Содержание
- 2. Why do we need to be able to measure things? Any Ideas? Suppose we wanted to
- 3. Estimation Estimation is using your knowledge of something similar in size or amount to determine the
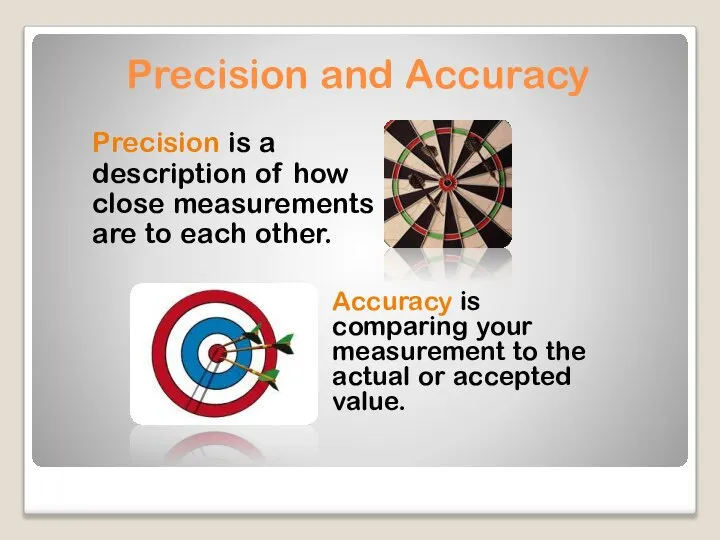
- 4. Precision is a description of how close measurements are to each other. Precision and Accuracy Accuracy
- 5. Measurements are easily understood by all scientists Measurements are easier to convert than the English system
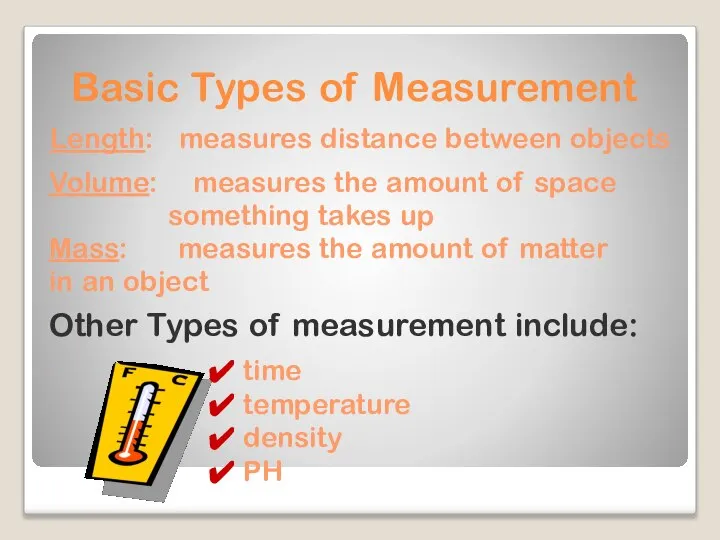
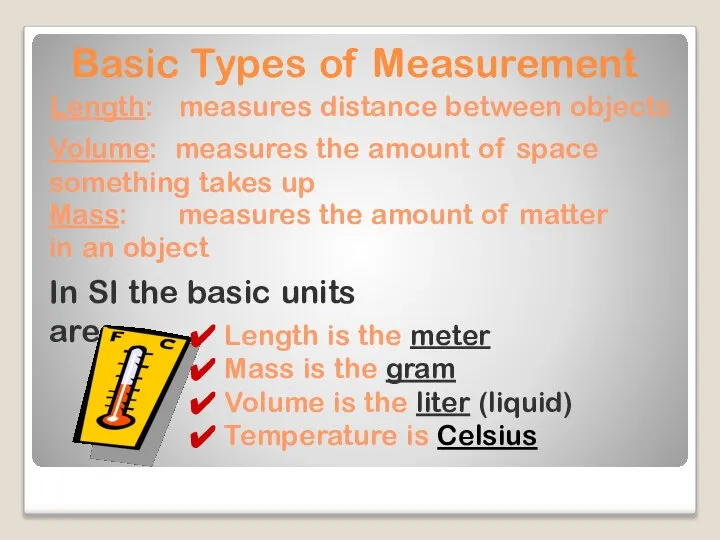
- 6. Basic Types of Measurement Length: measures distance between objects Mass: measures the amount of matter in
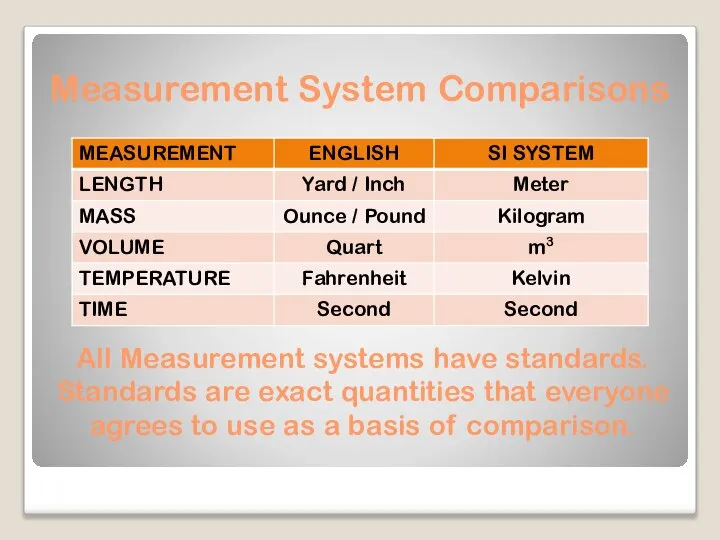
- 7. Measurement System Comparisons All Measurement systems have standards. Standards are exact quantities that everyone agrees to
- 8. In the English system you have to remember so many numbers . . . 12 inches
- 9. The SI System uses the following prefixes: This system works with any SI measurement. The UNIT
- 10. It works for all types of measurement. If your measuring . . . Volume then it
- 11. How does converting units work? Unlike the English system converting in the SI System is very
- 12. The SI system is much easier. For example in the metric system if you wanted to
- 13. More Conversions . . . Kilo Hecto Deca UNIT Deci Centi Milli 2,321.0 millimeters to meters
- 14. Things to Remember All measurements need a number and a unit! Basic units of Measurement (meter,
- 15. Nature of Science The International System of Units
- 16. Basic Types of Measurement Length: measures distance between objects Mass: measures the amount of matter in
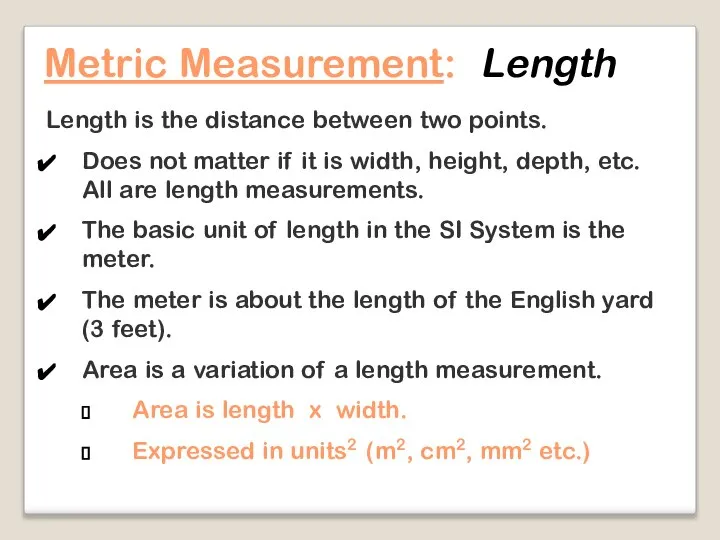
- 17. Length is the distance between two points. Does not matter if it is width, height, depth,
- 18. Metric Measurement: Mass Mass is a measurement of the amount of matter in an object. Basic
- 19. Metric Measurement: Volume Volume is a measurement of the amount of space something takes up. The
- 20. Metric Measurement: Temperature Temperature is a measure of the kinetic energy of the atoms in an
- 21. Nature of Science The International System of Units
- 22. Which is heavier . . . A kilogram of feathers or a kilogram of lead? Which
- 24. Скачать презентацию














 Учитель ИЗО МБОУ гимназии №45 г. Владикавказа Дзасохова Т.Г.
Учитель ИЗО МБОУ гимназии №45 г. Владикавказа Дзасохова Т.Г. Лабораторная работа. Ряды Фурье
Лабораторная работа. Ряды Фурье Работа системы управление рисками в таможенных органах Республики Узбекистан
Работа системы управление рисками в таможенных органах Республики Узбекистан Аппаратное обеспечение ПК
Аппаратное обеспечение ПК Свойства древесины
Свойства древесины ОСНОВОПОЛАГАЮЩИЕ ИДЕИ И ПРИНЦИПЫ УПРАВЛЕНИЯ ИЗМЕНЕНИЯМИ
ОСНОВОПОЛАГАЮЩИЕ ИДЕИ И ПРИНЦИПЫ УПРАВЛЕНИЯ ИЗМЕНЕНИЯМИ Презентация на тему "ЛАРВА ЦЕСТОД. (ЦЕНУР, ЭХИНОК)" - скачать презентации по Медицине
Презентация на тему "ЛАРВА ЦЕСТОД. (ЦЕНУР, ЭХИНОК)" - скачать презентации по Медицине Средства массовой информации как основной институт политической коммуникации. Проблема независимости СМИ
Средства массовой информации как основной институт политической коммуникации. Проблема независимости СМИ Прихожая, шкаф
Прихожая, шкаф Геометрические построения на чертежах
Геометрические построения на чертежах Дельфи ортасында бағдарламалау
Дельфи ортасында бағдарламалау Буксирное устройство судна и его техническая эксплуатация
Буксирное устройство судна и его техническая эксплуатация Отклонения и допуски формы (ГОСТ 24462-83)
Отклонения и допуски формы (ГОСТ 24462-83) Lista Światowego Dziedzictwa Kulturowego i Przyrodniczego UNESCO
Lista Światowego Dziedzictwa Kulturowego i Przyrodniczego UNESCO ТЕМА 5 ЭКОНОМИКА ПЕРСОНАЛА
ТЕМА 5 ЭКОНОМИКА ПЕРСОНАЛА  lektsia_-_Myshtsa_kak_organ_1
lektsia_-_Myshtsa_kak_organ_1 American pronunciation
American pronunciation История Парламента РК
История Парламента РК Событийно-ориентированные архитектуры. Программирование с использованием POSIX thread library
Событийно-ориентированные архитектуры. Программирование с использованием POSIX thread library Міжнародний тероризм
Міжнародний тероризм CoDeSys CNC functionality
CoDeSys CNC functionality Ханс (Ганс) Кристиан Андерсен
Ханс (Ганс) Кристиан Андерсен Формирование системы государственного управления в России в+ современный период Выполнили студентки 1 курса ФТД группы Т-1205
Формирование системы государственного управления в России в+ современный период Выполнили студентки 1 курса ФТД группы Т-1205  Презентация на тему "ТЭЛА" - скачать презентации по Медицине
Презентация на тему "ТЭЛА" - скачать презентации по Медицине Поглощающие аппараты. Устройство пружинно-фрикционного аппарата
Поглощающие аппараты. Устройство пружинно-фрикционного аппарата Поперечные электромагнитные волны
Поперечные электромагнитные волны Презентация ТРПО.ppt
Презентация ТРПО.ppt Отчет о доходах и расходах Некоммерческого партнерства за январь-август 2015 года
Отчет о доходах и расходах Некоммерческого партнерства за январь-август 2015 года