Содержание
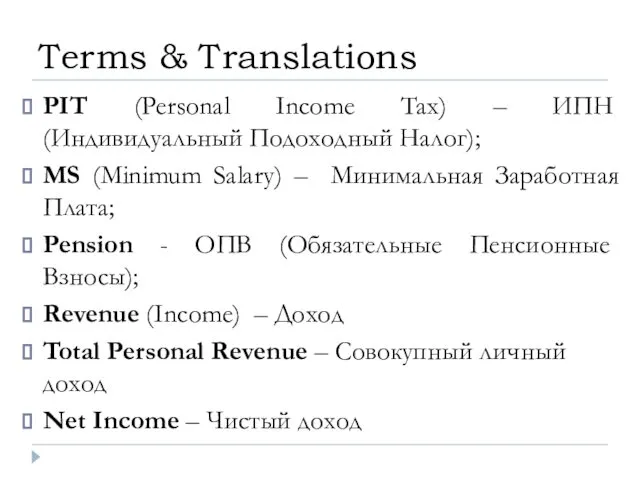
- 2. PIT (Personal Income Tax) – ИПН (Индивидуальный Подоходный Налог); MS (Minimum Salary) – Минимальная Заработная Плата;
- 3. Tax Burden under Employment Contract; Tax Burden under Civil Contract; Tax Burden of Individual Entrepreneurs; Goal
- 4. Tax Legislation is based on the: Constitution; Code of the RK on Taxes and other Obligatory
- 5. Tax Law regulate the government-directed relations associated with establishing, introduction and the procedure for the payment
- 6. Sub-par.34 par.1 art.1 TC Taxes - obligatory monetary payments to the budget as established by the
- 7. Subject of the tax law – taxpayer who obliged to pay taxes. Taxpayers divided into physical
- 8. Article 27. A Taxable Item and (or) Item Related to Taxation The taxable item and (or)
- 9. Principle of Personal Law – attraction of national (local) physical persons and legal entities; Principle of
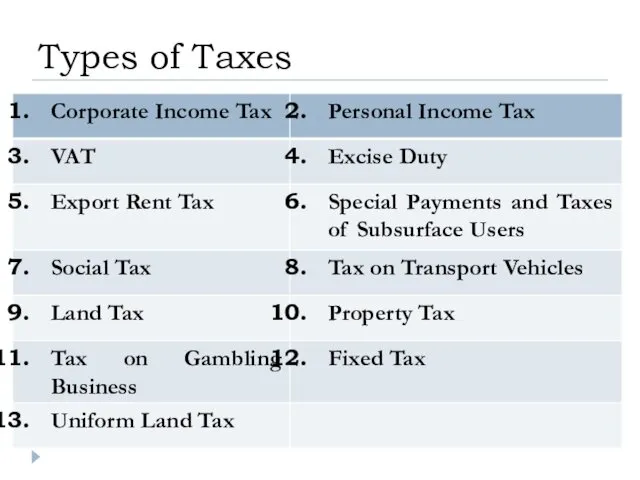
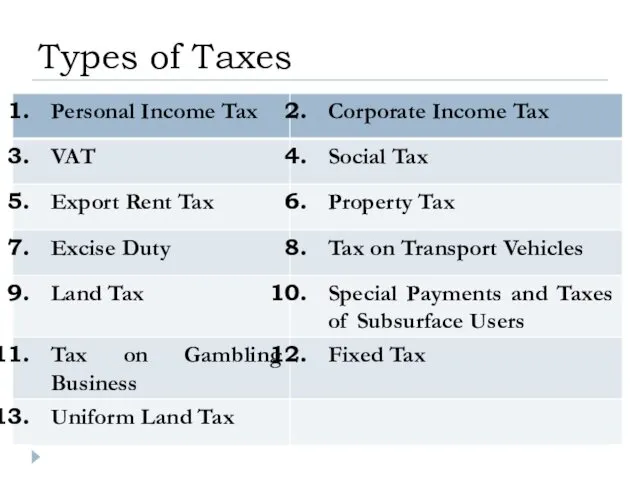
- 10. Types of Taxes
- 11. VAT, taxable items: taxable turnovers (selling goods, works and services in the RK); taxable import. VAT
- 12. Excisable Products: Alcohol; Tobacco; Gasoline; Diesel; Crude Oil; Gas Condensate; Excise Duty Subjects – producers/importers of
- 13. Export Rent Tax: Crude Oil; Gas Condensate; Coal Export Rent Tax Subjects – exporters;
- 14. Hydrocarbon Resources; Solid Minerals; Common Minerals. Subsurface Users Special Payments and Taxes of Subsurface Users:
- 15. Paid by the owners of the Real-Estate; Subsurface Users Property Tax:
- 16. Article 26. Tax Liability The tax liability the taxpayer’s obligation to be registered by the tax
- 17. Who has to pay PIT? Subjects of the PIT: Physical person – resident; Physical person –
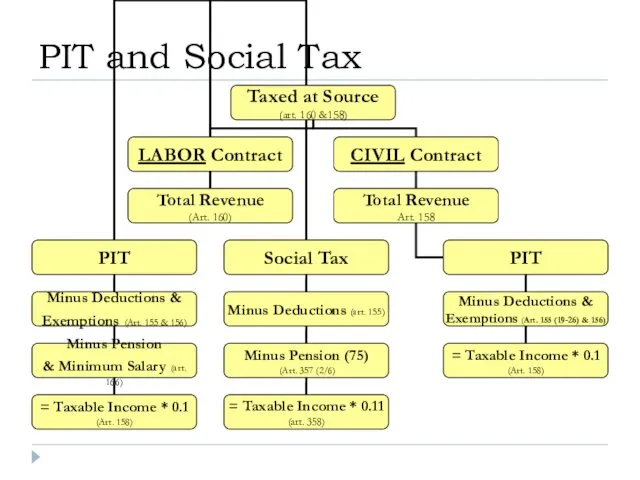
- 18. PIT and Social Tax
- 19. Object of the PIT: Revenues taxed at source (i.e. income from: salary, dividends, interest, gains, pensions,
- 20. Rates of the PIT: Revenues taxed at source - at the rate of 10%; Income from
- 21. Labor Contract: Your Official Salary is KZT 500,000; What will be the amount of your PIT?
- 22. PIT – 10%; Social Tax = 11% Pension – 10%; Minimum Salary – for 2015 is
- 23. Calculation: Monthly pension payments are 10%; Minimum Salary equals to – 21,364 tenge. Every employee is
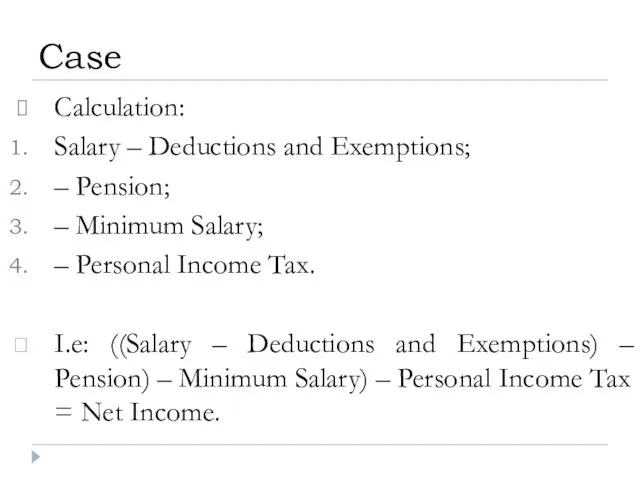
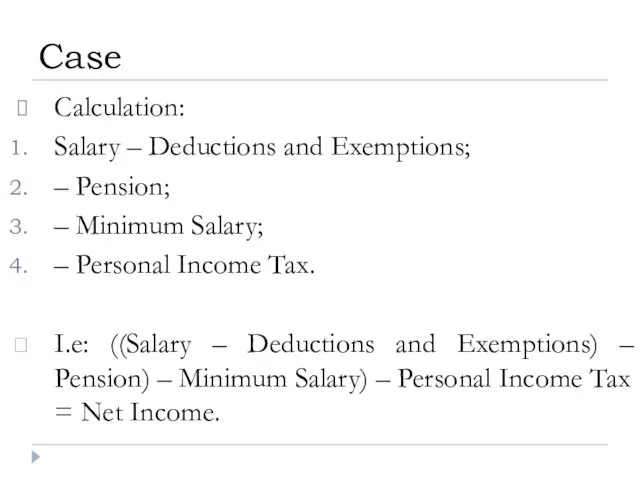
- 24. Calculation: Salary – Deductions and Exemptions; – Pension; – Minimum Salary; – Personal Income Tax. I.e:
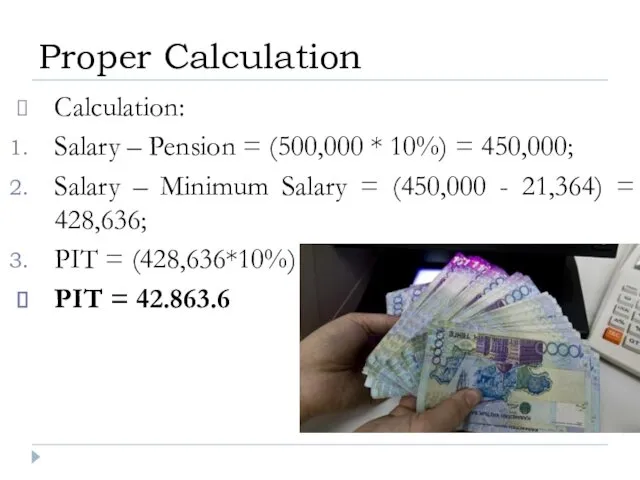
- 25. Calculation: Salary – Pension = (500,000 * 10%) = 450,000; PIT = (450,000*10%) = 45,000; PIT
- 26. Calculation: Salary – Pension = (500,000 * 10%) = 450,000; Salary – Minimum Salary = (450,000
- 27. When COMPANY (Tax Agent) has to pay Personal Income Tax?
- 28. Who pays PIT?
- 29. “LLP GARANT” wants to sign a contract for provision of legal services with Arman – the
- 30. PIT and Social Tax
- 31. Calculation: Salary – Deductions and Exemptions; – Pension; – Social Tax. I.e: ((Salary – Deductions and
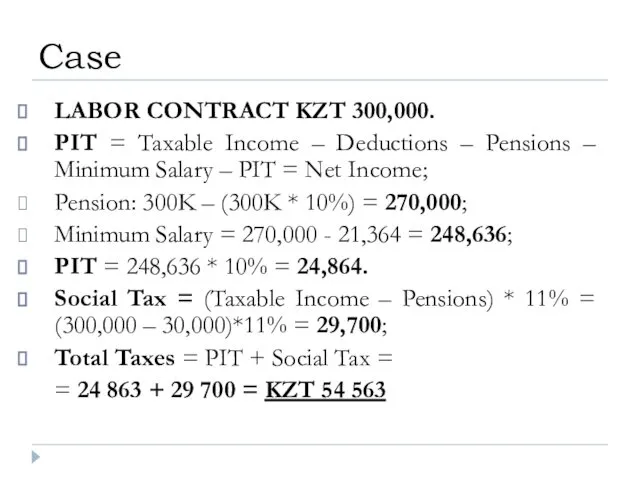
- 32. LABOR CONTRACT KZT 300,000. PIT = Taxable Income – Deductions – Pensions – Minimum Salary –
- 33. Calculation: Salary – Deductions and Exemptions; – Pension; – Minimum Salary; – Personal Income Tax. I.e:
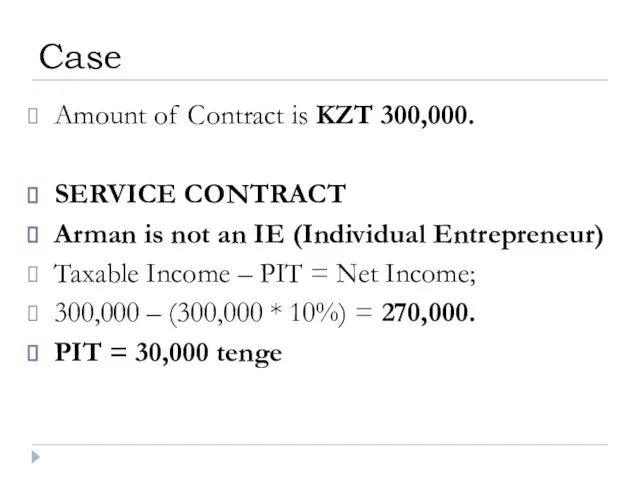
- 34. Amount of Contract is KZT 300,000. SERVICE CONTRACT Arman is not an IE (Individual Entrepreneur) Taxable
- 35. Amount of Contract is KZT 300,000. SERVICE CONTRACT Arman is not an IE (Individual Entrepreneur) Company
- 36. Amount of Contract is KZT 300,000. SERVICE CONTRACT Arman is an IE (Individual Entrepreneur) Company doesn’t
- 37. “LLP GARANT” wants to sign a contract for provision of legal services with Arman – the
- 38. Tax Regimes of the IP: Generally Established Procedures; Special Tax Regimes: On the Basis of Patent;
- 39. Generally Established Procedures: PIT – 10%; Social Tax – 2 MS for oneself and 1 MS
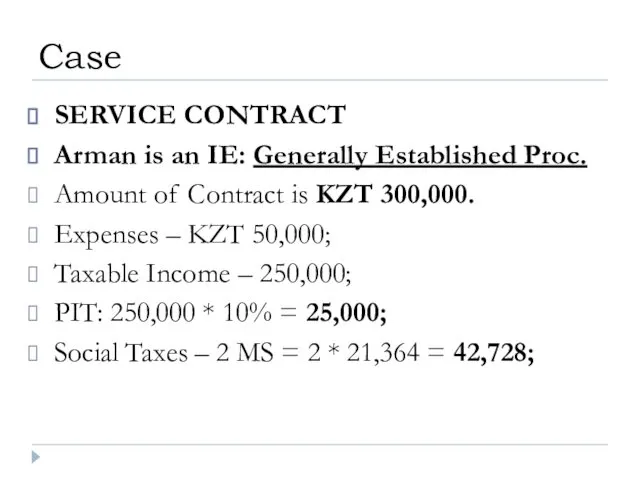
- 40. SERVICE CONTRACT Arman is an IE: Generally Established Proc. Amount of Contract is KZT 300,000. Expenses
- 41. Special Tax Regime - Patent: PIT – 1%; Social Tax – 1% *Note: IP can not
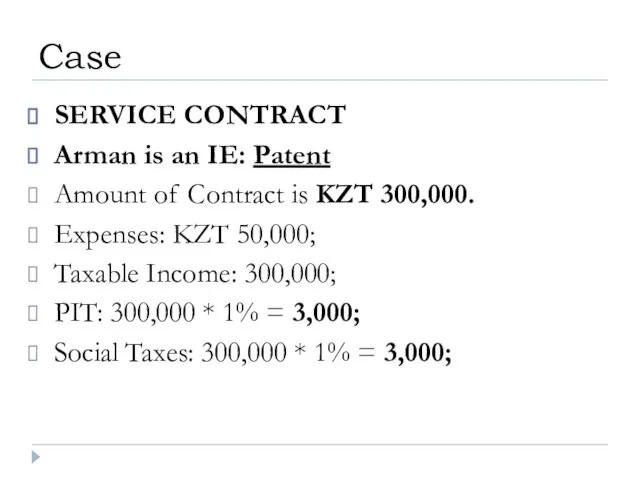
- 42. SERVICE CONTRACT Arman is an IE: Patent Amount of Contract is KZT 300,000. Expenses: KZT 50,000;
- 43. Special Tax Regime – Simplified Declaration: PIT – 1,5%; Social Tax – 1,5%; *Note: IP doesn’t
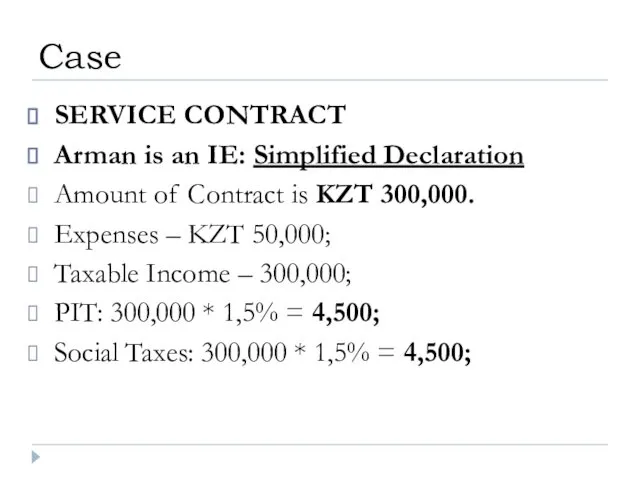
- 44. SERVICE CONTRACT Arman is an IE: Simplified Declaration Amount of Contract is KZT 300,000. Expenses –
- 45. Types of Taxes
- 47. Скачать презентацию
































 Презентация к уроку английского языка "Урок – КВН" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Урок – КВН" - скачать  Creating a holiday card "Holidays in Russia and Britain"
Creating a holiday card "Holidays in Russia and Britain" Welcome to Berlin
Welcome to Berlin  Guess the Season
Guess the Season Whose room is this
Whose room is this Внешность человека, характер и части тела
Внешность человека, характер и части тела Сравнительный анализ пословиц, поговорок и идиом со словом «dog» на русском и английском языках
Сравнительный анализ пословиц, поговорок и идиом со словом «dog» на русском и английском языках Who wants to be a millionaire?
Who wants to be a millionaire? Friends forever
Friends forever  The world of work
The world of work PRINT ADVERTISING
PRINT ADVERTISING  Conformity Quotes
Conformity Quotes Welcome to “ A Fairy Cafe”
Welcome to “ A Fairy Cafe”  New English File Unit 5a
New English File Unit 5a Формирование коммуникативной компетенции учащихся на уроках английского языка через использование ситуативных картин
Формирование коммуникативной компетенции учащихся на уроках английского языка через использование ситуативных картин Устная речь. Задание 4. Тематическое монологическое высказывание с элементами рассуждения
Устная речь. Задание 4. Тематическое монологическое высказывание с элементами рассуждения There is or there are
There is or there are My business is Antique Shop
My business is Antique Shop The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland What are you like? English 6, Unit 2, lesson 1 Signs of the Zodiac
What are you like? English 6, Unit 2, lesson 1 Signs of the Zodiac  Kazimir Malevich
Kazimir Malevich  Jack London
Jack London  Letter to my friend
Letter to my friend Исчисляемые и неисчисляемые существительные
Исчисляемые и неисчисляемые существительные Внеклассное мероприятие Путешествие в страну Знаний Учитель английского языка Корнилова Наталья Геннадьевна МБОУ «ДСОШ №3»
Внеклассное мероприятие Путешествие в страну Знаний Учитель английского языка Корнилова Наталья Геннадьевна МБОУ «ДСОШ №3»  Cycling Koroleva Dasha сlass 11 School №3
Cycling Koroleva Dasha сlass 11 School №3 Phrasal verbs
Phrasal verbs Презентация к уроку английского языка "В зоопарке на английском" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "В зоопарке на английском" - скачать бесплатно