Sports in Society: Issues & Controversies Chapter 1 The Sociology of Sport: What Is It and Why Study It?
Содержание
- 2. Sports Are Social Phenomena Sports are related to the social and cultural contexts in which we
- 3. SOCIOLOGY is a tool for studying sports in society Sociology provides useful Concepts Theories Research methods
- 4. CULTURE Consists of the “ways of life” people create in a group or society These ways
- 5. SOCIETY A collection of people Living in a defined geographical territory United through a political system
- 6. SOCIOLOGY Vs. PSYCHOLOGY Psychologists study behavior in terms of attributes & processes that exist inside individuals
- 7. Critical thinking about sports helps us Identify & understand social problems and social issues associated with
- 8. SOCIOLOGY may lead to controversial recommendations Sociological research may produce findings that suggest changes in the
- 9. Why study sports as social phenomena? Sports activities and images are part of people’s lives Sports
- 10. Ideologies The sets of interrelated ideas that people use To give meaning to the world To
- 11. The characteristics of Ideologies are: They are never established “once and for all time” They emerge
- 12. “Dominant Ideology” Represents the perspectives and ideas favored by people who have power and influence in
- 13. Gender Ideology refers to A set of interrelated ideas about masculinity, femininity, and relationships between men
- 14. Racial Ideology refers to A set of interrelated ideas that people use to give meaning to
- 15. Why study sports as social phenomena? Sports are connected with major spheres of social life Family
- 16. Major Professional Organizations in the Sociology of Sport : The International Sociology of Sport Association (ISSA)
- 17. Disagreements in the Sociology of Sport Scholars in the field see themselves as Sport sociologists concerned
- 18. SPORT Is Defined by Some Scholars As Activities That Are Physical Competitive Institutionalized Motivated by a
- 19. Institutionalization Occurs When Rules become standardized Official agencies enforce rules Organizational & technical aspects of the
- 20. Play vs. Dramatic Spectacle Play involves expressive activity done for its own sake; it is often
- 21. An Alternative Approach to Defining Sports: Determine what activities are identified as sports in a society
- 23. Скачать презентацию




















 Изучаем английский алфавит
Изучаем английский алфавит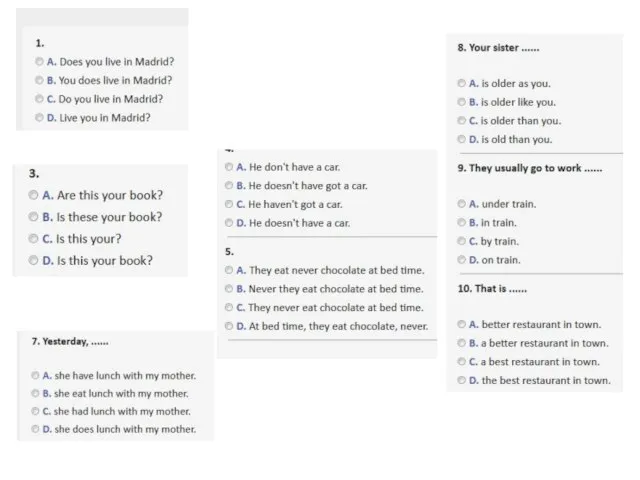 Grammar revision
Grammar revision Present Continuous
Present Continuous Презентация к уроку английского языка "School uniform in different countries" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "School uniform in different countries" - скачать бесплатно Использование технологии дебатов на уроках английского языка Сметанина Н.И. МОУ ЧСОШ № 1 Саяногорск
Использование технологии дебатов на уроках английского языка Сметанина Н.И. МОУ ЧСОШ № 1 Саяногорск МОУ ЧСШ № 1 Self-education is, I firmly believe ,the only kind of education there is. Isaac Asimov Интерактивная доска на уроках английского языка , как э
МОУ ЧСШ № 1 Self-education is, I firmly believe ,the only kind of education there is. Isaac Asimov Интерактивная доска на уроках английского языка , как э Тема урока:Цветик-семицветик Проведение конкурсов
Тема урока:Цветик-семицветик Проведение конкурсов  The British Parliament
The British Parliament Синтаксис делового письма
Синтаксис делового письма Youth public organizations
Youth public organizations How do we learn english
How do we learn english Some interesting facts about English language
Some interesting facts about English language Презентация к уроку английского языка в 5 классе по теме:The sights of London. Автор: учитель английского языка ГБОУ СОШ 883 г. Москвы Парамон
Презентация к уроку английского языка в 5 классе по теме:The sights of London. Автор: учитель английского языка ГБОУ СОШ 883 г. Москвы Парамон МОУ СОШ №7 г.Ртищево Саратовской области Бердникова Татьяна Анатольевна учитель английского языка ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ К УРОКУ «Как
МОУ СОШ №7 г.Ртищево Саратовской области Бердникова Татьяна Анатольевна учитель английского языка ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ К УРОКУ «Как English Participle
English Participle 3D Animation I
3D Animation I American car
American car Wild Animals
Wild Animals Fairy tale characters
Fairy tale characters Present Simple 3
Present Simple 3 МБОУ СОШ№6 с.Миндяк МР Учалинский район РБ Health 5 класс УМК “Happy English.ru” Выполнил учитель первой категории Гусева Юлия Николаевна 2013
МБОУ СОШ№6 с.Миндяк МР Учалинский район РБ Health 5 класс УМК “Happy English.ru” Выполнил учитель первой категории Гусева Юлия Николаевна 2013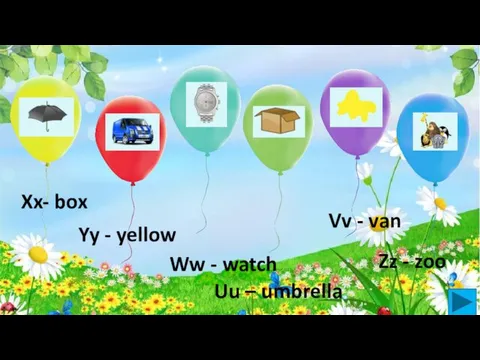 Alphabet
Alphabet Презентация Money
Презентация Money Presented by Sermons4Kids
Presented by Sermons4Kids Time
Time At the zoo
At the zoo Presentation in English on the topic: My idol
Presentation in English on the topic: My idol Crime
Crime