- Главная
- Английский язык
- CNLC International Kazakhstan

Содержание
- 2. Scope of Services
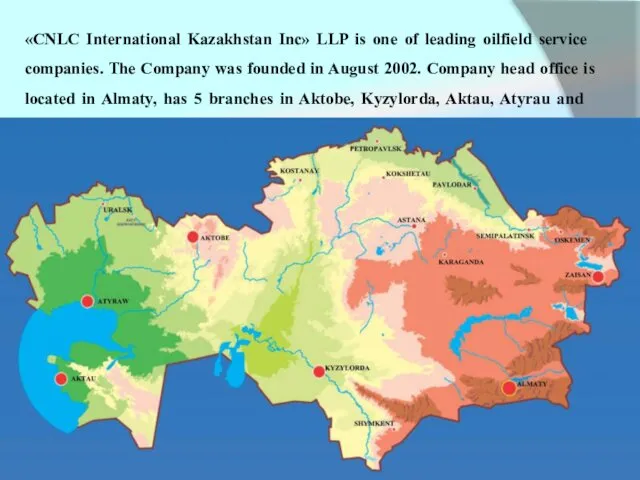
- 3. «CNLC International Kazakhstan Inc» LLP is one of leading oilfield service companies. The Company was founded
- 4. Providing of major wireline logging services in Kazakhstan: Openhole wireline logging; Casedhole wireline logging; Perforation; Mud
- 5. WAREHOUSE FOR 6 SET OF RADIOACTIVE SOURCES EXPLOSIVE GOODS WAREHOUSE WITH STORAGE CAPACITY OF EXPLOSIVES FOR
- 6. Presentation Topic: Research&Development; Core Analysis; Reservoir evaluation; Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services;
- 7. Research work (abbr. - R & D) is a scientific work related to scientific research, research,
- 8. RESEARCH REPORTS/MATERIALS RENDERED TO CUSTOMERS INCLUDES: Influencing factors of low oil rates and a large drop
- 9. To carry out these works, it is necessary to possess: Accreditation certificate for the Test Laboratory
- 10. The results of the research on each topic contain 80 - 100 pages in the PPT
- 11. R&D Service Experience: The Contracts concluded in 2012 – 2018 y.:
- 12. R&D Service Experience: The Contracts concluded in 2012 – 2018 y.:
- 13. R&D; Core Analysis; Reservoir evaluation; Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services; CBL and
- 14. Core is a sample of rock extracted from a well by means of a specially designed
- 15. Core is jammed, torn from the bottomCore is jammed, torn from the bottom and raised to
- 16. Routine Core Analysis laboratories perform a number of services, such as gamma core logging, to correlate
- 17. Core Analysis The results of standard and special studies. Correlation of core to Wireline logging data,
- 18. Core Analysis To carry out these works, it is necessary to posses: A license for activities
- 19. Core Analysis The Contracts concluded in 2015 - 2019:
- 20. R&D; Core Analysis; Reservoir evaluation; Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services; CBL and
- 21. FORMATION EVALUATION Stratum is a layer of rock of relatively constant thickness, located between similar formations.
- 22. Formation Evaluation
- 23. Formation Evaluation Collectors of Oil and Gas
- 24. Formation Evaluation Reservoir Features:
- 25. Formation Evaluation Reservoir Features:
- 26. Isolation of reservoirs is carried out at lithological dissection of the section. The characteristics by which
- 27. Collectors of Oil and Gas Formation Evaluation
- 28. R&D; Core Analysis; Reservoir evaluation; Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services; CBL and
- 29. Coiled tubing operations are used in such areas as: • drilling; •repair cementing; •electrical wiring and
- 30. Coiled tubing operations include: Acid treatment Nitrogen gaslift Borehole cleaning Horizontal well operations Chemical injection Rinsing
- 31. Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services In order to increase the economic efficiency
- 32. METHODS Oil recovery can only increase through the use of new modern techniques and technologies. Moreover,
- 33. Engineering maintenance: Specialists conduct technological engineering, which is necessary for successful work at the stages of
- 34. R&D; Core Analysis; Reservoir evaluation; Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services; CBL and
- 35. Gauging allows to exclude the possibility of loss of the device. The diameter of the gauging
- 36. Cement Bond Logging (CBL) refers to the main research, is carried out in each exploratory well,
- 37. CBL method, based on the use of the laws of propagation of ultrasonic waves in various
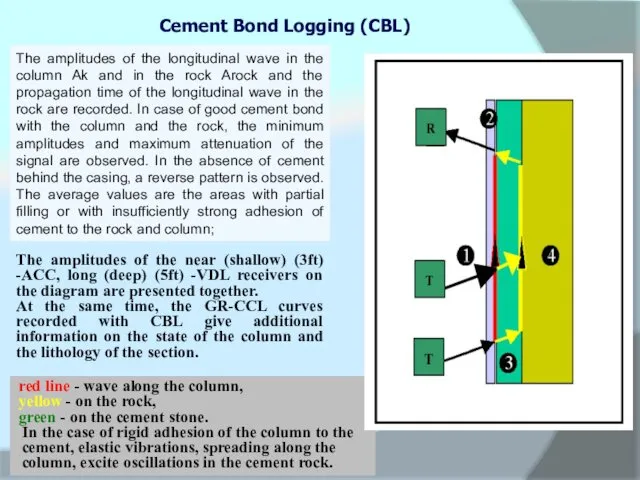
- 38. Cement Bond Logging (CBL) The amplitudes of the near (shallow) (3ft) -ACC, long (deep) (5ft) -VDL
- 39. Cement Bond Logging (CBL) Processing and interpretation of CBL data allows to solve the following tasks:
- 40. R&D; Core Analysis; Reservoir evaluation; Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services; CBL and
- 41. Bridge plug setting One of the types of packer equipment used in the oil industry is
- 42. Bridge plugs settings: Application area For installation of bridges and temporary disconnection of seams; For the
- 43. - Bridge plug is used to overlap the insulation interval at producing casing. - Cementing plug
- 44. R&D; Core Analysis; Reservoir evaluation; Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services; CBL and
- 45. Any matters left in the borehole that interfere further work at the oilfield are called emergency
- 46. Fishing operations and their purposes:
- 47. Fishing operations and their purposes.
- 48. Fishing operations and their purposes.
- 50. Скачать презентацию
Scope of Services
Scope of Services
«CNLC International Kazakhstan Inc» LLP is one of leading oilfield service
«CNLC International Kazakhstan Inc» LLP is one of leading oilfield service
Providing of major
wireline logging services
in Kazakhstan:
Openhole wireline logging;
Casedhole wireline
Providing of major
wireline logging services
in Kazakhstan:
Openhole wireline logging;
Casedhole wireline
Perforation;
Mud logging;
Well testing
WAREHOUSE FOR 6 SET OF RADIOACTIVE SOURCES
EXPLOSIVE GOODS WAREHOUSE WITH STORAGE
WAREHOUSE FOR 6 SET OF RADIOACTIVE SOURCES
EXPLOSIVE GOODS WAREHOUSE WITH STORAGE
Temporary explosive good storages
ZHANAZHOL BASE IS MAIN BASE, WHERE LOCATED WAREHOUSE FOR 6 SET OF RADIOACTIVE SOURCES AND EXPLOSIVE GOODS WAREHOUSE WITH STORAGE CAPACITY OF EXPLOSIVES FOR 100000 SHOOTS.
Presentation Topic:
Research&Development;
Core Analysis;
Reservoir evaluation;
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering
Presentation Topic:
Research&Development;
Core Analysis;
Reservoir evaluation;
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering
CBL and borehole gauging;
Bridge plug setting;
Fishing Operations.
Research work (abbr. - R & D) is a scientific work
Research work (abbr. - R & D) is a scientific work
The main result of research is the report on the implementation of scientific research, it is also possible to create mock-ups, as opposed to development work, which results in a prototype product, design documentation or a new technology.
In accordance with contract for the performance of scientific research, the contractor undertakes to conduct scientific research, determined by the technical task of the customer, the customer undertakes to accept and pay for the work.
Research Works (R&D)
Terms of the contract for the performance of scientific research should comply
with laws and other legal acts on intellectual property.
RESEARCH REPORTS/MATERIALS RENDERED TO CUSTOMERS INCLUDES:
Influencing factors of low oil rates
RESEARCH REPORTS/MATERIALS RENDERED TO CUSTOMERS INCLUDES:
Influencing factors of low oil rates
Techniques of oil reservoir engineering, detailed geological models and numerical modeling, determination of rational limits of technical operation policy;
Tracking the dynamics of production of the deposit, providing a proposal for measures to regulate production wells;
In combination with the distribution characteristics of reservoirs, oil and water, the design of well placement options;
BACKGROUND DATA
(ON THE BASIS OF WHICH FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH IS CONDUCTED):
Static parameters: complex logging curves, stratification parameters, perforation parameters and basic parameters of oil reservoir interpretation, physical properties at high pressure and analysis of core parameters;
Dynamic parameters: parameters of well testing, daily reports of water-oil wells, monthly reports;
Control parameters: annual temperature data, pressure control data; laboratory data on the analysis of oil and water;
Advances in preliminary research ...
Research & Development
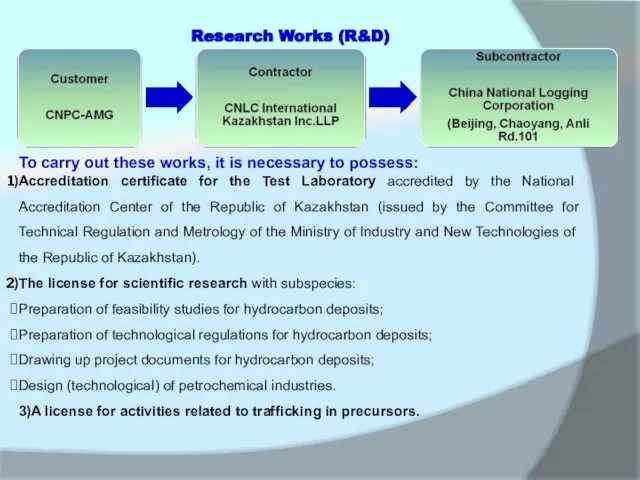
To carry out these works, it is necessary to possess:
Accreditation certificate
To carry out these works, it is necessary to possess:
Accreditation certificate
The license for scientific research with subspecies:
Preparation of feasibility studies for hydrocarbon deposits;
Preparation of technological regulations for hydrocarbon deposits;
Drawing up project documents for hydrocarbon deposits;
Design (technological) of petrochemical industries.
3)A license for activities related to trafficking in precursors.
Research Works (R&D)
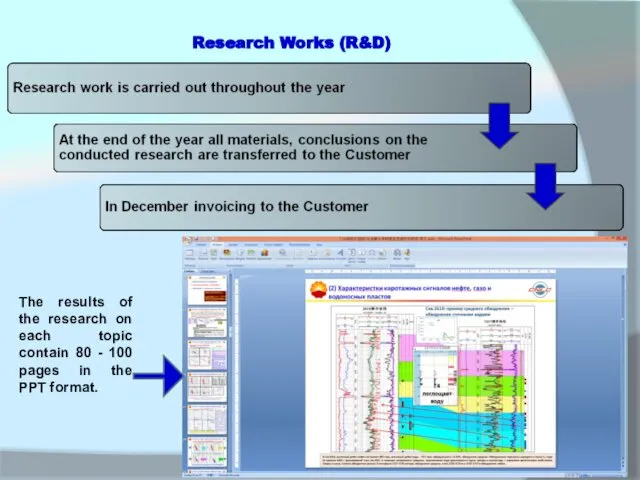
The results of the research on each topic contain 80 -
The results of the research on each topic contain 80 -
Research Works (R&D)
R&D Service Experience:
The Contracts concluded in 2012 – 2018 y.:
R&D Service Experience:
The Contracts concluded in 2012 – 2018 y.:
R&D Service Experience:
The Contracts concluded in 2012 – 2018 y.:
R&D Service Experience:
The Contracts concluded in 2012 – 2018 y.:
R&D;
Core Analysis;
Reservoir evaluation;
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services;
CBL
R&D;
Core Analysis;
Reservoir evaluation;
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services;
CBL
Bridge plug setting;
Fishing Operations.
Presentation Topic:
Core is a sample of rock extracted from a
Core is a sample of rock extracted from a
It is a primary source of information on the geological structure of subsoil, sedimentation conditions and the material composition of rocks.
In most cases, the core is sampled when drilling a rock with a hollow steel pipe, called a core pipe, and the core drilling itself is core drilling. Inside the core pipe is the core receiver (sampler). The core receiver consists mainly of a head, a core-receiving tube and a core cutter.
Core
The core diameter is usually from 4.45 to 13.3 cm (1.75 to 5.25 inches), they are drilled in fragments of 10 m (30 ft).
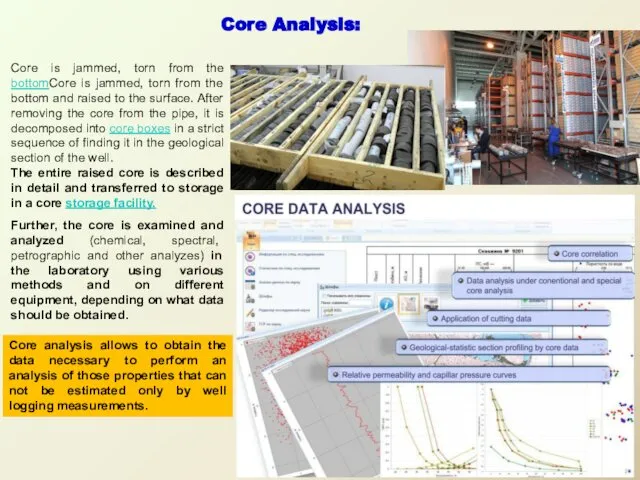
Core is jammed, torn from the bottomCore is jammed, torn from
Core is jammed, torn from the bottomCore is jammed, torn from
The entire raised core is described in detail and transferred to storage in a core storage facility.
Further, the core is examined and analyzed (chemical, spectral, petrographic and other analyzes) in the laboratory using various methods and on different equipment, depending on what data should be obtained.
Core analysis allows to obtain the data necessary to perform an analysis of those properties that can not be estimated only by well logging measurements.
Core Analysis:
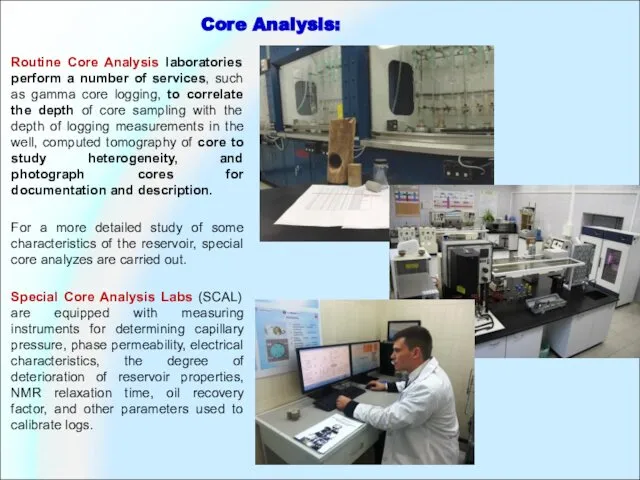
Routine Core Analysis laboratories perform a number of services, such as
Routine Core Analysis laboratories perform a number of services, such as
For a more detailed study of some characteristics of the reservoir, special core analyzes are carried out.
Special Core Analysis Labs (SCAL) are equipped with measuring instruments for determining capillary pressure, phase permeability, electrical characteristics, the degree of deterioration of reservoir properties, NMR relaxation time, oil recovery factor, and other parameters used to calibrate logs.
Core Analysis:
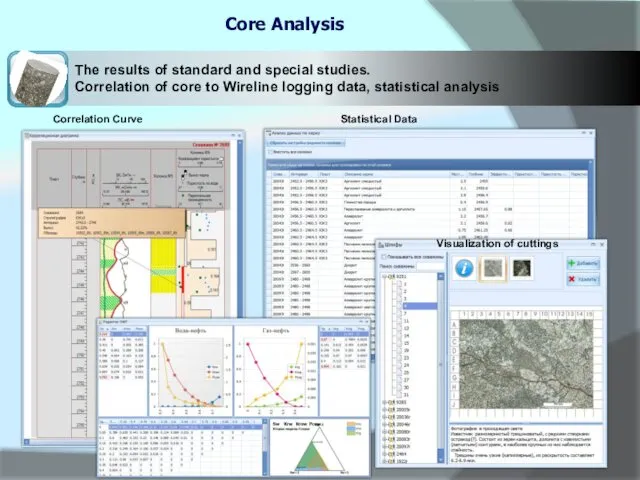
Core Analysis
The results of standard and special studies.
Correlation of core to
Core Analysis
The results of standard and special studies.
Correlation of core to
Correlation Curve
Statistical Data
Visualization of cuttings
Core Analysis
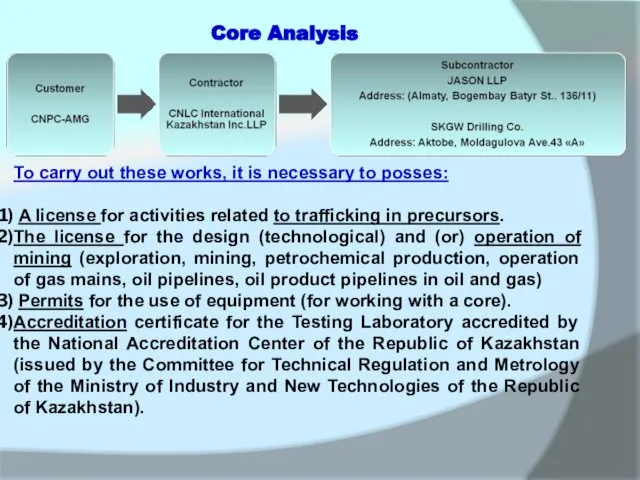
To carry out these works, it is necessary to posses:
Core Analysis
To carry out these works, it is necessary to posses:
The license for the design (technological) and (or) operation of mining (exploration, mining, petrochemical production, operation of gas mains, oil pipelines, oil product pipelines in oil and gas)
Permits for the use of equipment (for working with a core).
Accreditation certificate for the Testing Laboratory accredited by the National Accreditation Center of the Republic of Kazakhstan (issued by the Committee for Technical Regulation and Metrology of the Ministry of Industry and New Technologies of the Republic of Kazakhstan).
Core Analysis
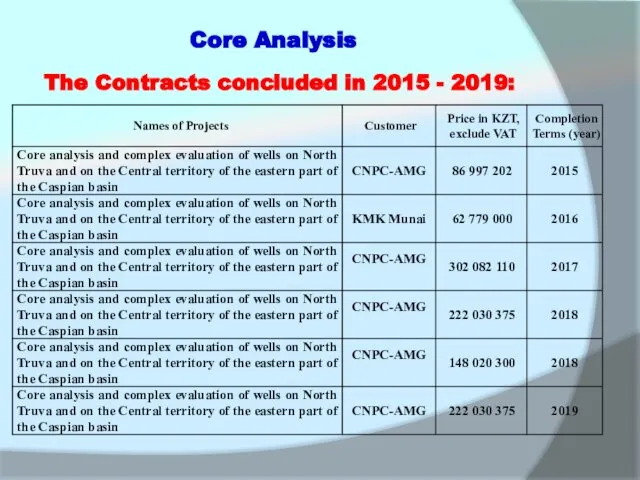
The Contracts concluded in 2015 - 2019:
Core Analysis
The Contracts concluded in 2015 - 2019:
R&D;
Core Analysis;
Reservoir evaluation;
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services;
CBL
R&D;
Core Analysis;
Reservoir evaluation;
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services;
CBL
Bridge plug setting;
Fishing Operations.
Presentation Topic:
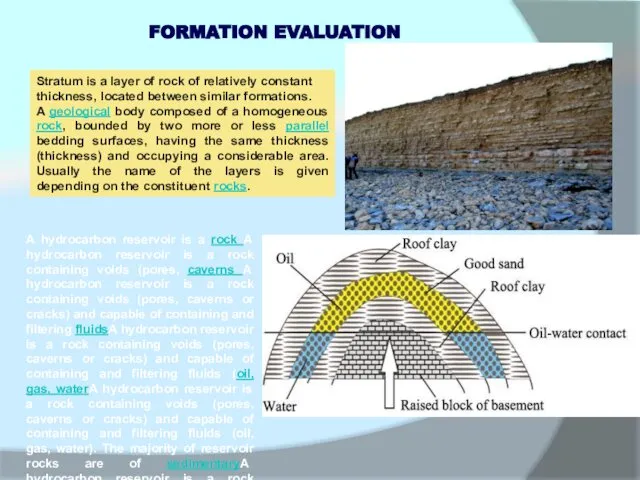
FORMATION EVALUATION
Stratum is a layer of rock of relatively constant thickness,
FORMATION EVALUATION
Stratum is a layer of rock of relatively constant thickness,
A geological body composed of a homogeneous rock, bounded by two more or less parallel bedding surfaces, having the same thickness (thickness) and occupying a considerable area. Usually the name of the layers is given depending on the constituent rocks.
A hydrocarbon reservoir is a rock A hydrocarbon reservoir is a rock containing voids (pores, caverns A hydrocarbon reservoir is a rock containing voids (pores, caverns or cracks) and capable of containing and filtering fluidsA hydrocarbon reservoir is a rock containing voids (pores, caverns or cracks) and capable of containing and filtering fluids (oil, gas, waterA hydrocarbon reservoir is a rock containing voids (pores, caverns or cracks) and capable of containing and filtering fluids (oil, gas, water). The majority of reservoir rocks are of sedimentaryA hydrocarbon reservoir is a rock containing voids (pores, caverns or cracks) and capable of containing and filtering fluids (oil, gas, water). The majority of reservoir rocks are of sedimentary origin. The collectors of oil and gas are both terrigenous A hydrocarbon reservoir is a rock containing voids (pores, caverns or cracks) and capable of containing and filtering fluids (oil, gas, water). The majority of reservoir rocks are of sedimentary origin. The collectors of oil and gas are both terrigenous (aleurites, sandstones, siltstones, some clay rocksA hydrocarbon reservoir is a rock containing voids (pores, caverns or cracks) and capable of containing and filtering fluids (oil, gas, water). The majority of reservoir rocks are of sedimentary origin. The collectors of oil and gas are both terrigenous (aleurites, sandstones, siltstones, some clay rocks), and chemogenic A hydrocarbon reservoir is a rock containing voids (pores, caverns or cracks) and capable of containing and filtering fluids (oil, gas, water). The majority of reservoir rocks are of sedimentary origin. The collectors of oil and gas are both terrigenous (aleurites, sandstones, siltstones, some clay rocks), and chemogenic and biochemogenic (limestones, chalk, dolomites), as well as mixed rocks.
Formation Evaluation
Formation Evaluation
Formation Evaluation
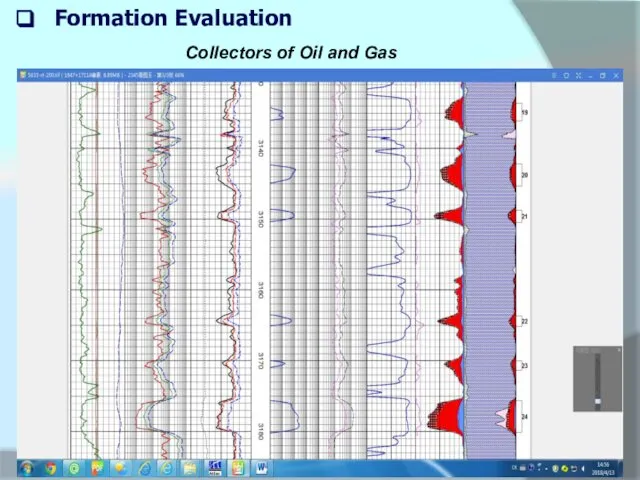
Collectors of Oil and Gas
Formation Evaluation
Collectors of Oil and Gas
Formation Evaluation
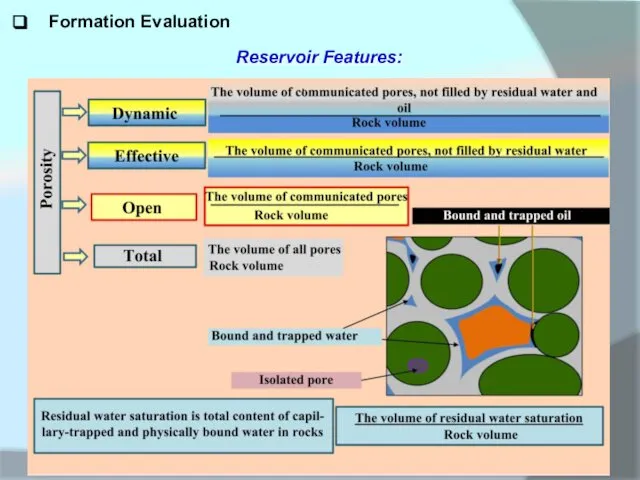
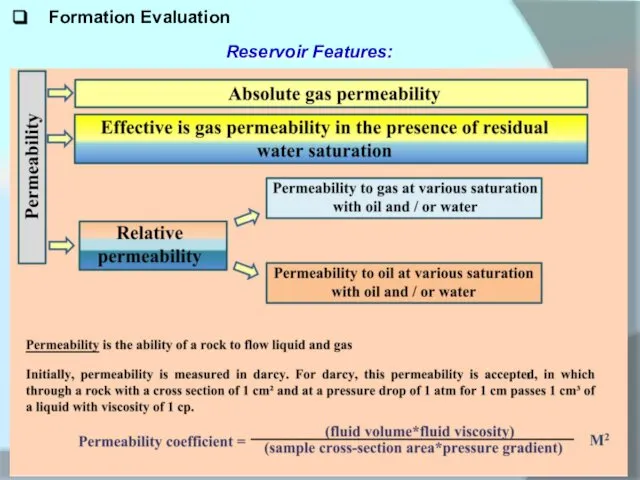
Reservoir Features:
Formation Evaluation
Reservoir Features:
Formation Evaluation
Reservoir Features:
Formation Evaluation
Reservoir Features:
Isolation of reservoirs is carried out at lithological dissection of the
Isolation of reservoirs is carried out at lithological dissection of the
Reservoirs are considered as rocks that can contain oil, gas or water and give them back during development. Under the conditions of formation, the oil and gas reservoirs are mainly sedimentary deposits. In terms of material composition, terrigenous, carbonate and mixed types are distinguished. According to the morphology of the porous space, the collectors are divided into pore (intergranular, granular), fissured, cavernous and mixed (pore-cracked-cavernous).
Resevoirs differ from the enclosing rocks with permeability, porosity and clayiness, which is a prerequisite for their separation according to geophysical methods.
Identification of reservoirs is carried out at lithological dissection of the section. Lithological dismemberment of the section of wells within the perspective intervals provides for the allocation of strata that differ in geophysical properties, the determination of their boundaries and the depth of occurrence.
The first group combines direct qualitative characteristics based on a higher permeability of the reservoir compared to the host rocks and on the penetration of the clay solution filtrate reservoir.
The second group includes indirect quantitative criteria of the reservoir, based on the difference between the reservoir and the host rock in terms of porosity, permeability and clay: this allows reservoirs to be isolated in intervals with increased porosity, permeability and reduced clayness according to the diagrams of the corresponding geophysical methods.
The belonging of the allocated seams to a specific lithological type is determined by the totality of the characteristics in the diagrams of the various Wireline logging techniques.
Reservoir evaluation
Collectors of Oil and Gas
Formation Evaluation
Collectors of Oil and Gas
Formation Evaluation
R&D;
Core Analysis;
Reservoir evaluation;
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services;
CBL
R&D;
Core Analysis;
Reservoir evaluation;
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services;
CBL
Bridge plug setting;
Fishing Operations.
Presentation Topic:
Coiled tubing operations are used in such areas as:
• drilling;
•repair cementing;
•electrical
Coiled tubing operations are used in such areas as:
• drilling;
•repair cementing;
•electrical
•fluid displacement;
•Sand binding;
•cleaning of the wellbore;
•setting and removal of plug-packers;
•fishing, testing, completion of wells;
•well control;
•intensification of production;
•use of a collapsible tubing as a discharge pipeline;
•Provide flow control when the horizontal or curved wellbore is completed.
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services
Coiled tubing is an another technology that has been known for decades and has had limited application until recently, when interest in it has increased dramatically due to significant technical achievements.
Coiled tubing system is a self-contained, easily transportable, hydraulically driven unit for repair work in the well, which allows the introduction (and extraction) of a continuous column of pipes into a tubing or casing of a larger diameter (Fig.).
The system can be used on land or at sea and does not require a special repair tower. The unit can be used in working wells, it allows continuous injection of liquid or nitrogen with continued movement of the pipe.
The main advantage of the technology of flexible pipes is that in many cases it is an economical replacement of expensive capital repair works using auxiliary towers.
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services
Coiled tubing operations include:
Acid treatment
Nitrogen gaslift
Borehole cleaning
Horizontal well operations
Chemical injection
Rinsing works
Wash
Coiled tubing operations include:
Acid treatment
Nitrogen gaslift
Borehole cleaning
Horizontal well operations
Chemical injection
Rinsing works
Wash
Fishing using coiled tubing
Secondary cementation
Drilling of cement bridges
Wireline logging using coiled tubing
Perforation using coiled tubing
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services
In order to
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services
In order to
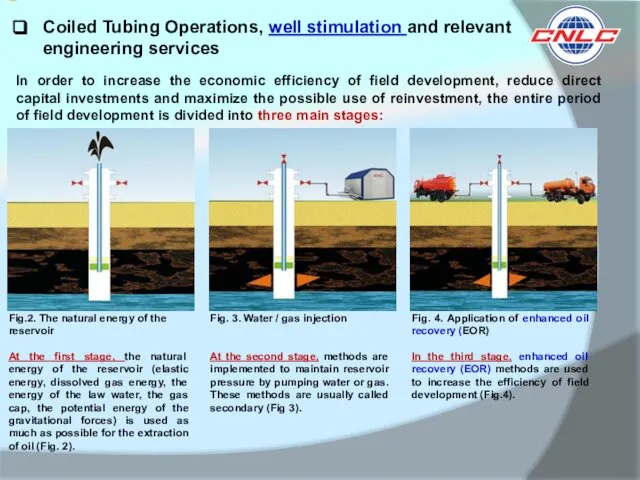
Fig.2. The natural energy of the reservoir
At the first stage, the natural energy of the reservoir (elastic energy, dissolved gas energy, the energy of the law water, the gas cap, the potential energy of the gravitational forces) is used as much as possible for the extraction of oil (Fig. 2).
Fig. 3. Water / gas injection
At the second stage, methods are implemented to maintain reservoir pressure by pumping water or gas. These methods are usually called secondary (Fig 3).
Fig. 4. Application of enhanced oil recovery (EOR)
In the third stage, enhanced oil recovery (EOR) methods are used to increase the efficiency of field development (Fig.4).
METHODS
Oil recovery can only increase through the use of new modern
METHODS
Oil recovery can only increase through the use of new modern
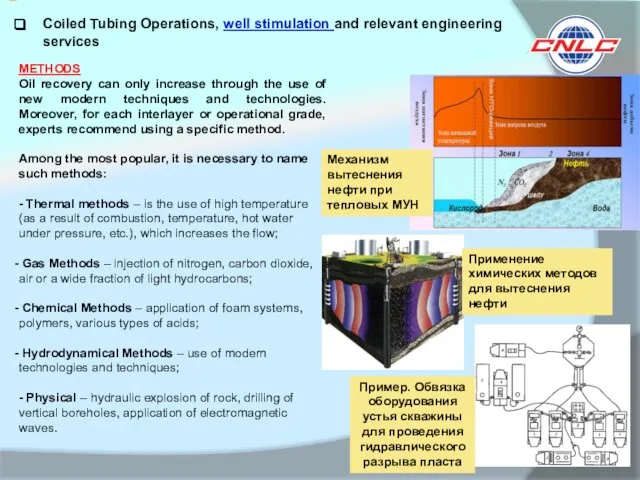
Among the most popular, it is necessary to name such methods:
- Thermal methods – is the use of high temperature (as a result of combustion, temperature, hot water under pressure, etc.), which increases the flow;
Gas Methods – injection of nitrogen, carbon dioxide, air or a wide fraction of light hydrocarbons;
Chemical Methods – application of foam systems, polymers, various types of acids;
Hydrodynamical Methods – use of modern technologies and techniques;
- Physical – hydraulic explosion of rock, drilling of vertical boreholes, application of electromagnetic waves.
Пример. Обвязка оборудования устья скважины для проведения гидравлического разрыва пласта
Механизм вытеснения нефти при тепловых МУН
Применение химических методов для вытеснения нефти
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services
Engineering maintenance:
Specialists conduct technological engineering, which is necessary for successful work
Engineering maintenance:
Specialists conduct technological engineering, which is necessary for successful work
Stimulation of oil production:
Treatment of carbonate reservoirs. Allows to conduct with the application of adapted acid systems an effective intensification of the treated interval and obtain a drainage area of the required geometry.
Treatment of terrigenous reservoirs. Increase the productivity of wells that exploit terrigenous reservoirs or reservoirs that have reduced their productivity due to secondary technogenic contamination of the wellbore zone (penetration of clay mud).
Acid packets. Taking into account the peculiarities of the geological structure, the Company's specialists propose a solution to intensify the flow rate to achieve the full potential of a particular well. Acid packs are used to eliminate individual problems (sludge, emulsion, iron control), as well as for a complex solution (optimally balanced acid systems).
Enhanced oil recovery:
Waterproofing systems. Minimizing the causes of waterlogging of wells that arise as a result of the breakthrough of water from the injection well zone, the approach of natural formation water from other horizons.
Deflection of the fluid flow. Increase the efficiency of the development of heterogeneous reservoirs with high water cut (more than 80%). Blocking of permeable zones is carried out with the help of viscous gel-like emulsion systems of the reverse type.
Conformance control
Increase in oil displacement ratio.
Recovering. Optimization of well operation due to advanced chemical technologies. Intraquired oilfield chemistry, aimed at reducing the cost of oil production operations.
Processing of asphaltenes. * Paraffin treatment. * Treatment of salt deposits.
Chemical technologies for hard-to-recover reserves. A wide range of technologies and chemical compositions for extraction of hard-to-recover oil reserves (high viscosity heavy oils, heterogeneous carbonate reservoirs, undrained oil reserves) using specialized laboratory studies.
Engineering solutions for mature fields. Technologies that allow to reduce costs on long-running fields by reducing water cut, involvement in development of non-draining and residual oil reserves.
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services
R&D;
Core Analysis;
Reservoir evaluation;
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services;
CBL
R&D;
Core Analysis;
Reservoir evaluation;
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services;
CBL
Bridge plug setting;
Fishing Operations.
Presentation Topic:
Gauging allows to exclude the possibility of loss of the device.
The
Gauging allows to exclude the possibility of loss of the device.
The
Gauging the production column to a depth of 100-200 m below the location of the cement ring behind the casing.
Gauging of production and tubing columns is carried out in order to ensure trouble-free descent of equipment, especially the packer, instruments and tools. Its body is made whole without chamfers on the lower and upper ends. The gauge has a through longitudinal hole for washing and preventing the accumulation of mechanical impurities during the launching and lifting operations.
CBL and borehole gauging services
borehole gauging services
Wellbore preparation
• Borehole gauging
After selective drifting of the borehole, will be checked the passage ability of the casing by patterning the borehole. For this, a section of casing about 25 m in length on the drill string is lowered to the bottom. The well is washed until the circulation fluid properties are completely equalized (at least two cycles of circulation). At the end of the washing, the pancreas is treated with a lubricating additive to facilitate the descent of the casing.
• Monitoring the length of the wellbore by measuring the total length of the drilling tool extracted from the well.
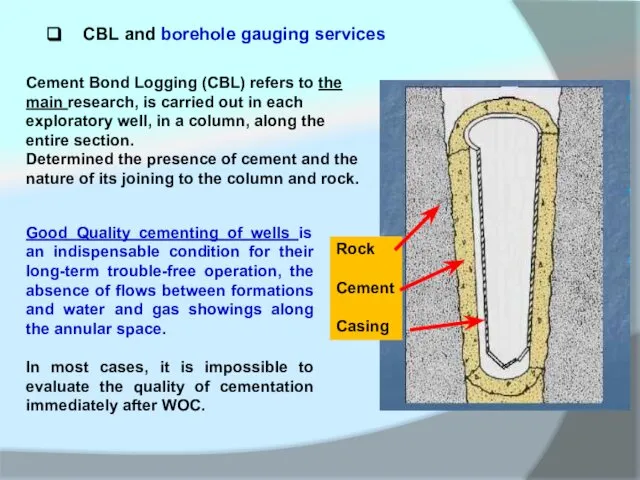
Cement Bond Logging (CBL) refers to the main research, is carried
Cement Bond Logging (CBL) refers to the main research, is carried
Determined the presence of cement and the nature of its joining to the column and rock.
Good Quality cementing of wells is an indispensable condition for their long-term trouble-free operation, the absence of flows between formations and water and gas showings along the annular space.
In most cases, it is impossible to evaluate the quality of cementation immediately after WOC.
Rock
Cement
Casing
CBL and borehole gauging services
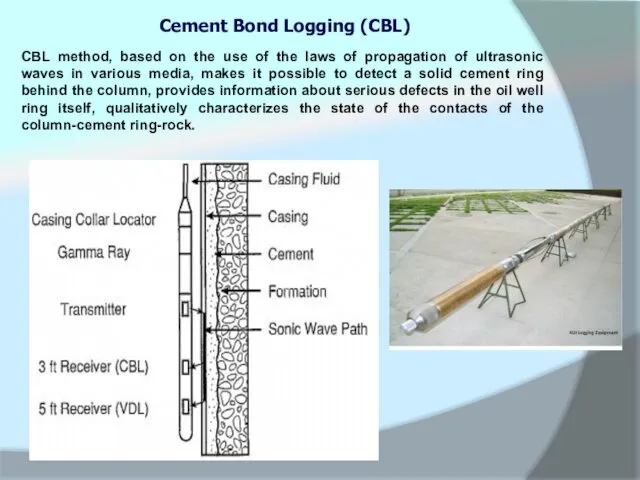
CBL method, based on the use of the laws of propagation
CBL method, based on the use of the laws of propagation
Cement Bond Logging (CBL)
Cement Bond Logging (CBL)
The amplitudes of the near (shallow) (3ft) -ACC, long
Cement Bond Logging (CBL)
The amplitudes of the near (shallow) (3ft) -ACC, long
At the same time, the GR-CCL curves recorded with CBL give additional information on the state of the column and the lithology of the section.
red line - wave along the column,
yellow - on the rock,
green - on the cement stone.
In the case of rigid adhesion of the column to the cement, elastic vibrations, spreading along the column, excite oscillations in the cement rock.
The amplitudes of the longitudinal wave in the column Ak and in the rock Arock and the propagation time of the longitudinal wave in the rock are recorded. In case of good cement bond with the column and the rock, the minimum amplitudes and maximum attenuation of the signal are observed. In the absence of cement behind the casing, a reverse pattern is observed. The average values are the areas with partial filling or with insufficiently strong adhesion of cement to the rock and column;
Cement Bond Logging (CBL)
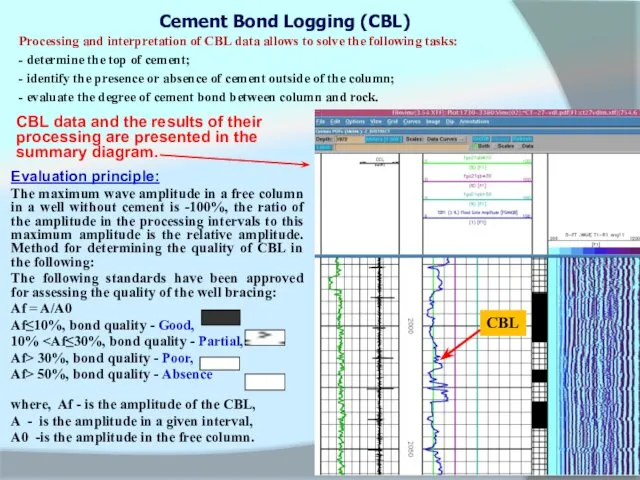
Processing and interpretation of CBL data allows to solve
Cement Bond Logging (CBL)
Processing and interpretation of CBL data allows to solve
- determine the top of cement;
- identify the presence or absence of cement outside of the column;
- evaluate the degree of cement bond between column and rock.
CBL data and the results of their processing are presented in the summary diagram.
Evaluation principle: CBL
The maximum wave amplitude in a free column in a well without cement is -100%, the ratio of the amplitude in the processing intervals to this maximum amplitude is the relative amplitude. Method for determining the quality of CBL in the following:
The following standards have been approved for assessing the quality of the well bracing:
Af = A/A0
Af≤10%, bond quality - Good,
10%
Af> 50%, bond quality - Absence
where, Af - is the amplitude of the CBL,
A - is the amplitude in a given interval,
A0 -is the amplitude in the free column.
R&D;
Core Analysis;
Reservoir evaluation;
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services;
CBL
R&D;
Core Analysis;
Reservoir evaluation;
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services;
CBL
Bridge plug setting;
Fishing Operations.
Presentation Topic:
Bridge plug setting
One of the types of packer equipment used in
Bridge plug setting
One of the types of packer equipment used in
Bridge plugs include a number of common structural elements, characteristic for almost any device of this class. Such elements include a lock assembly (whose function is to hold the rest of the elements during transportation and packing), a sealing unit (which provides a sealed separation of volumes) and an anchor assembly (which secures the device in the well).
The drillable bridge plugs are packers of lightly drillable materials. In addition to such devices, there are also recoverable bridge plugs that imply the possibility of creating a temporary or switching to permanent insulation. The installation and lifting of the extracted bridge plugs is carried out using a flexible pipe and a set of hydraulic equipment.
Bridge plugs settings:
Application area
For installation of bridges and temporary disconnection
Bridge plugs settings:
Application area
For installation of bridges and temporary disconnection
For the liquidation of wells or conservation of deposits;
For use as a support for a wedge-deflector;
For carrying out repair and insulation work using a plugging material under pressure (elimination of casing circulation, leakage of the casing string).
Distinctive features:
setting of the packer is carried out with the help of the hydraulic installation string of the corresponding design, by creating excess pressure in standard tubing;
It is designed for uninterrupted operation at a differential pressure up to 35 MPa;
the integral design of the slips eliminates the risk of premature installation during descent;
is manufactured in accordance with strict technical conditions for materials and with strict quality control of products, due to which the best combination of high strength characteristics and good drillability.
Benefits:
simplicity, low metal consumption compared to similar structures and good packer drillability;
Packing in inclined, horizontal, deep wells;
the use of a bridge plug during repair and insulation works significantly reduces the time of carrying out technological operations, reduces the cost of work, increases their reliability.
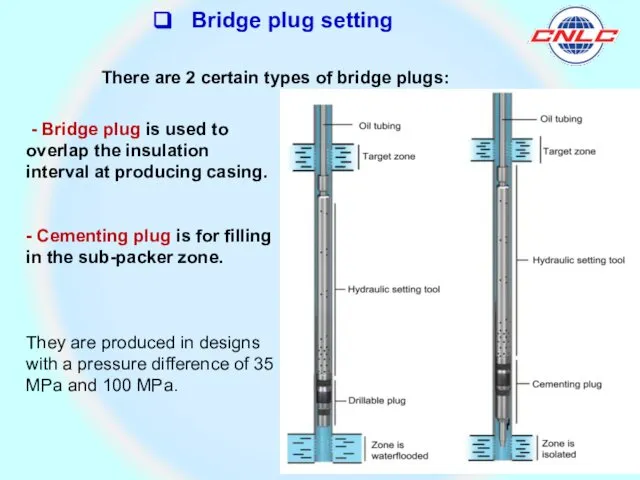
- Bridge plug is used to overlap the insulation interval
- Bridge plug is used to overlap the insulation interval
- Cementing plug is for filling in the sub-packer zone.
They are produced in designs with a pressure difference of 35 MPa and 100 MPa.
There are 2 certain types of bridge plugs:
Bridge plug setting
R&D;
Core Analysis;
Reservoir evaluation;
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services;
CBL
R&D;
Core Analysis;
Reservoir evaluation;
Coiled Tubing Operations, well stimulation and relevant engineering services;
CBL
Bridge plug setting;
Fishing Operations.
Presentation Topic:
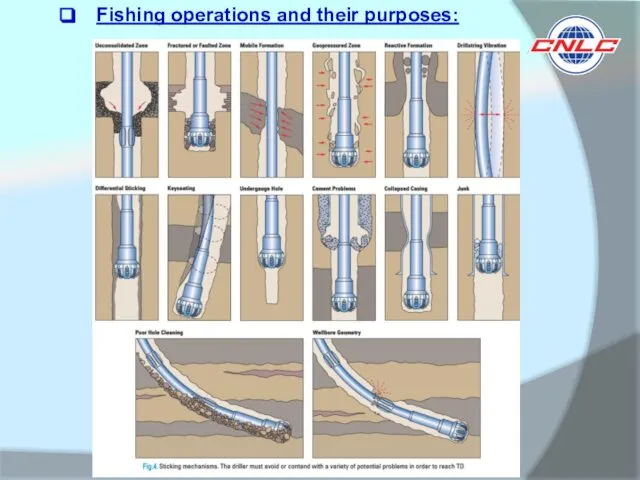
Any matters left in the borehole that interfere further work at
Any matters left in the borehole that interfere further work at
Reasons for fishing operations:
Human factor
2) Equipment malfunction
3) Wellbore instability
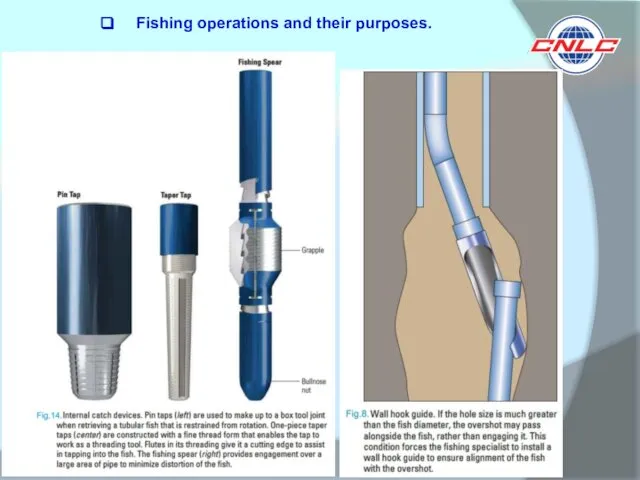
Fishing operations and their purposes.
Fishing operations and their purposes:
Fishing operations and their purposes:
Fishing operations and their purposes.
Fishing operations and their purposes.
Fishing operations and their purposes.
Fishing operations and their purposes.

























 Неличные формы глагола
Неличные формы глагола Презентация к уроку английского языка "Hello my friends. I am Jasmine. " - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Hello my friends. I am Jasmine. " - скачать  Аттестационная работа. Программа внеурочной деятельности по английскому языку для обучающихся 6 класса Говорим по-английски
Аттестационная работа. Программа внеурочной деятельности по английскому языку для обучающихся 6 класса Говорим по-английски Lead -in
Lead -in Past Simple and Past Continuous
Past Simple and Past Continuous October, the 13th
October, the 13th Pronunciation
Pronunciation Transportation and vehicles
Transportation and vehicles Which food am i. A dart game
Which food am i. A dart game Презентация к уроку английского языка "Соединенные Штаты Америки" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Соединенные Штаты Америки" - скачать  Аттестационная работа. Пути самостоятельного изучения иностранных языков на примере английского и немецкого языков
Аттестационная работа. Пути самостоятельного изучения иностранных языков на примере английского и немецкого языков Mixed conditionals
Mixed conditionals I am a blot. I am naughty. I like spoiling everything
I am a blot. I am naughty. I like spoiling everything Find with Judy
Find with Judy History, life and creativity of the Kino group
History, life and creativity of the Kino group Учимся писать эссе. Письмо. Написание развернутого высказывания. Задание 2(С2)
Учимся писать эссе. Письмо. Написание развернутого высказывания. Задание 2(С2) Презентация к уроку английского языка "Christmas Traditions" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Christmas Traditions" - скачать  MOONSHINE Moonshine is a common name for home-distilled alcohol, especially in places where this practice is illegal. The term is commonly believed to derive from producers and smugglers of moonshine working at night under the light of the
MOONSHINE Moonshine is a common name for home-distilled alcohol, especially in places where this practice is illegal. The term is commonly believed to derive from producers and smugglers of moonshine working at night under the light of the Summer stories
Summer stories Phonics A - M
Phonics A - M Past simple tense. Irregular verbs
Past simple tense. Irregular verbs How to write an essay
How to write an essay How to organize your answer. Use the following guide to plan, organize and paragraph an essay in IELTS Writing
How to organize your answer. Use the following guide to plan, organize and paragraph an essay in IELTS Writing Презентация к уроку английского языка "Guy Fawkes Day" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Guy Fawkes Day" - скачать  Collective noun. Game
Collective noun. Game She's got blue eyes. (Module 4, lesson 47)
She's got blue eyes. (Module 4, lesson 47) - Ed pronunciation. Game
- Ed pronunciation. Game Holidays Types of holidays Pictures Vocabulary Ибрагимова В.В. ГОУ гимназия№399 СПб
Holidays Types of holidays Pictures Vocabulary Ибрагимова В.В. ГОУ гимназия№399 СПб