Содержание
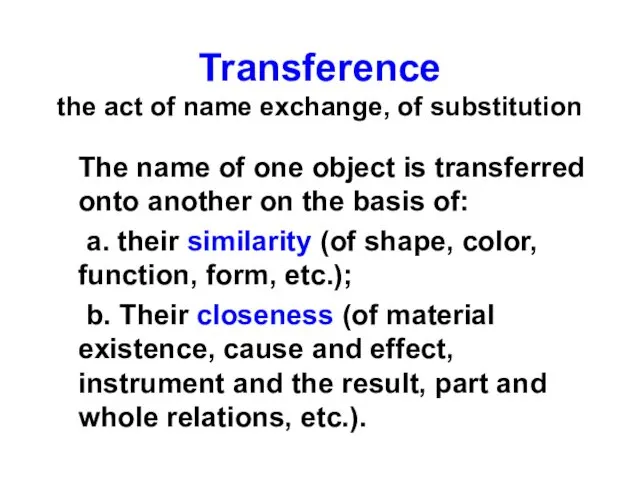
- 2. Transference the act of name exchange, of substitution The name of one object is transferred onto
- 3. Expressive means of a language (EMs) EMs of a language are: a) phonetic means, morphological forms,
- 4. What is a stylistic device? A SD - is a conscious and intentional literary use of
- 5. Examples of SDs a) Andrew’s face looked as if it were made of a wrotten apple
- 6. Convergence of EMs and SDs … And heaved and heaved, still unrestingly heaved the black sea,
- 7. Convergence of EMs and SDs in H.Melville’s phrase 1. Inversion 2. Repetition 3. Polysyndeton 4. Rhythm
- 8. CONVERGENCE Ex.: Define the EMs and SDs in this example. Sara was a menace and a
- 9. Check yourselves 1) Parallel constructions. 2) Antithesis: enemy-friend, worst - best. 3) Antonymical metaphors: tonic -
- 10. Phonetic EMs 1. Onomatopoeia - murmur, hiss, bump, etc. 2. Alliteration - «And the silken, sad,
- 11. Phonetic EMs -2 3. Graphon: a) «Yetalians», «peerading» (parading). b) stumbling: N-n-nice weather, isn’t it? c)
- 12. METAPHOR A SD based on similarity
- 13. What Is a Metaphor? A metaphor is a relation between the dictionary and contextual logical meanings
- 14. The Structure of a Metaphor A metaphor consists of the following parts: 1) tenor (the thing/object
- 15. Carl Sandburg Fog The fog comes On little cat feet. It sits looking Over harbour and
- 17. Скачать презентацию













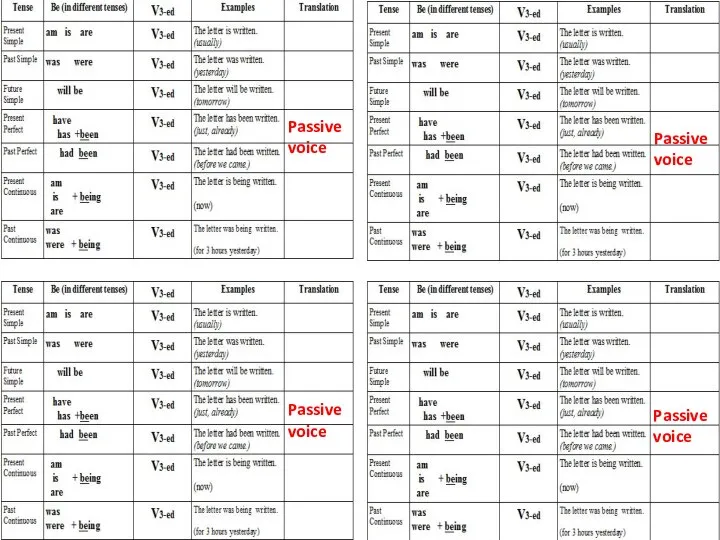 Passive voice
Passive voice Valentine’s Day
Valentine’s Day Sunken Treasure. The Guessing Game for Treasure on the High Seas
Sunken Treasure. The Guessing Game for Treasure on the High Seas Johann Wolfgang von Goethe Aljona Bondar 11-A
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe Aljona Bondar 11-A  Module 2g
Module 2g Marpol. Regulations for the prevention of pollution by sewage from ships
Marpol. Regulations for the prevention of pollution by sewage from ships William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare Sports equipment
Sports equipment С новым годом
С новым годом Презентация к уроку английского языка "In der Freizeit" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "In der Freizeit" - скачать бесплатно Презентация к уроку английского языка "Иностранные языки" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Иностранные языки" - скачать бесплатно Comparison of the fashion in England and America)
Comparison of the fashion in England and America)  ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ на тему: «Диалогическая речь в английском языке». Выполнила: учитель английского языка Апраксина Л.А. МОУ лицей №10
ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ на тему: «Диалогическая речь в английском языке». Выполнила: учитель английского языка Апраксина Л.А. МОУ лицей №10  Comparatives. English (Exam)
Comparatives. English (Exam) Выполнил Захаров Е. 9а класс. Учитель Романенко Е.Ф. МБОУ СОШ №28 ст. Тамань.
Выполнил Захаров Е. 9а класс. Учитель Романенко Е.Ф. МБОУ СОШ №28 ст. Тамань.  Sports and leisure (Movers word list)
Sports and leisure (Movers word list) ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ К УРОКУ К УМК И.Н.Верещагиной, О.В. Афанасьевой, 5 класс LESSON 5
ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ К УРОКУ К УМК И.Н.Верещагиной, О.В. Афанасьевой, 5 класс LESSON 5  Правила чтения учитель англ. яз. Кулешова Е.В.
Правила чтения учитель англ. яз. Кулешова Е.В. EDUCATION IN THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
EDUCATION IN THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA 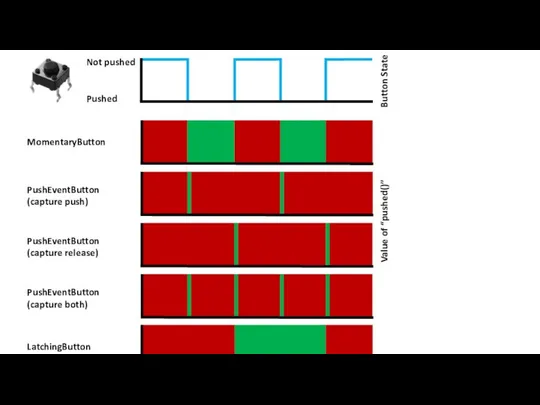 Documentation. Pushed
Documentation. Pushed We eat how we feel!
We eat how we feel! Present Continuous
Present Continuous Формирование социокультурной компетенции через организацию внеурочной деятельности по иностранному языку
Формирование социокультурной компетенции через организацию внеурочной деятельности по иностранному языку Цвета (продолжение) (1)
Цвета (продолжение) (1) School objects. Part 2
School objects. Part 2 What is useful for us? Presentation was made by the pupil 7B Yurova Yuliya
What is useful for us? Presentation was made by the pupil 7B Yurova Yuliya  Хорошие публикации
Хорошие публикации Facts Against School Uniforms Подготовлено учителем МБОУ г.Владимира «Лингвистическая гимназия № 23» Трубицыной М.С.
Facts Against School Uniforms Подготовлено учителем МБОУ г.Владимира «Лингвистическая гимназия № 23» Трубицыной М.С.