические сообщества как форма самообразования и повышения квалификации учителей" - скача Ролан Барт и его лингвосемиотические идеи
Ролан Барт и его лингвосемиотические идеи Патологическая анатомия, ее содержание и задачи. Патологоанатомическая служба, её роль и место в системе здравоохранения. Лекци
Патологическая анатомия, ее содержание и задачи. Патологоанатомическая служба, её роль и место в системе здравоохранения. Лекци Инженерная графика. Начертательная геометрия. Машиностроительное черчение
Инженерная графика. Начертательная геометрия. Машиностроительное черчение Переработка на таможенной территории Подготовил: Студент I курса ФТД группы Тс 02/1407 Арсентьева Валентина
Переработка на таможенной территории Подготовил: Студент I курса ФТД группы Тс 02/1407 Арсентьева Валентина Т Е М А «ПОСТАВКА ТОВАРОВ. КОНТРАКТАЦИЯ»
Т Е М А «ПОСТАВКА ТОВАРОВ. КОНТРАКТАЦИЯ» Компьютерная алгебра системы счисления
Компьютерная алгебра системы счисления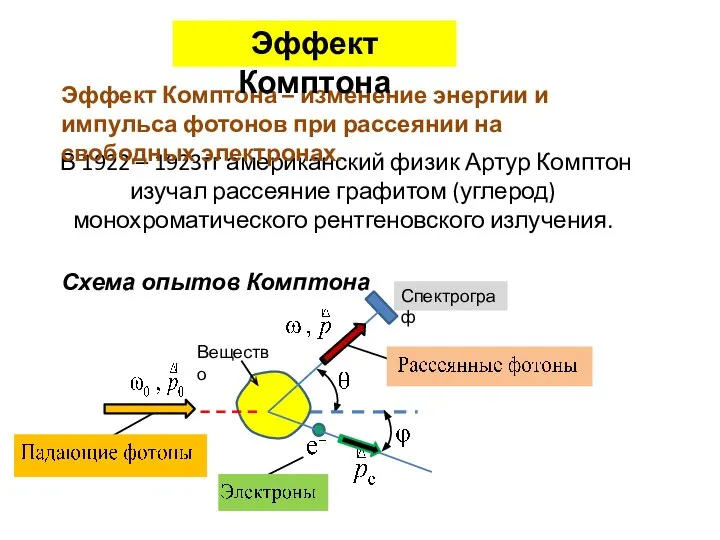 3.ЭФФЕКТ КОМПТОНА
3.ЭФФЕКТ КОМПТОНА Проблемы защиты прав на интеллектуальную собственность в сети Интернет
Проблемы защиты прав на интеллектуальную собственность в сети Интернет Этапы развития квантовой механики.
Этапы развития квантовой механики. Презентация на тему "Информационное совещание заместителей заведующего и старших воспитателей дошкольных образовательных учр
Презентация на тему "Информационное совещание заместителей заведующего и старших воспитателей дошкольных образовательных учр Технологии и системы коммутации. Основа временного разделения каналов
Технологии и системы коммутации. Основа временного разделения каналов Урок чтения в 4 классе по теме «Сказка о царе Салтане…» Учитель начальных классов Замалетдинова Г.А. Лицей №1 Г.Зеленодольск, Татарстан
Урок чтения в 4 классе по теме «Сказка о царе Салтане…» Учитель начальных классов Замалетдинова Г.А. Лицей №1 Г.Зеленодольск, Татарстан Права человека. Исторический обзор
Права человека. Исторический обзор Технология ATM. (Лекция 3)
Технология ATM. (Лекция 3) Презентация "Видеореклама в Интернете" - скачать презентации по Экономике
Презентация "Видеореклама в Интернете" - скачать презентации по Экономике