Содержание
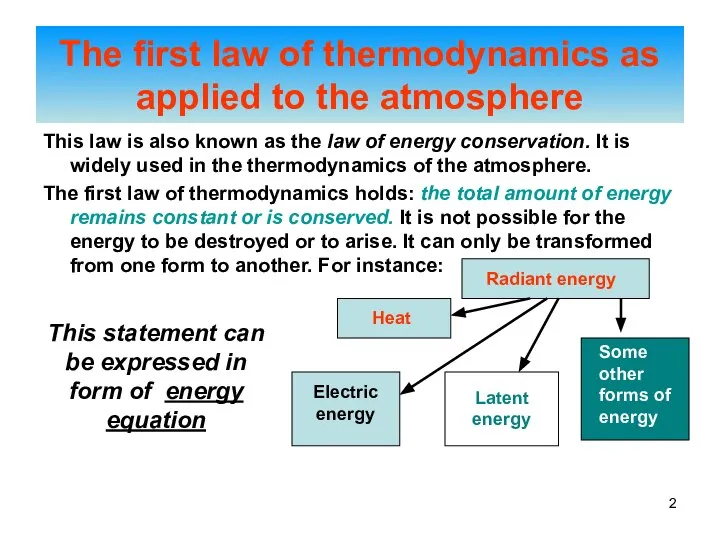
- 2. This law is also known as the law of energy conservation. It is widely used in
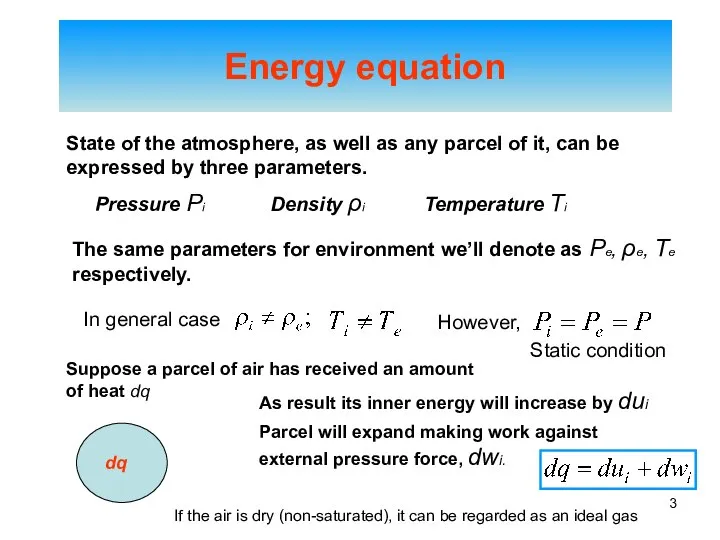
- 3. Energy equation State of the atmosphere, as well as any parcel of it, can be expressed
- 4. Ideal Gas An ideal gas is a theoretical is a theoretical gas is a theoretical gas
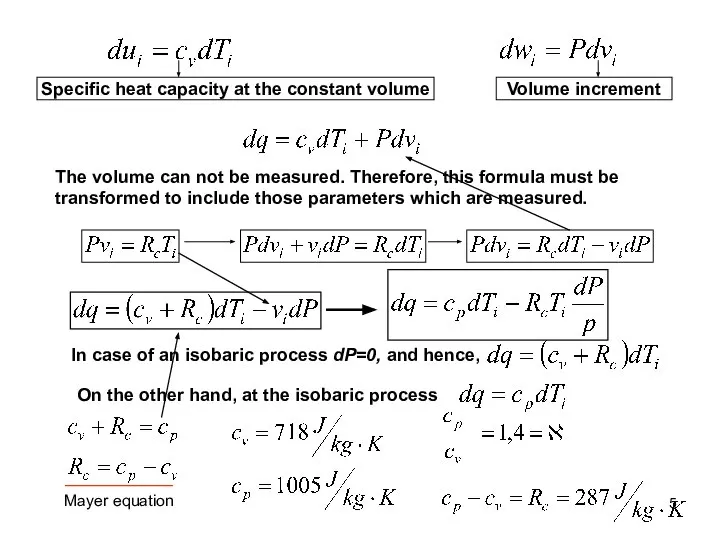
- 5. Specific heat capacity at the constant volume Volume increment The volume can not be measured. Therefore,
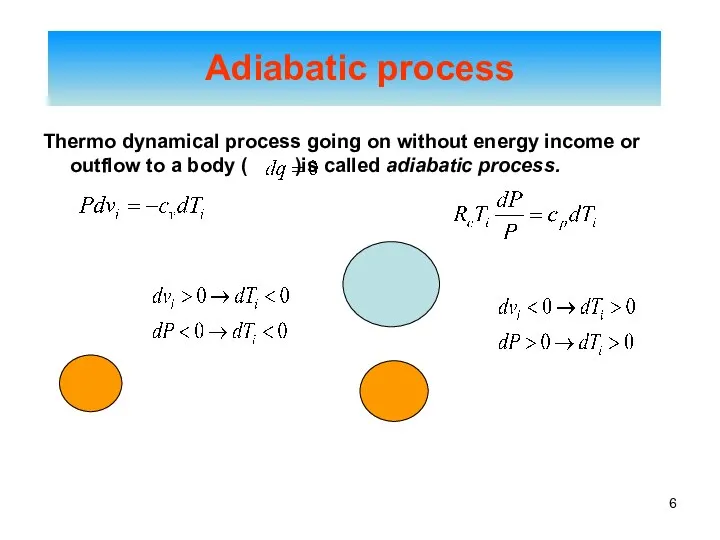
- 6. Adiabatic process Thermo dynamical process going on without energy income or outflow to a body (
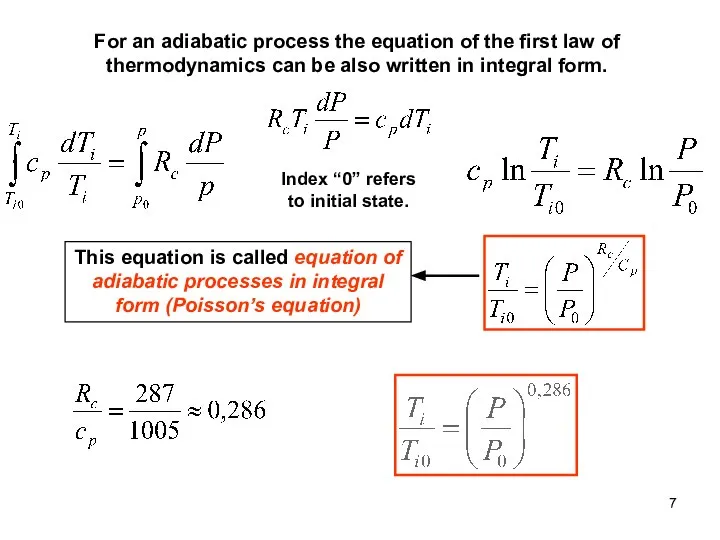
- 7. For an adiabatic process the equation of the first law of thermodynamics can be also written
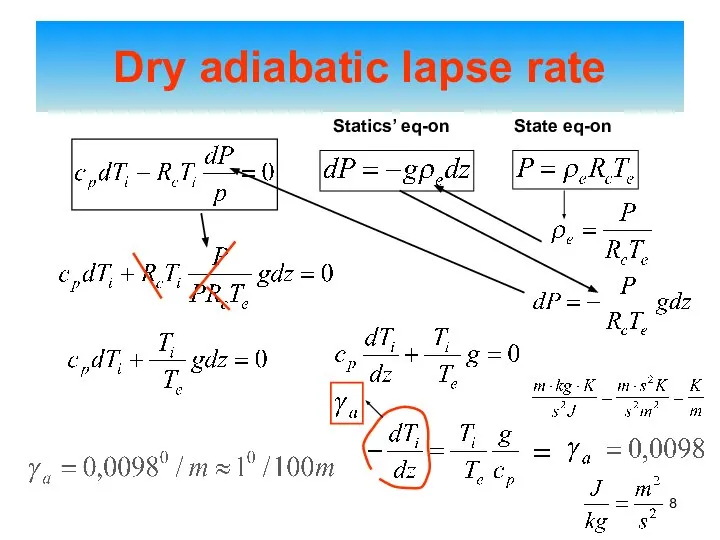
- 8. Dry adiabatic lapse rate Statics’ eq-on State eq-on
- 9. Regarding dry adiabatic lapse rate as a constant value, the expression γa=-dTi/dz can be integrated and
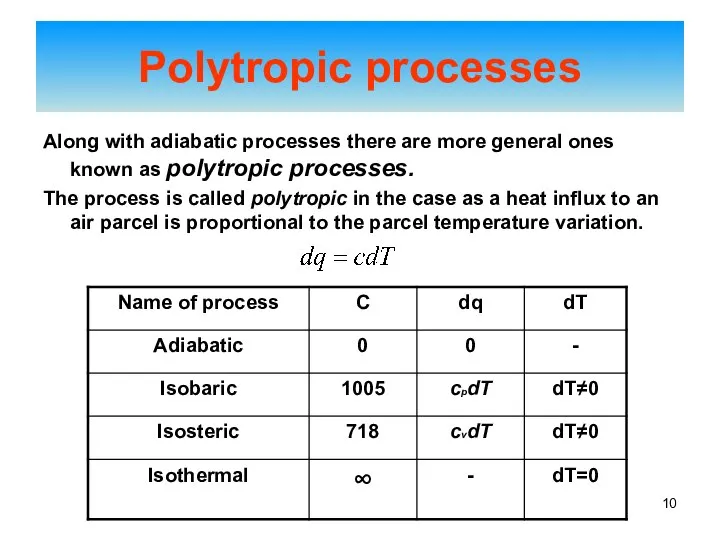
- 10. Along with adiabatic processes there are more general ones known as polytropic processes. The process is
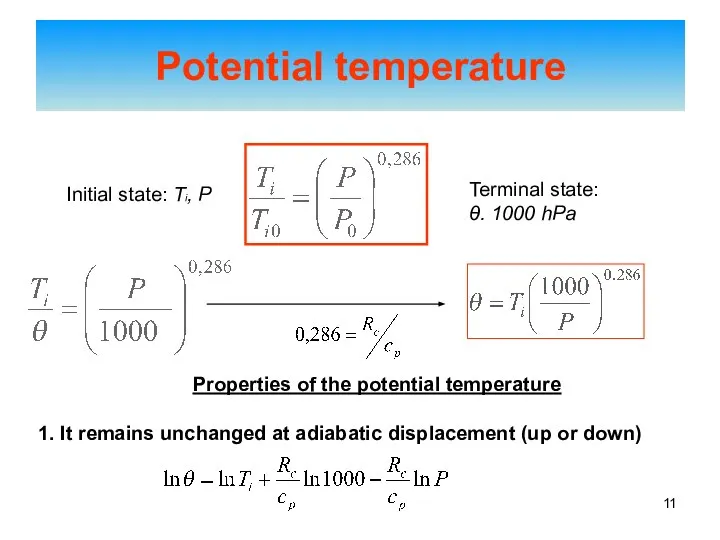
- 11. Potential temperature Initial state: Ti, P Terminal state: θ. 1000 hPa Properties of the potential temperature
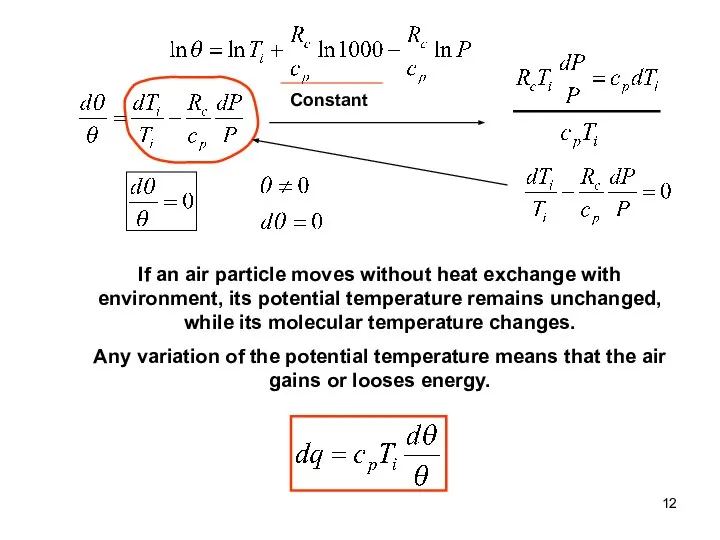
- 12. Constant If an air particle moves without heat exchange with environment, its potential temperature remains unchanged,
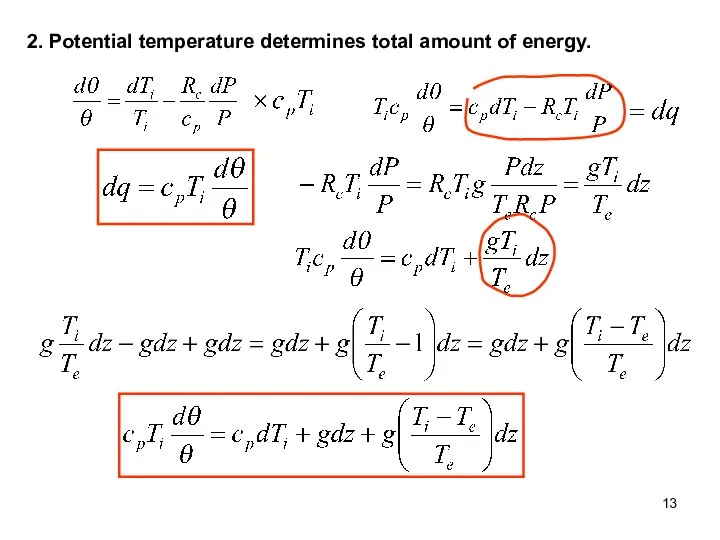
- 13. 2. Potential temperature determines total amount of energy.
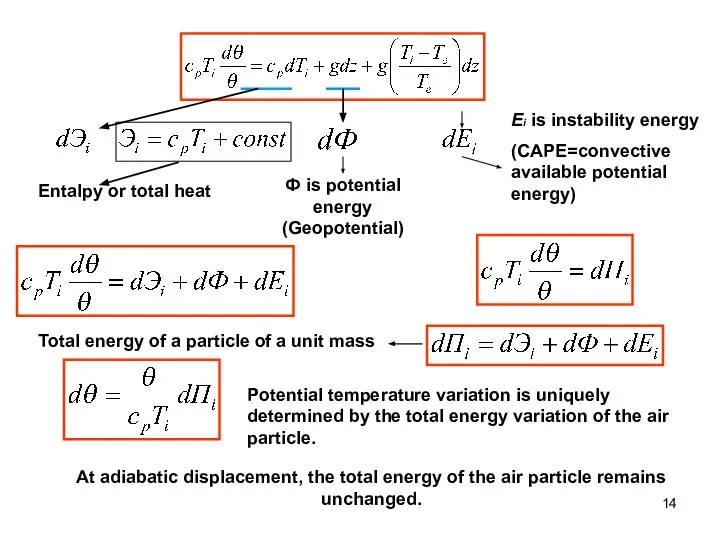
- 14. Entalpy or total heat Ф is potential energy (Geopotential) Ei is instability energy (CAPE=convective available potential
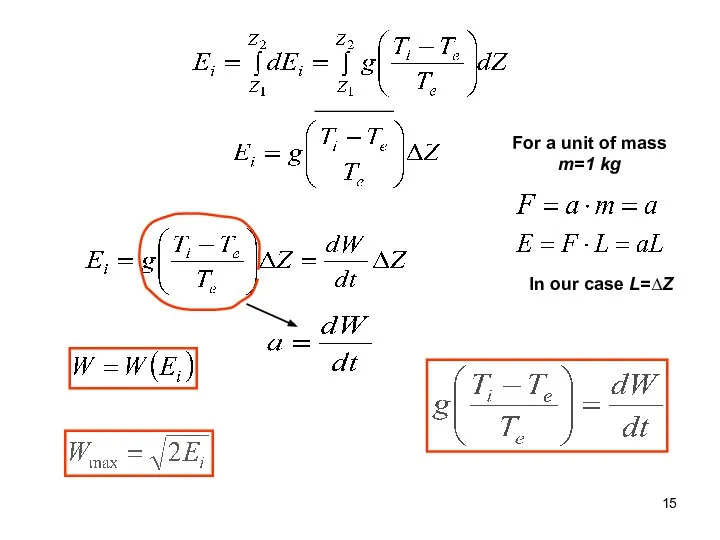
- 15. For a unit of mass m=1 kg In our case L=∆Z
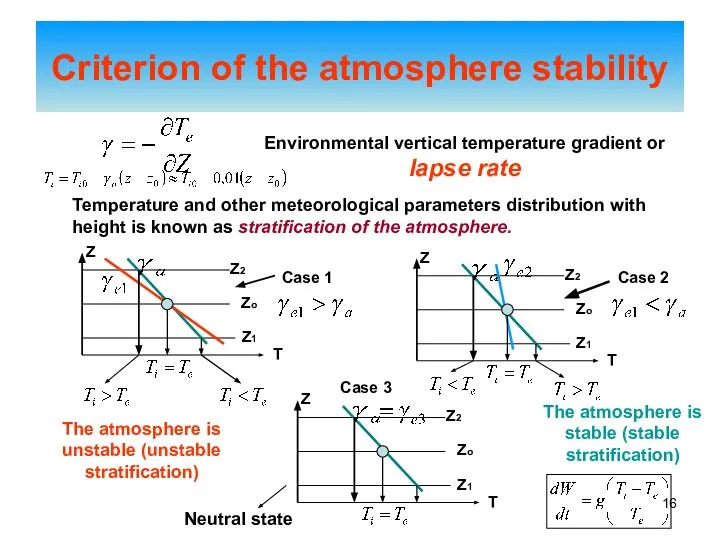
- 16. Criterion of the atmosphere stability Environmental vertical temperature gradient or lapse rate Temperature and other meteorological
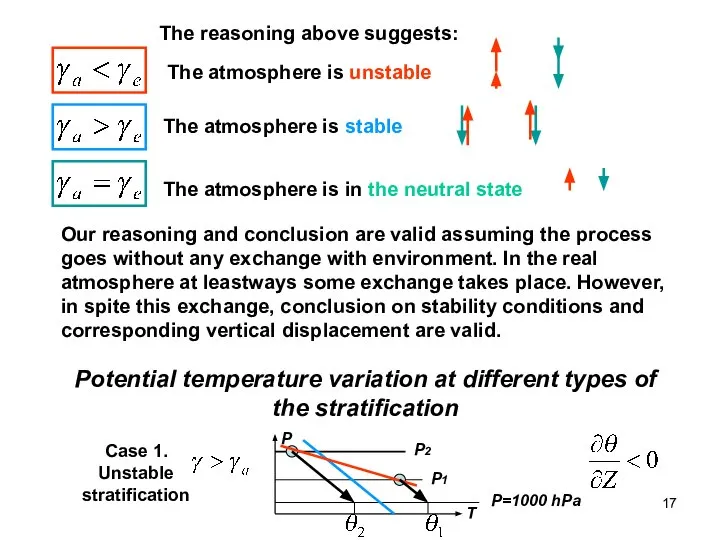
- 17. The reasoning above suggests: The atmosphere is unstable The atmosphere is stable The atmosphere is in
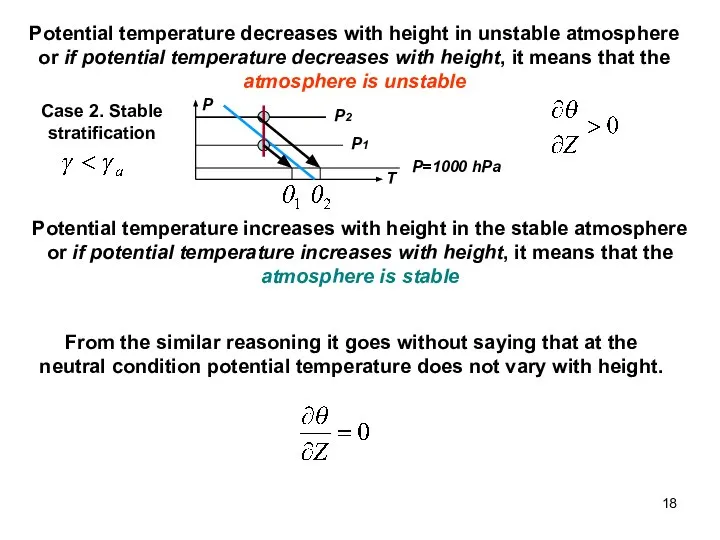
- 18. Potential temperature decreases with height in unstable atmosphere or if potential temperature decreases with height, it
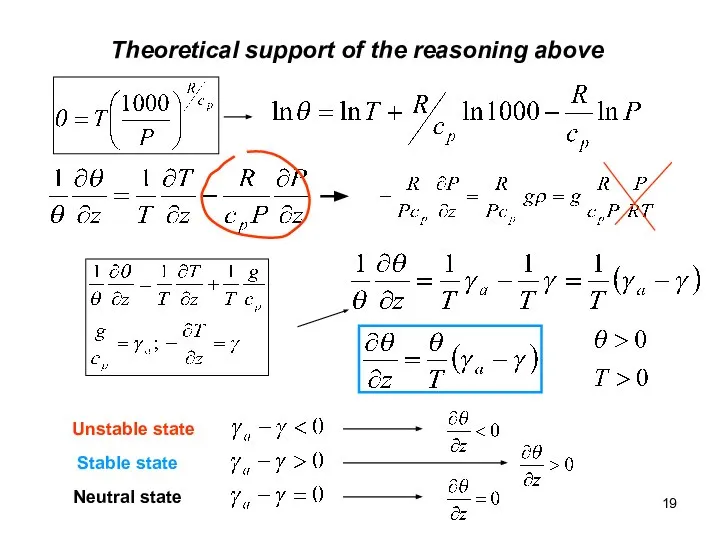
- 19. Theoretical support of the reasoning above Unstable state Stable state Neutral state
- 20. All above refers to the dry air (non-saturated air) Very hot surface In case of very
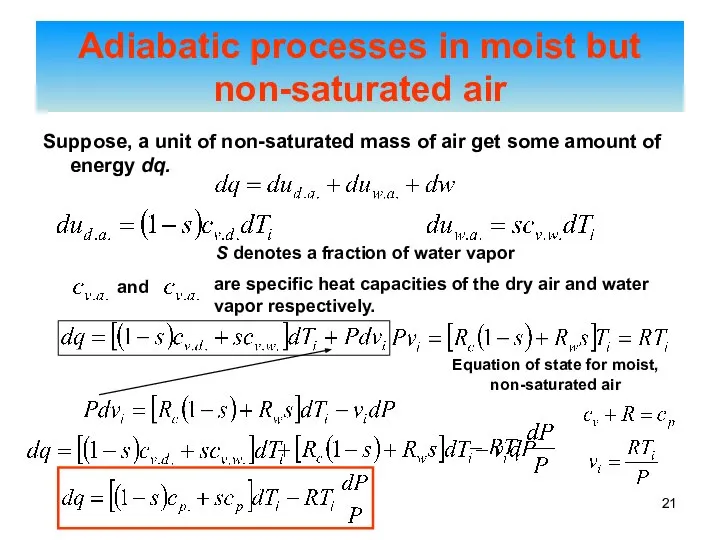
- 21. Suppose, a unit of non-saturated mass of air get some amount of energy dq. Adiabatic processes
- 23. Скачать презентацию



 Компьютерные сети Лекция 1
Компьютерные сети Лекция 1 Презентация "Театр средневековья" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Театр средневековья" - скачать презентации по МХК Совет Школы МОУ Ундино –Посельской СОШ Председатель СШ Лаврентьева С.А. Секретарь СШ Гордеева М.К Члены
Совет Школы МОУ Ундино –Посельской СОШ Председатель СШ Лаврентьева С.А. Секретарь СШ Гордеева М.К Члены Проект соревнований по картингу среди детей и подростков в возрасте от 5 до 14 лет «Formula SMi e»
Проект соревнований по картингу среди детей и подростков в возрасте от 5 до 14 лет «Formula SMi e» Модельные характеристики спорта высших достижений. Лекция 2
Модельные характеристики спорта высших достижений. Лекция 2 КОРРЕКЦИОННАЯ ПРОГРАММА по работе с гиперактивными детьми
КОРРЕКЦИОННАЯ ПРОГРАММА по работе с гиперактивными детьми Управление процессами. Системы управления
Управление процессами. Системы управления Семь чудес Москвы
Семь чудес Москвы Повышение физической и технической подготовки юных баскетболистов
Повышение физической и технической подготовки юных баскетболистов Китайский традиционный костюм
Китайский традиционный костюм Психология рекламы Виды рекламы
Психология рекламы Виды рекламы Презентация "Белов "Скворцы"" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Белов "Скворцы"" - скачать презентации по МХК Работа с базами данных
Работа с базами данных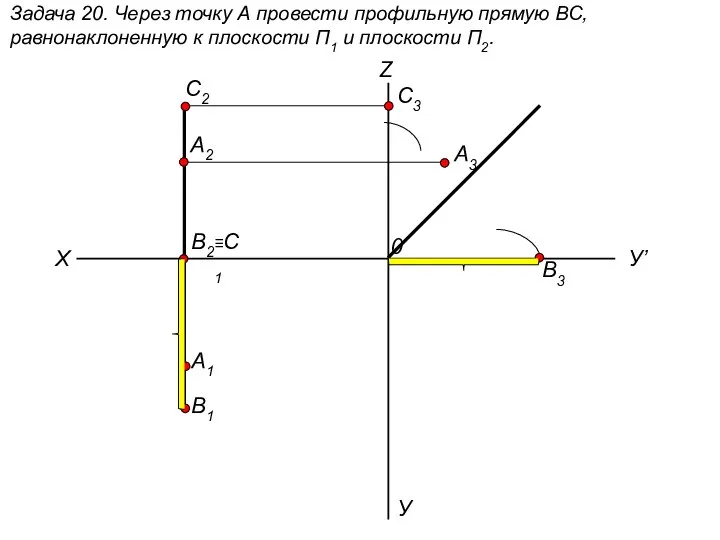 Через точку А провести профильную прямую ВС, равнонаклоненную к плоскости П1 и плоскости П2. (задача 20)
Через точку А провести профильную прямую ВС, равнонаклоненную к плоскости П1 и плоскости П2. (задача 20) Механізоване зварювання, наплавлення
Механізоване зварювання, наплавлення Политические элиты и политическое лидерство
Политические элиты и политическое лидерство Лекція № 2 КОНЦЕПЦІЯ, СИСТЕМА ТА ЦІЛІ МАРКЕТИНГУ
Лекція № 2 КОНЦЕПЦІЯ, СИСТЕМА ТА ЦІЛІ МАРКЕТИНГУ  Конкурентоспособность стран и ее факторы, теории МРТ
Конкурентоспособность стран и ее факторы, теории МРТ  Понятие и виды профессиональной этики
Понятие и виды профессиональной этики Основные правовые системы современности
Основные правовые системы современности Цикличность экономического развития. Типы и модели циклов. Подготовил: Нурлан Гулиев
Цикличность экономического развития. Типы и модели циклов. Подготовил: Нурлан Гулиев Сенім дегеніміз не? Евр 11:1-2
Сенім дегеніміз не? Евр 11:1-2 Гиревой спорт
Гиревой спорт Коррекция уровня физической подготовленности детей
Коррекция уровня физической подготовленности детей Бетоноведение
Бетоноведение Народы Северного Кавказа
Народы Северного Кавказа Вероучение и богослужение Православной Церкви. Учение о таинствах
Вероучение и богослужение Православной Церкви. Учение о таинствах История календарей
История календарей