Содержание
- 2. Groups Personal Demonstrative Interrogative Indefinite
- 3. Morphological categories Person Number (singular, dual and plural) Case Gender (in the 3rd person singular) Personal
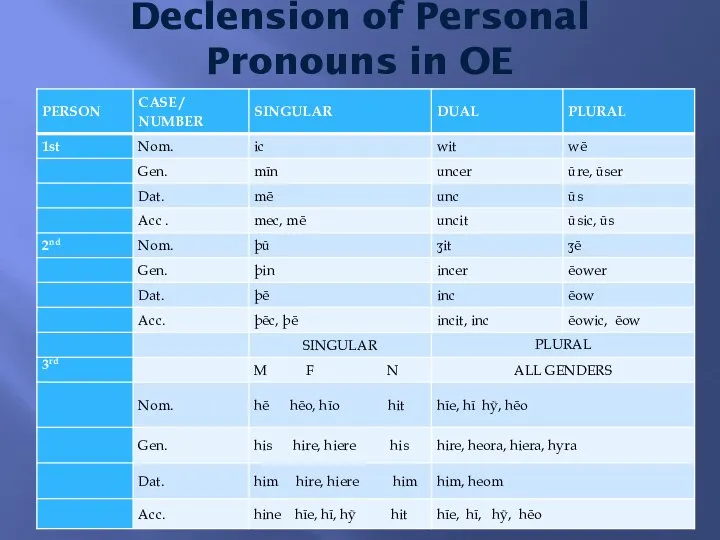
- 4. Declension of Personal Pronouns in OE
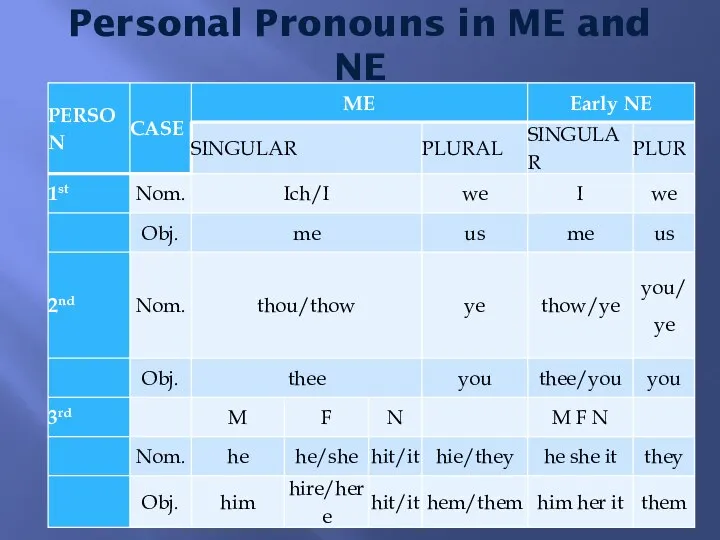
- 5. Personal Pronouns in ME and NE
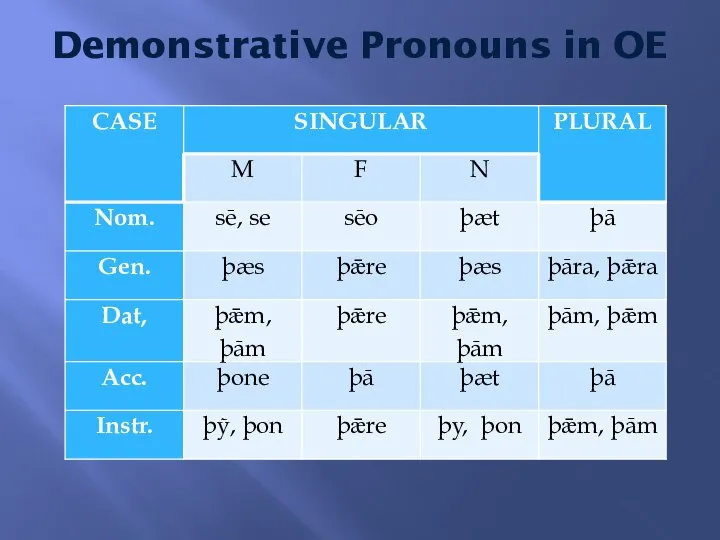
- 6. Demonstrative Pronouns in OE
- 7. Demonstrative Pronouns in ME and NE
- 8. Indefinite and Negative Pronouns Simple pronouns - ‘sum’ (NE ‘some’), ‘an’ and ‘ǣniʒ’ (NE ‘one, any’);
- 9. Interrogative Pronouns ‘hwā’ (Masc. and Fem.) - NE ‘who’ ‘hwæt’ (Neut.) – NE ‘what’ ‘hwylc’ -
- 10. Possessive Pronouns Developed from the Genitive case of personal pronouns: mīn, þīn, his, hire, ēōwer
- 12. Скачать презентацию






 Мир животных. Изучение интересных животных и их особенностей, посредством решения математических заданий и задач - презентация дл
Мир животных. Изучение интересных животных и их особенностей, посредством решения математических заданий и задач - презентация дл Владилен Владимирович Фуфаров - Управляющий ОАО «СМАК»
Владилен Владимирович Фуфаров - Управляющий ОАО «СМАК» Экономическая характеристика в абсолютных и относительных величинах 1991-2012 России и развитых стран мира
Экономическая характеристика в абсолютных и относительных величинах 1991-2012 России и развитых стран мира Weihnachten ist das größte Fest in Deutschland
Weihnachten ist das größte Fest in Deutschland Применение спортивного массажа в восстановительном цикле футболистов 16-17 лет
Применение спортивного массажа в восстановительном цикле футболистов 16-17 лет Опыт взаимодействия Роскомнадзора с интернет-компаниями по пресечению распространения экстремистского контента
Опыт взаимодействия Роскомнадзора с интернет-компаниями по пресечению распространения экстремистского контента Движение по окружности. Решение задач
Движение по окружности. Решение задач Денежно-кредитная политика: основные направления, инструменты, проблемы
Денежно-кредитная политика: основные направления, инструменты, проблемы  Школа социальных систем Подготовили: Студенты I курса экономического факультета РТА Юсов Алексей и Сафонов Михаил М112б 2012
Школа социальных систем Подготовили: Студенты I курса экономического факультета РТА Юсов Алексей и Сафонов Михаил М112б 2012  Конкуренция. Структура рынка Урок экономики. 9 класс
Конкуренция. Структура рынка Урок экономики. 9 класс Независимое поведение: объемная конкуренция. Модель Курно. Выполнила студентка 1 курса экономического факультета Редок Полина
Независимое поведение: объемная конкуренция. Модель Курно. Выполнила студентка 1 курса экономического факультета Редок Полина Законы экологии и природопользования
Законы экологии и природопользования Полупроводниковые лазеры
Полупроводниковые лазеры Презентация на тему "Гимнастика 5-11 класс" - скачать презентации по Педагогике
Презентация на тему "Гимнастика 5-11 класс" - скачать презентации по Педагогике Перечень работ, которые могут быть выполнены на кафедре промышленного и гражданского строительства (ПГС)
Перечень работ, которые могут быть выполнены на кафедре промышленного и гражданского строительства (ПГС) Презентация Понятие, признаки и классификация должностей федеральной гражданской службы
Презентация Понятие, признаки и классификация должностей федеральной гражданской службы  Основное назначение и возможности Word
Основное назначение и возможности Word  Самый полезный вид спорта
Самый полезный вид спорта Праздники Новый год и Рождество: сходства и различия
Праздники Новый год и Рождество: сходства и различия Идеал человека в христианстве
Идеал человека в христианстве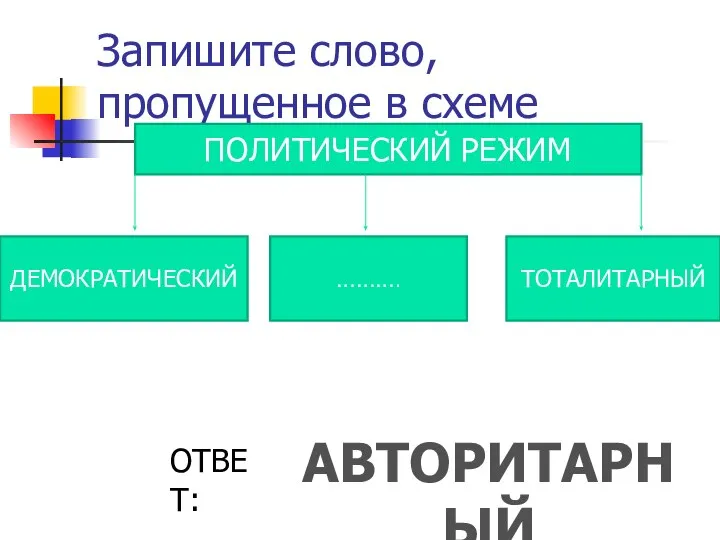 Тесты по обществоведению
Тесты по обществоведению Занимательная математика Алгебра и начала математического анализа, 10 класс.
Занимательная математика Алгебра и начала математического анализа, 10 класс.  Презентация Свободные экономические зоны во Франции
Презентация Свободные экономические зоны во Франции Предмет и методы политологии
Предмет и методы политологии Проектирование сети связи на базе медных и волоконно-оптических линий связи
Проектирование сети связи на базе медных и волоконно-оптических линий связи Герменевтика – наука и искусство толкования Священного Писания
Герменевтика – наука и искусство толкования Священного Писания Правила Карьеры Ник Фролов
Правила Карьеры Ник Фролов Урок как педагогический феномен
Урок как педагогический феномен