Содержание
- 2. Previous Lesson Recap 15/04/17 Sonali The concepts/terms learnt: Inefficiency Misallocation of resources (2 min)
- 3. 15/04/17 Sonali Activity 1 (6.47 min)
- 4. Topic of the Day Market Failure Market failure occurs when freely-functioning markets, fail to deliver an
- 5. Group Division GROUP 1: Animal World (3- 4 members) GROUP 2: Plant World (3- 4 members)
- 6. Activity 2-Critical Thinking (25 min) GROUP WORK- PRESENTATION : GROUP DISCUSSION Preparation Time: 10 min Presentation:
- 7. Reflection What did you learn today ? Чему вы научились сегодня?
- 8. Unit: 11.4B-2 15/04/17 Sonali Externalities Spill over effect The cost or benefit that affects a party
- 9. Previous Lesson Recap 15/04/17 Sonali The concepts/terms learnt: Inefficiency Misallocation of resources Market Failure (2 min)
- 10. Word Search 15/04/17 Sonali Positive externalities/ External benefits Negative externalities/ External costs Private Cost Private Benefits
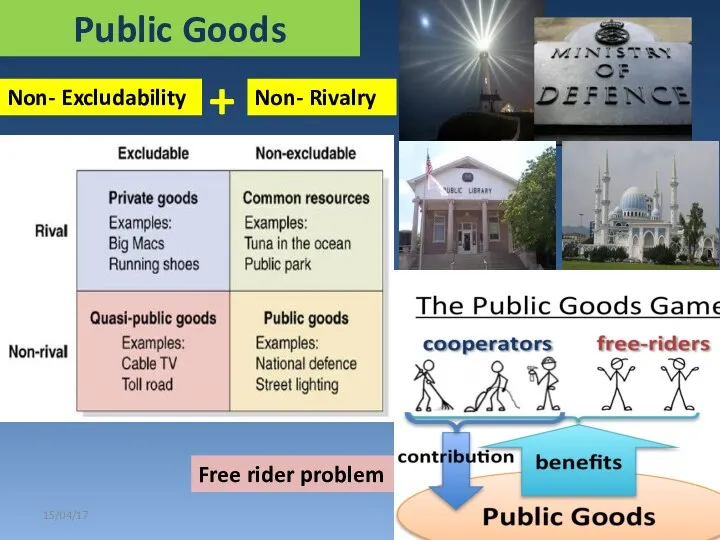
- 11. Public Goods 15/04/17 Non- Excludability Non- Rivalry Free rider problem +
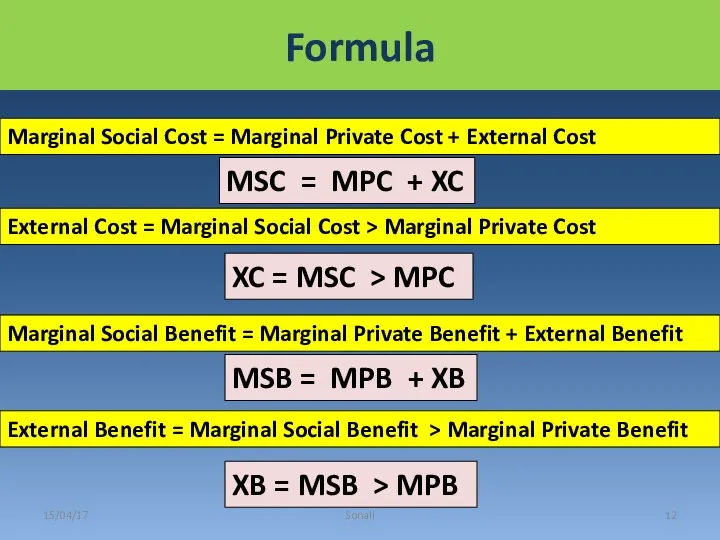
- 12. Formula 15/04/17 Sonali Marginal Social Benefit = Marginal Private Benefit + External Benefit MSB = MPB
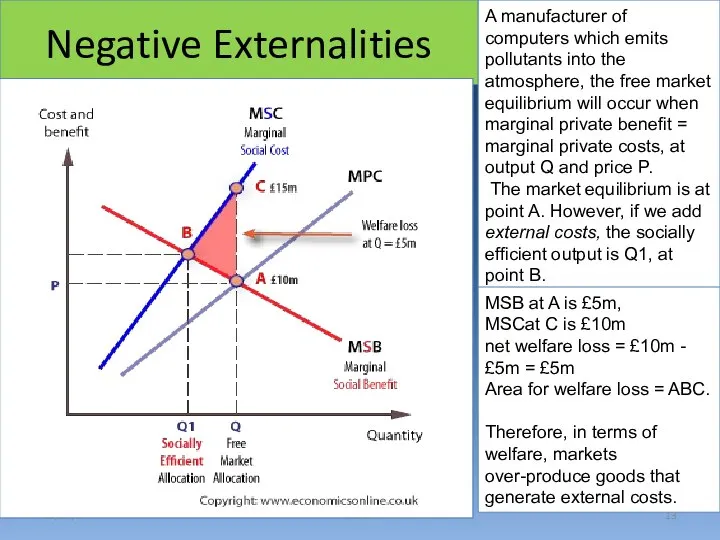
- 13. Negative Externalities 15/04/17 Sonali A manufacturer of computers which emits pollutants into the atmosphere, the free
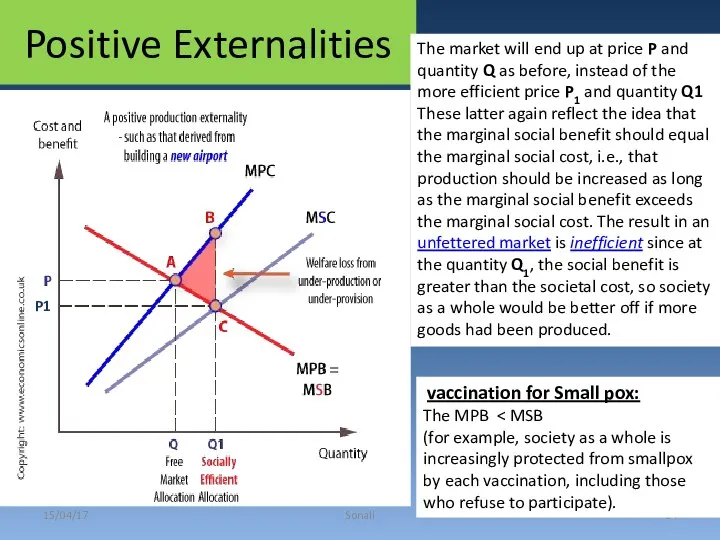
- 14. Positive Externalities 15/04/17 Sonali vaccination for Small pox: The MPB (for example, society as a whole
- 15. Group Division GROUP 1: GROUP 2: GROUP 3: GROUP 4:
- 16. Activity 2-Critical Thinking (25 min) GROUP WORK- PRESENTATION : GROUP DISCUSSION Preparation Time: 10 min Presentation:
- 17. Unit: 11.4B-3 15/04/17 Sonali Government Intervention
- 18. Previous Lesson Recap 15/04/17 Sonali The concepts/terms learnt: Negative externality Positive externality Taxes Subsidies (2 min)
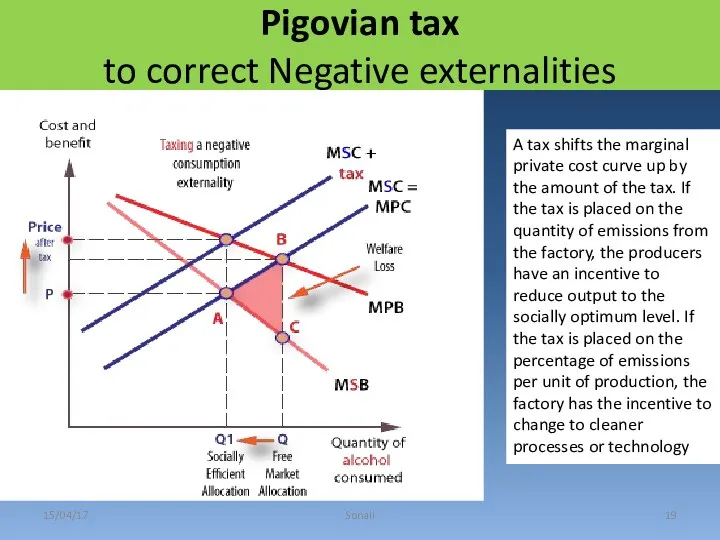
- 19. Pigovian tax to correct Negative externalities 15/04/17 Sonali A tax shifts the marginal private cost curve
- 20. Property Rights to correct Negative externalities 15/04/17 Sonali Extend property rights so that third parties can
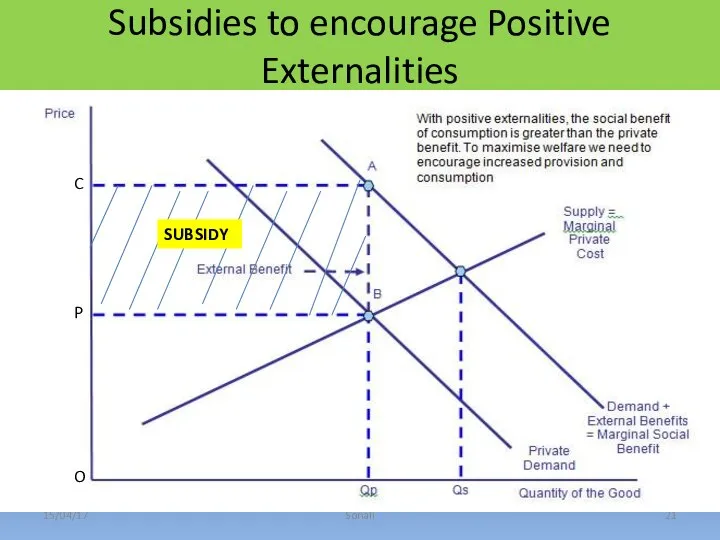
- 21. Subsidies to encourage Positive Externalities 15/04/17 Sonali C P O SUBSIDY
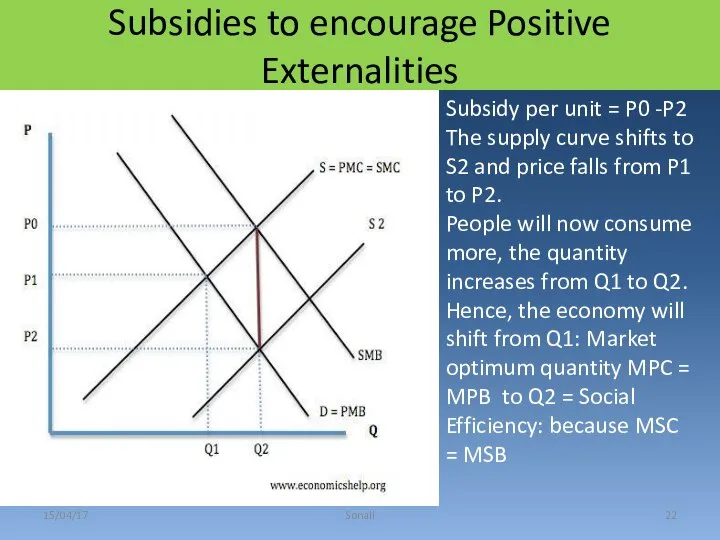
- 22. 15/04/17 Sonali Subsidies to encourage Positive Externalities Subsidy per unit = P0 -P2 The supply curve
- 24. Скачать презентацию












 Правила чтения английских гласных
Правила чтения английских гласных Определённый артикль THE
Определённый артикль THE John Ruskin
John Ruskin  Strategy, aims, and principles of sustainable development
Strategy, aims, and principles of sustainable development The dance of the fire
The dance of the fire Ivan Kupala Day Project Form 11 Pernata Kate
Ivan Kupala Day Project Form 11 Pernata Kate TWO GENERATIONS: HOW TO BUILD A BRIDGE BETWEEN THEM? Irina Krasovitova, pupil of 8”C” school №7
TWO GENERATIONS: HOW TO BUILD A BRIDGE BETWEEN THEM? Irina Krasovitova, pupil of 8”C” school №7 When I am
When I am Alphabet
Alphabet The “Mother” of Barbie Doll Author: Zubakova Alyona form 7 A school 88 Teacher: Kuznetsova Galina Genrikhovna
The “Mother” of Barbie Doll Author: Zubakova Alyona form 7 A school 88 Teacher: Kuznetsova Galina Genrikhovna Kostanai state pedagogical University named after Umirzak Sultangazin
Kostanai state pedagogical University named after Umirzak Sultangazin Theaters in Spain
Theaters in Spain  London is the capital Great Britain
London is the capital Great Britain Презентация к уроку английского языка "Australian food" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Australian food" - скачать  Learning to describe a person. 3 класс
Learning to describe a person. 3 класс Отличие фильма и книги «Гарри Поттер и философский камень»
Отличие фильма и книги «Гарри Поттер и философский камень» Ukrainian cuisine 7 most popular Ukrainian dishes
Ukrainian cuisine 7 most popular Ukrainian dishes  Articles
Articles Christmas “Who wants to be a millionaire”
Christmas “Who wants to be a millionaire” Презентация к уроку по теме «Traditional Holidays in English –Speaking Countries»
Презентация к уроку по теме «Traditional Holidays in English –Speaking Countries» Where's Grandma Interactive
Where's Grandma Interactive How do we learn english
How do we learn english What am I?
What am I? Презентация к уроку английского языка "Mountaineering" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Mountaineering" - скачать  Question tags
Question tags Презентация по английскому языку Plural of nouns (множественное число существительных)
Презентация по английскому языку Plural of nouns (множественное число существительных)  Scientific traditions and scientific revolutions
Scientific traditions and scientific revolutions Farm animals. With sounds
Farm animals. With sounds