Содержание
- 2. Agenda What is 'jQuery'? Launching Code on Document Ready jQuery Selectors DOM Manipulation Event Handling Effects
- 3. What is 'jQuery'?
- 4. jQuery: Write Less, Do More Query is a fast, small, and feature-rich JavaScript library. It makes
- 5. Linking jQuery jQuery is available at official website: http://jQuery.com You may download jQuery to local folder
- 6. $ Alias jQuery uses '$' symbol as alias to object 'jQuery' This symbol available as a
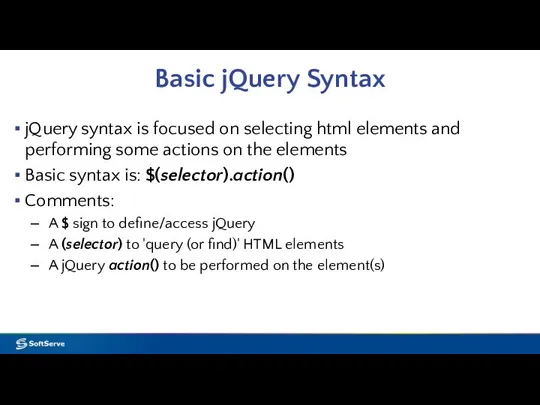
- 7. Basic jQuery Syntax jQuery syntax is focused on selecting html elements and performing some actions on
- 8. Launching Code on Document Ready
- 9. window.onload Very common task in web programming is to run JS code when the browser finishes
- 10. jQuery Ready Event To run code as soon as the document is ready to be manipulated,
- 11. Alternate Form of jQuery Ready Event There is an alternative form of jQuery Ready event: $(function()
- 12. jQuery Selectors
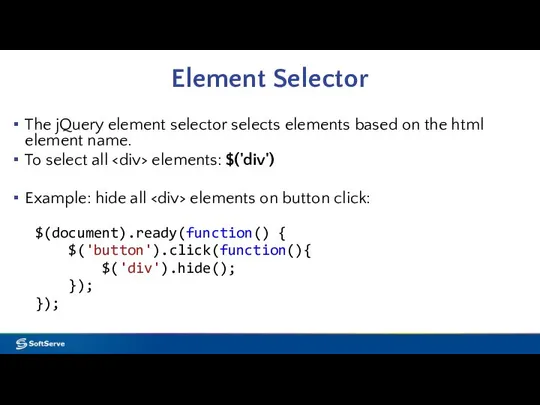
- 13. Element Selector The jQuery element selector selects elements based on the html element name. To select
- 14. The #id Selector The jQuery #id selector uses the id attribute of an html tag to
- 15. The .class Selector The jQuery .class selector uses the class attribute of an html tag to
- 16. CSS Selectors jQuery allows to use same selectors as used in CSS versions 1-3 Incomplete list
- 17. DOM Manipulation
- 18. Introduction to DOM Manipulation with jQuery jQuery provides powerful methods to manipulate the DOM in some
- 19. Reading and Changing HTML Contents Method .html() allows to get or set HTML contents of elements
- 20. Reading and Changing Class Info jQuery allows to read, add or remove information about class for
- 21. Reading and Changing Styles jQuery provides method .css() that allows to read or set style data.
- 22. jQuery Event Handling
- 23. jQuery Event Basics It is very convenient to use jQuery to set up event-driven responses on
- 24. Setting Up Browser onclick Event Next example setups onclick event handler for all paragraphs on a
- 25. Usin .on() Method There is an alternate method to set event handlers: jQuery .on() method. The
- 26. Setting Up Browser onclick Event With .on() Method Using .on() method we may setup any native
- 27. Using Different Handlers for Multiple Events In the example below shown how to use different event
- 28. Tearing Down Event Listeners To remove an event listener, you use the .off() method and pass
- 29. Setting Up Events to Run Only Once Sometimes you need a particular handler to run only
- 30. jQuery Effects
- 31. Introduction to Effects jQuery makes it trivial to add simple effects to your page. Effects can
- 32. Showing and Hiding Content jQuery can show or hide content instantaneously with .show() or .hide(). When
- 33. Animated Showing and Hiding jQuery can also show or hide content by means of animation effects.
- 34. Fade and Slide Animations jQuery uses combination of fade and slide effects while showing and hiding
- 35. Changing Display Based on Current Visibility State jQuery can also let you change a content's visibility
- 36. Doing Something After an Animation Completes If we want to do something after animation completes, we
- 37. Useful links
- 38. Links Official jQuery Website: http://jquery.com/ Official jQuery Learning Center: http://learn.jquery.com/ w3schools.com jQuery Tutorial: http://www.w3schools.com/jquery/
- 40. Скачать презентацию



































 Политическая история и политическая культура
Политическая история и политическая культура Зимовье зверей - презентация для начальной школы
Зимовье зверей - презентация для начальной школы Единая трактовка правил игры в футбол. Нарушения Правил и недисциплинированное поведение
Единая трактовка правил игры в футбол. Нарушения Правил и недисциплинированное поведение Информационные технологии. Visual Basic
Информационные технологии. Visual Basic Политическая наука в республике Беларусь
Политическая наука в республике Беларусь Линейка женской одежды over size
Линейка женской одежды over size международный валютный фонд и особенности его функционирования Выполнили:Макарова А.С. и Лазарюк А.С.
международный валютный фонд и особенности его функционирования Выполнили:Макарова А.С. и Лазарюк А.С. The olympics games
The olympics games Пасха в США
Пасха в США The Volkswagen Käfer Convertible Police
The Volkswagen Käfer Convertible Police Отчет о доходах и расходах Некоммерческого партнерства за cентябрь - декабрь 2014 года
Отчет о доходах и расходах Некоммерческого партнерства за cентябрь - декабрь 2014 года Охрана западной границы России регулярными войсками Выполнила студентка 2-го курса группы Э101 Овсянникова Надежда
Охрана западной границы России регулярными войсками Выполнила студентка 2-го курса группы Э101 Овсянникова Надежда Android gestures. Стандартные жесты
Android gestures. Стандартные жесты Зимбабве
Зимбабве Презентация Причины и виды безработицы
Презентация Причины и виды безработицы Коллизионные нормы в международном частном праве. (Тема 3)
Коллизионные нормы в международном частном праве. (Тема 3) Кардиология
Кардиология  Новации контрактной системы в сфере закупок. Федеральный закон от 01.05.2019 № 71-ФЗ
Новации контрактной системы в сфере закупок. Федеральный закон от 01.05.2019 № 71-ФЗ Техника упражнений для развития мышц голени и икроножных мышц
Техника упражнений для развития мышц голени и икроножных мышц Физкультурно-спортивный комплекс ГТО
Физкультурно-спортивный комплекс ГТО Экологический аудит
Экологический аудит  Технології програмування КС. Лекція 2 (частина 2)
Технології програмування КС. Лекція 2 (частина 2) Закон Мура и развитие информационных технологий
Закон Мура и развитие информационных технологий Тема Коммуникация как процесс. Принципы организации эффективного коммуникационного процесса.
Тема Коммуникация как процесс. Принципы организации эффективного коммуникационного процесса. Конденсаторные микрофоны
Конденсаторные микрофоны Собственные векторы и собственные значения линейного оператора
Собственные векторы и собственные значения линейного оператора Космічний. Комікси
Космічний. Комікси Философия: предмет и структура
Философия: предмет и структура