Содержание
- 2. Еconomic policy The objectives of the economic policy The types of economic policy By industry Functionally-oriented
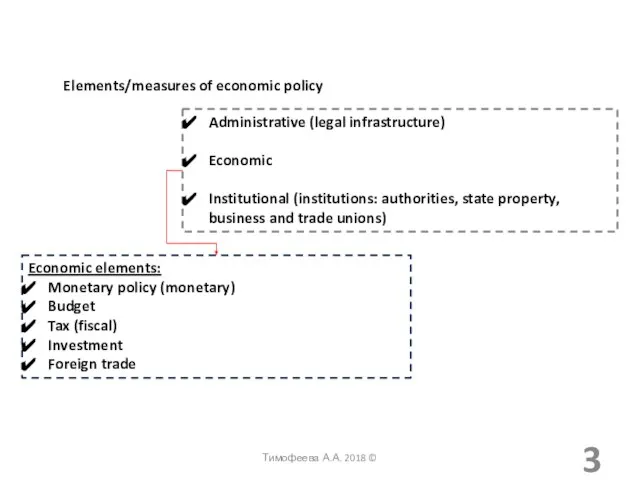
- 3. Elements/measures of economic policy Administrative (legal infrastructure) Economic Institutional (institutions: authorities, state property, business and trade
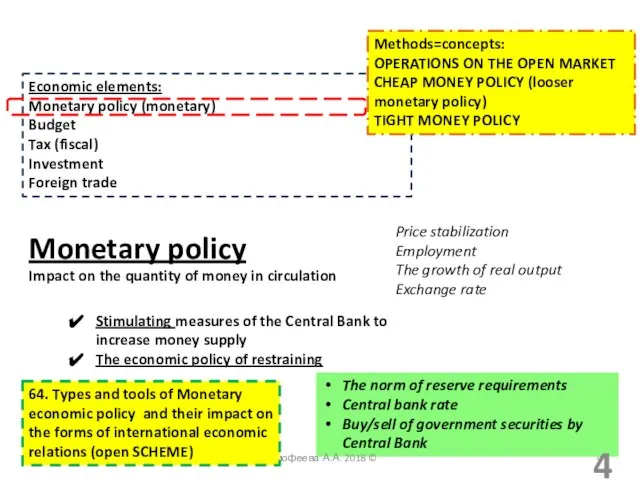
- 4. Economic elements: Monetary policy (monetary) Budget Tax (fiscal) Investment Foreign trade Monetary policy Impact on the
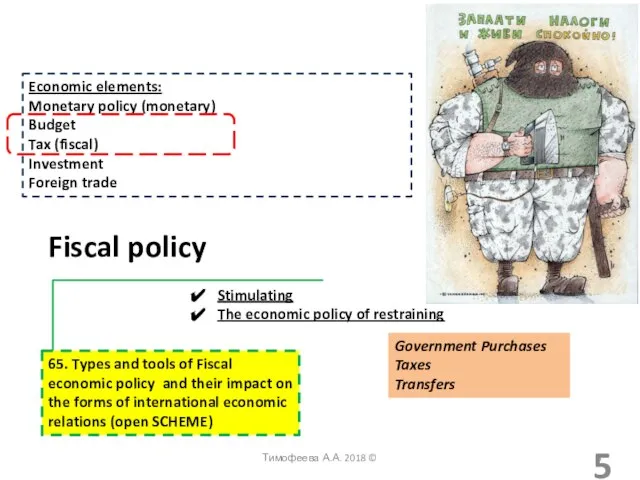
- 5. Economic elements: Monetary policy (monetary) Budget Tax (fiscal) Investment Foreign trade Fiscal policy Government Purchases Taxes
- 6. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
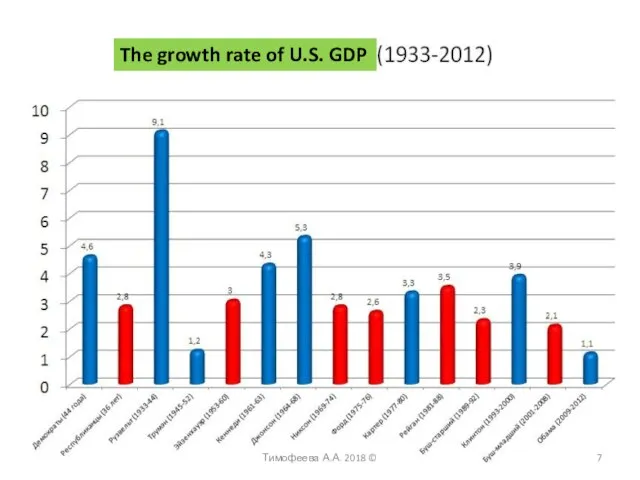
- 7. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 © The growth rate of U.S. GDP
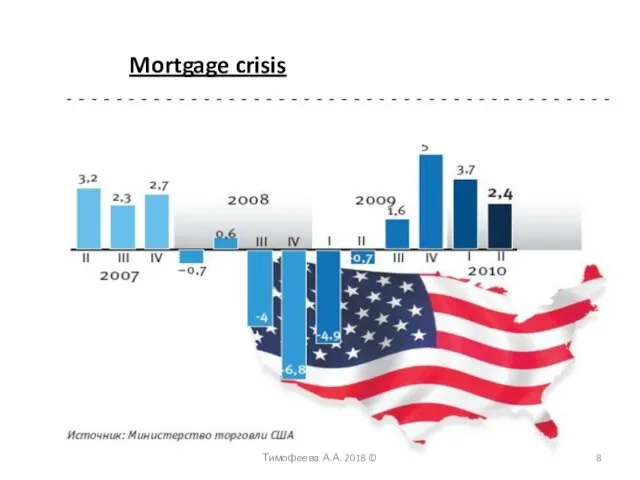
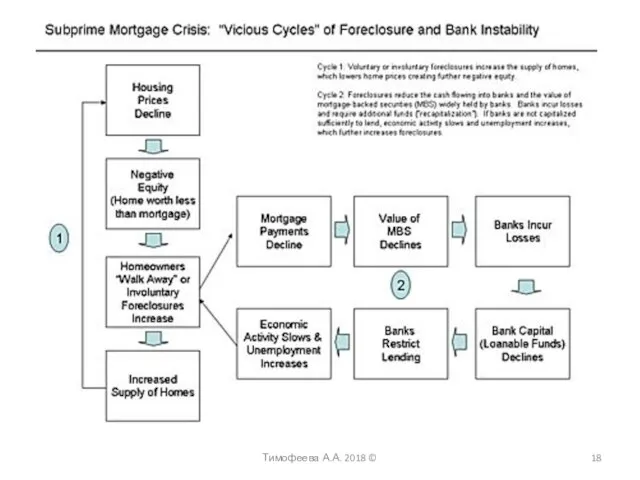
- 8. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 © Mortgage crisis
- 9. Global recession 2009 Financial crisis or mortgage crisis of USA 2007-2008 Mortgage loans with a high
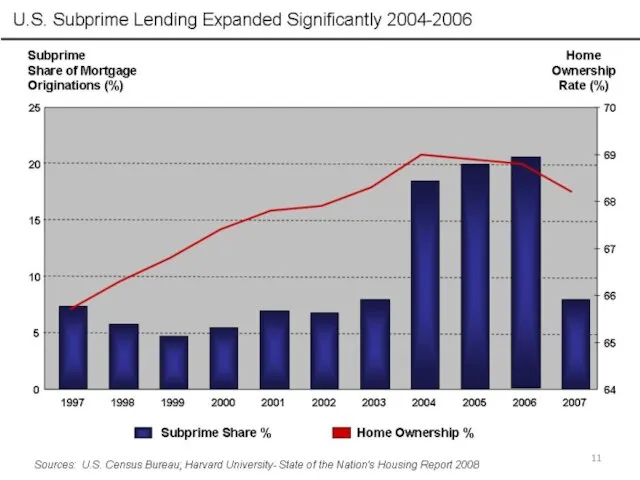
- 10. Standard lending is reduced Subprime mortgage credit Reduction of influence of the enterprises with state participation
- 11. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
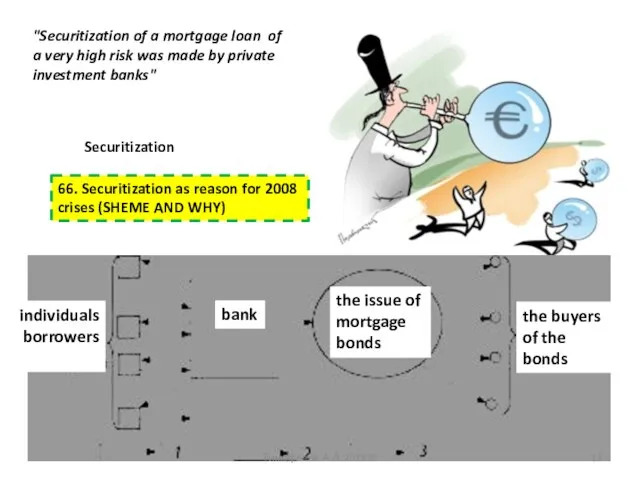
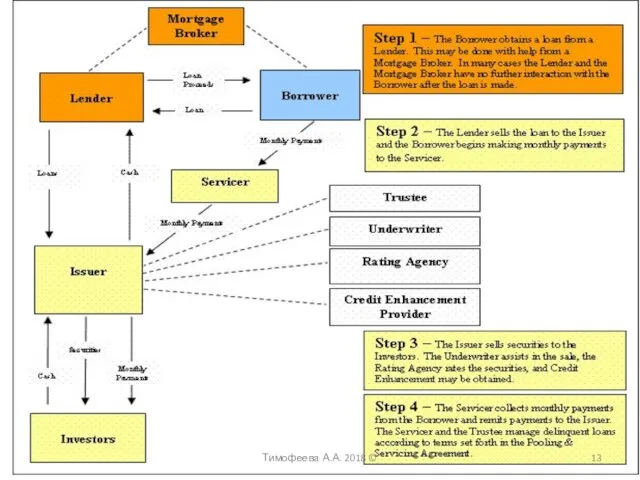
- 12. "Securitization of a mortgage loan of a very high risk was made by private investment banks"
- 13. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
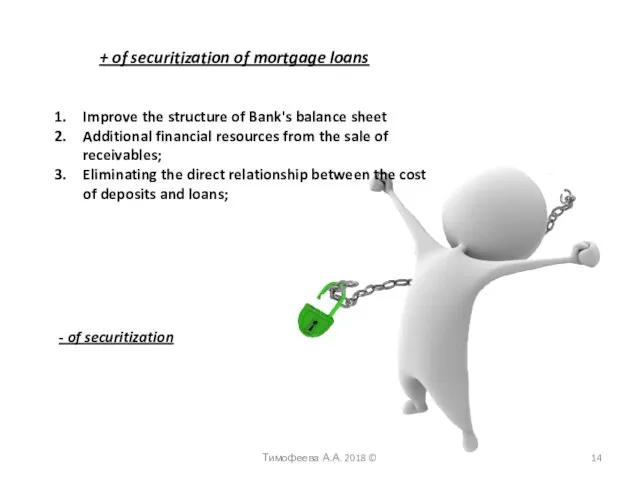
- 14. + of securitization of mortgage loans Improve the structure of Bank's balance sheet Additional financial resources
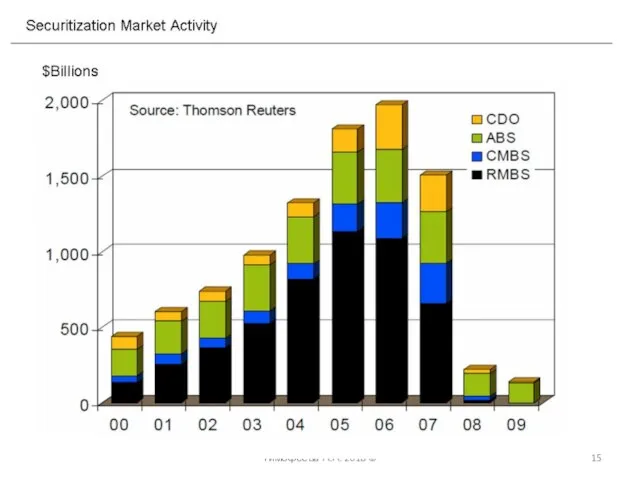
- 15. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
- 16. 2006-2007 Refinancing Rise in % Falling prices for residential property September 2007 – 23% of residential
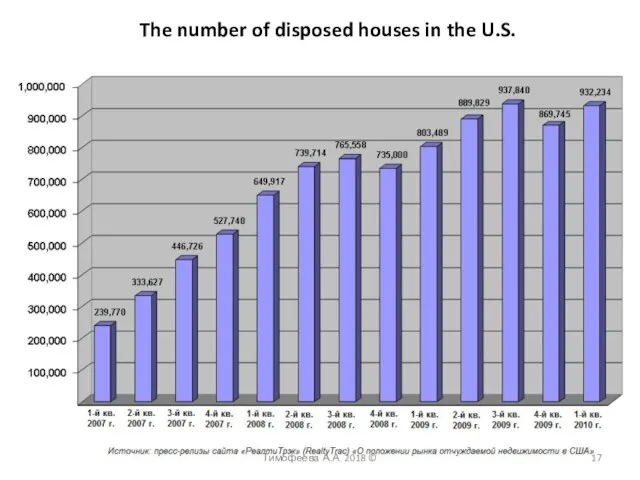
- 17. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 © The number of disposed houses in the U.S.
- 18. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
- 19. Why did availability of credit increase? Foreign investment in the U.S. + cheap credit => the
- 20. Some of the factors that contributed to the development of the crisis: Sub-Prime lending; Securitization of
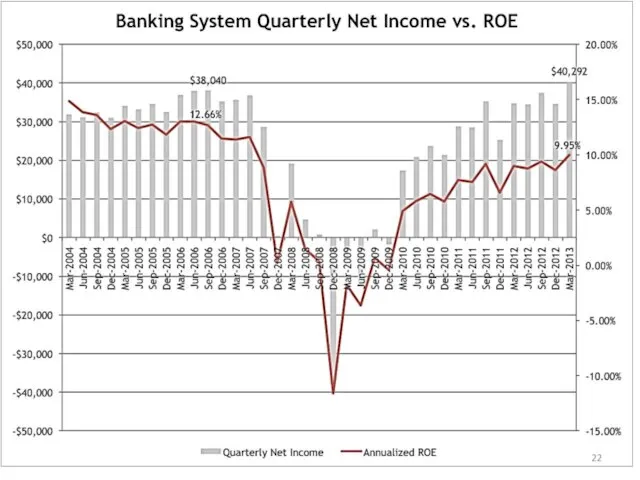
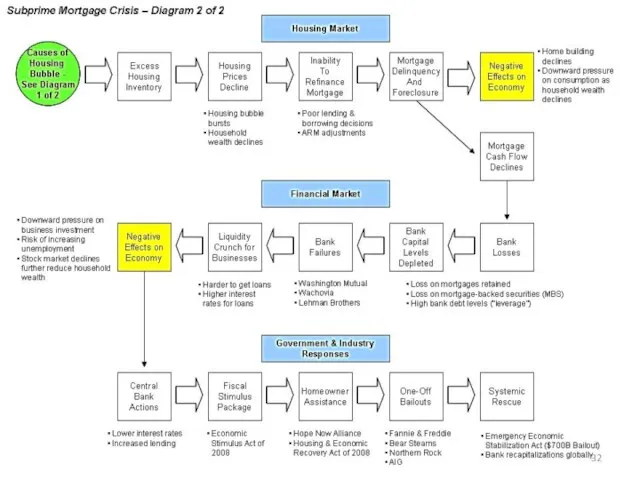
- 21. The impact of the crisis on the U.S. economy 2007 By the beginning of 2008, the
- 22. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
- 23. 2007: about 100 companies associated with the mortgage stop operations=> the panic in the financial markets
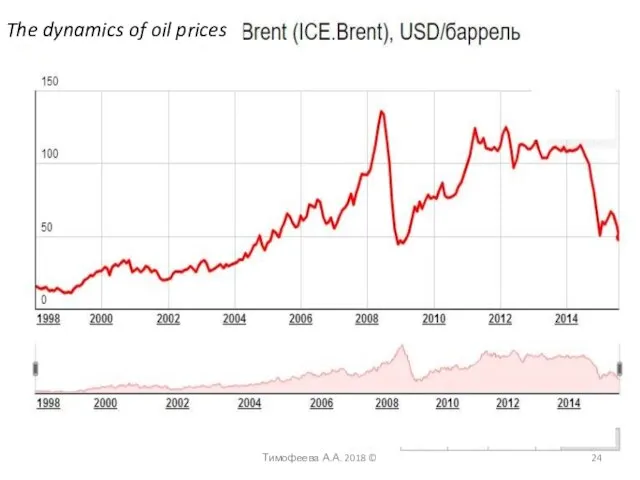
- 24. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 © The dynamics of oil prices
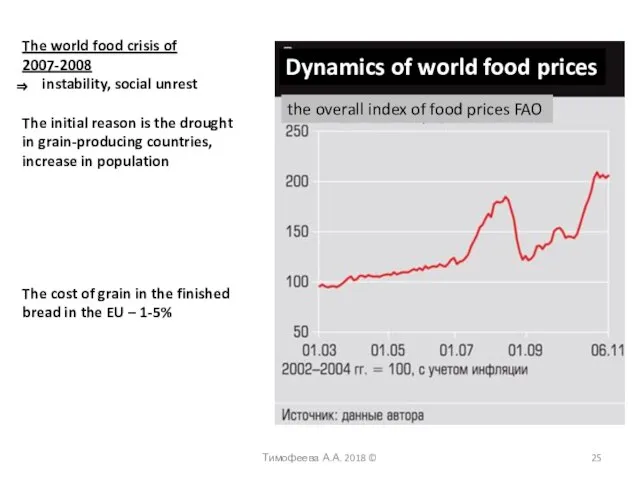
- 25. The world food crisis of 2007-2008 instability, social unrest The initial reason is the drought in
- 26. The impact of the crisis on the US economy 2008 The key is bankruptcy of Lehman
- 27. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
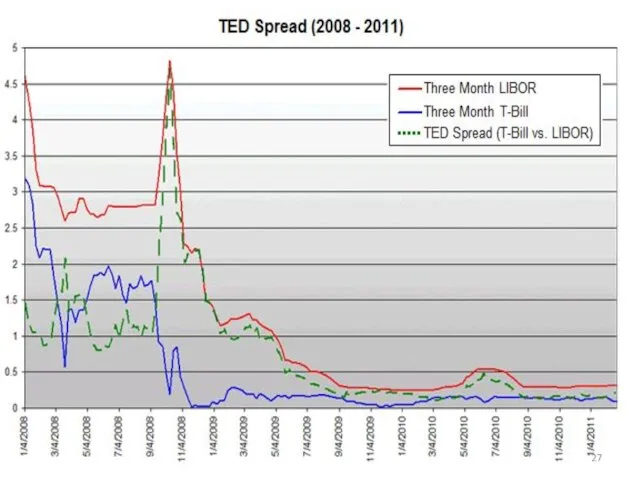
- 28. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
- 29. The fed buys toxic assets and government debt in the amount of $2.5 trillion + buying
- 30. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
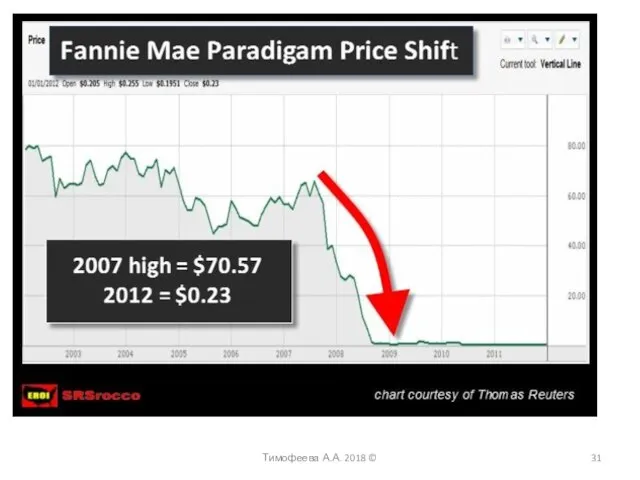
- 31. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
- 32. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
- 34. Скачать презентацию












 Berlin Berlin ist die Hauptstadt Deutschlands. Berlin ist eine alte Stadt. Es liegt an der Spree.
Berlin Berlin ist die Hauptstadt Deutschlands. Berlin ist eine alte Stadt. Es liegt an der Spree.  Welcome to Kirillo-Belozersky Monastery. By Arina Minicheva School №3 Kadui 2010
Welcome to Kirillo-Belozersky Monastery. By Arina Minicheva School №3 Kadui 2010 Презентация к уроку английского языка "Добро пожаловать в СТАР СПб!" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Добро пожаловать в СТАР СПб!" - скачать  Repetition and chiasmus
Repetition and chiasmus Аттестационная работа. Использование метода проектов на уроках английского языка
Аттестационная работа. Использование метода проектов на уроках английского языка Образцы картинок для 3 задания ВПР
Образцы картинок для 3 задания ВПР English language exams. Certificates and language levels
English language exams. Certificates and language levels RFTA Jessup Team. Отбор в команду. Устные раунды
RFTA Jessup Team. Отбор в команду. Устные раунды How to ask questions in the Past Simple
How to ask questions in the Past Simple Lecture 2. Stylistic lexicology
Lecture 2. Stylistic lexicology Articles
Articles Weather Future
Weather Future Выполняла Нестерова Александра, ученица 10 «Б» класса МОУ СОШ №103
Выполняла Нестерова Александра, ученица 10 «Б» класса МОУ СОШ №103 History of the discovery of Antarctica
History of the discovery of Antarctica  Shopping. Which of these words are the names of the shops
Shopping. Which of these words are the names of the shops About IELTS
About IELTS Хохломская роспись
Хохломская роспись Презентация к уроку английского языка "Настоящее совершенное время. Наречия времени" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Настоящее совершенное время. Наречия времени" - скачать бесплатно Презентация к уроку английского языка "Nokia" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Nokia" - скачать  Рекомендации для учащихся 5 -11 классов Английский язык Советует Т.Г. Митюгина
Рекомендации для учащихся 5 -11 классов Английский язык Советует Т.Г. Митюгина  Past Simple VS Past Continuous
Past Simple VS Past Continuous Holidays and festivals in Britain выполнила учитель английского языка МОУ «СОШ №77», г. Омска, Тонких Т.А.
Holidays and festivals in Britain выполнила учитель английского языка МОУ «СОШ №77», г. Омска, Тонких Т.А. Презентация к уроку английского языка "«Великобритания. Флаг. Гимн. Символика»" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "«Великобритания. Флаг. Гимн. Символика»" - скачать  Past Simple Tense
Past Simple Tense Verb go
Verb go Person's character. Характер человека
Person's character. Характер человека Адаптация учащихся к условиям образовательного учреждения
Адаптация учащихся к условиям образовательного учреждения Monuments of World War I
Monuments of World War I