Содержание
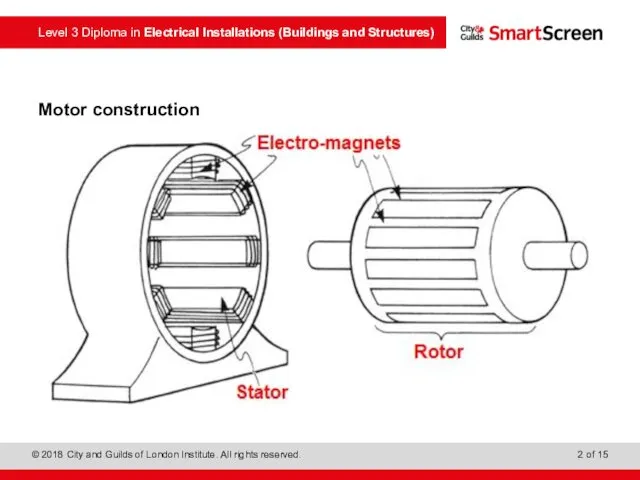
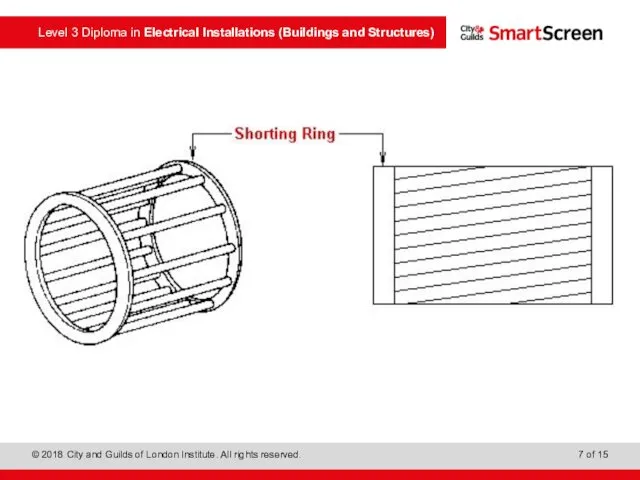
- 2. Motor construction
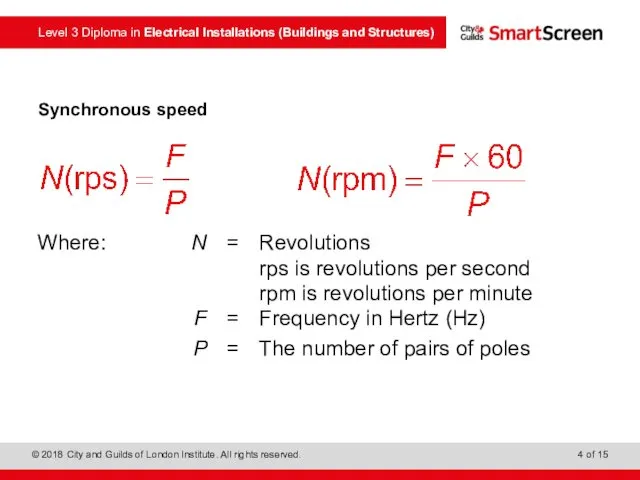
- 4. Synchronous speed
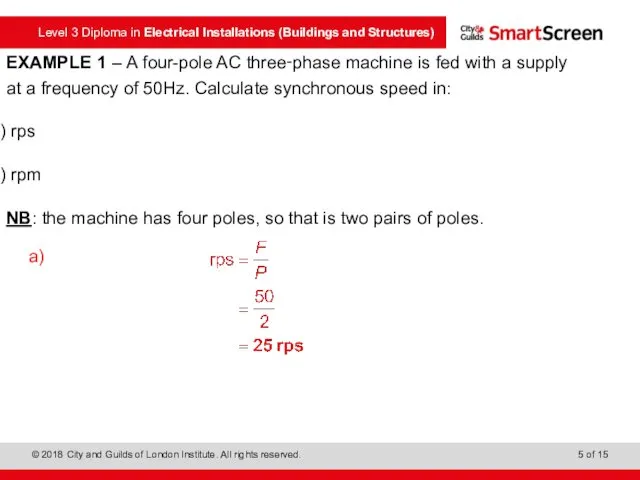
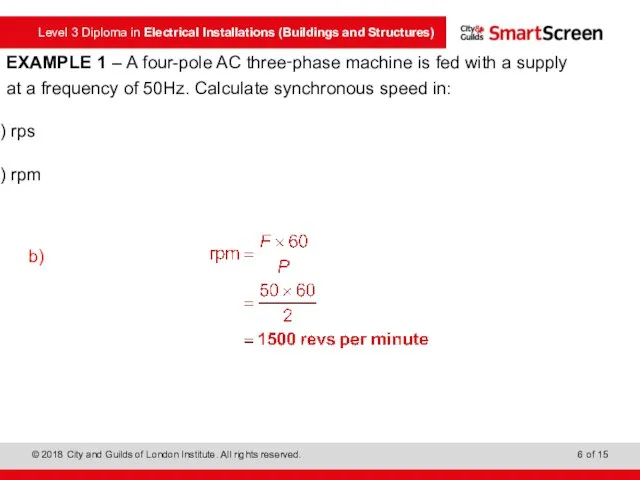
- 5. EXAMPLE 1 – A four-pole AC three‑phase machine is fed with a supply at a frequency
- 6. EXAMPLE 1 – A four-pole AC three‑phase machine is fed with a supply at a frequency
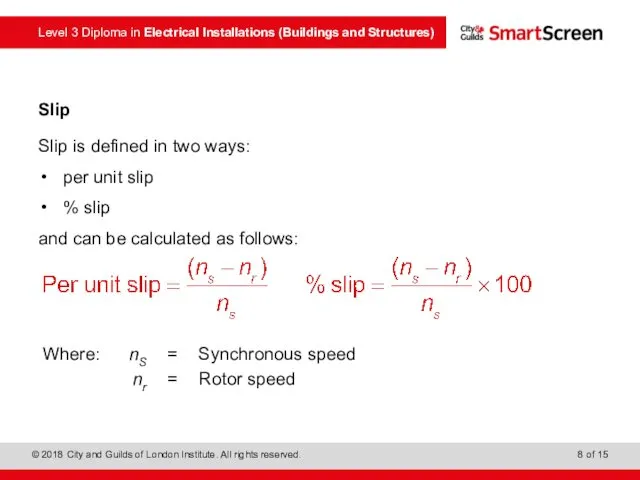
- 8. Slip Slip is defined in two ways: per unit slip % slip and can be calculated
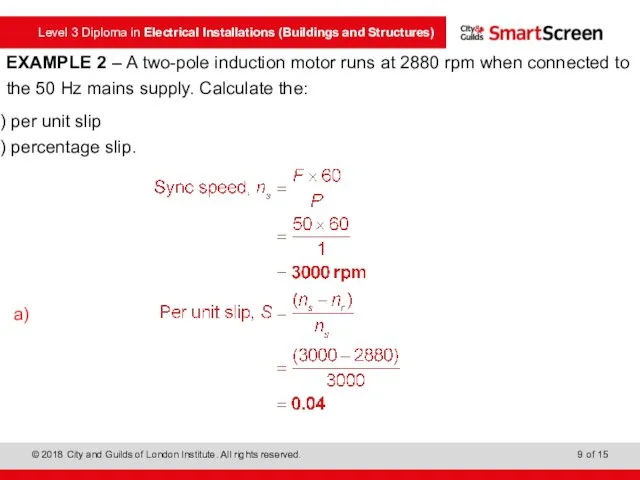
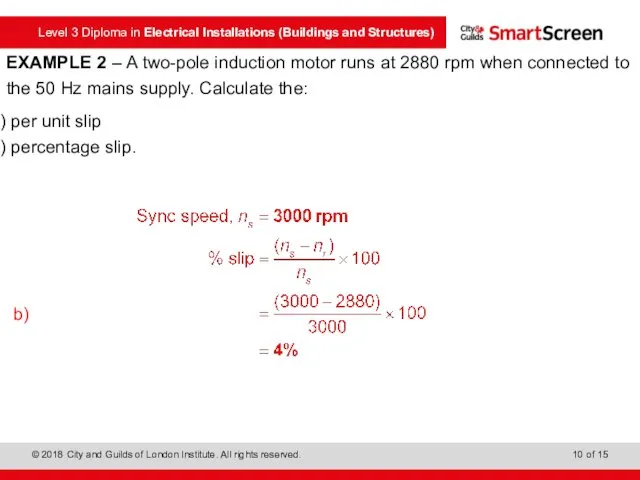
- 9. EXAMPLE 2 – A two-pole induction motor runs at 2880 rpm when connected to the 50
- 10. EXAMPLE 2 – A two-pole induction motor runs at 2880 rpm when connected to the 50
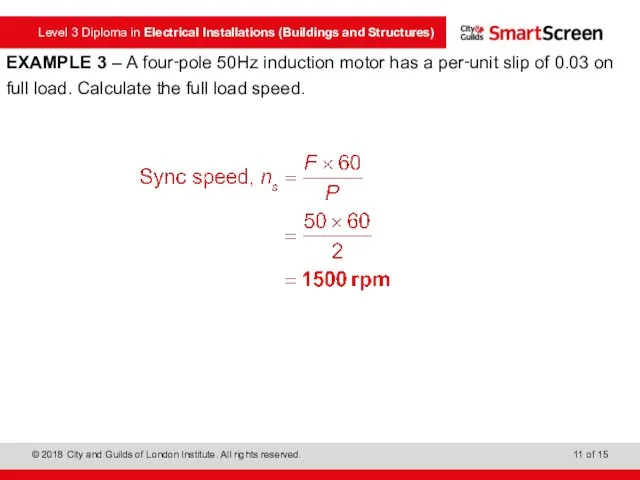
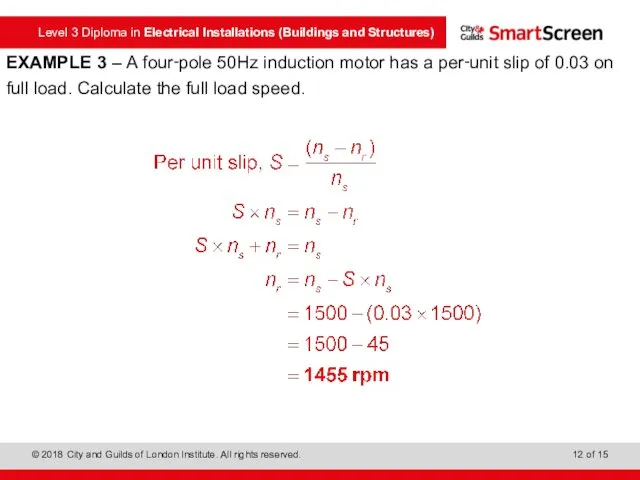
- 11. EXAMPLE 3 – A four‑pole 50Hz induction motor has a per‑unit slip of 0.03 on full
- 12. EXAMPLE 3 – A four‑pole 50Hz induction motor has a per‑unit slip of 0.03 on full
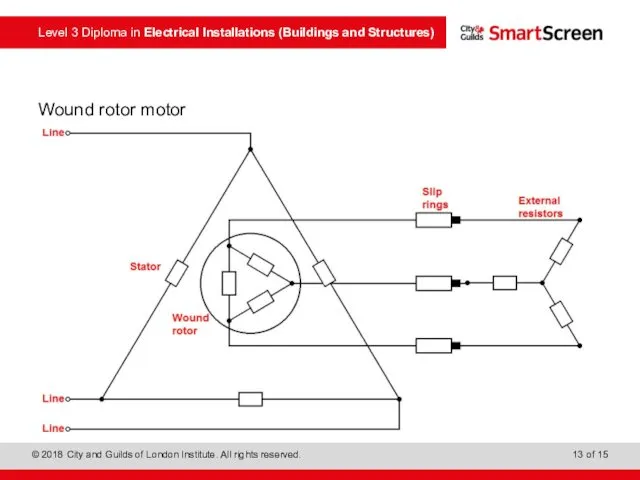
- 13. Wound rotor motor
- 14. AC three phase generator
- 16. Скачать презентацию


 Язык и межкультурная коммуникация. Язык как зеркало культуры
Язык и межкультурная коммуникация. Язык как зеркало культуры Презентация Cristmas: customs and traditions
Презентация Cristmas: customs and traditions Аттестационная работа. Методическая разработка творческой проектной работы В гостях у сказки на английском языке
Аттестационная работа. Методическая разработка творческой проектной работы В гостях у сказки на английском языке My summer
My summer Pets. Classroom
Pets. Classroom Презентация к уроку английского языка "National Days in Britain" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "National Days in Britain" - скачать бесплатно ЕГЭ по английскому языку (вариант 2)
ЕГЭ по английскому языку (вариант 2) Презентация к уроку английского языка "The Civil War and Oliver Cromwell " - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "The Civil War and Oliver Cromwell " - скачать  The dolphin is a cetacean. It is a mammal, but live in seas. Usually they live in herds.
The dolphin is a cetacean. It is a mammal, but live in seas. Usually they live in herds. How to write an essay
How to write an essay Презентация к уроку английского языка "Husky" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Husky" - скачать  Презентация к уроку английского языка "Antarctica / Антарктида (EN)" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Antarctica / Антарктида (EN)" - скачать бесплатно How to make small talk
How to make small talk Презентация к уроку английского языка "Health is the Greatest wealth" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Health is the Greatest wealth" - скачать  Тravels Kazan
Тravels Kazan Конкурс интерактивных презентаций «Интерактивная мозаика» Название сайта: Pedsovet.su Выполнила: Литовченко Елена Вячеславовна Мест
Конкурс интерактивных презентаций «Интерактивная мозаика» Название сайта: Pedsovet.su Выполнила: Литовченко Елена Вячеславовна Мест Мурманский государственный педагогический университет Работа по предмету «Современные технологии преподавания иностранного яз
Мурманский государственный педагогический университет Работа по предмету «Современные технологии преподавания иностранного яз Учитель английского языка Учитель английского языка МБОУ СОШ №2 г.Белореченск Козьменко Л.Н.
Учитель английского языка Учитель английского языка МБОУ СОШ №2 г.Белореченск Козьменко Л.Н. Презентация к уроку английского языка "Areas of London" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Areas of London" - скачать бесплатно School. Урок-повторение лексики
School. Урок-повторение лексики Colours
Colours Teacher of physical culture in public institutions
Teacher of physical culture in public institutions Презентация к уроку английского языка "Hello my friends. I am Jasmine. " - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Hello my friends. I am Jasmine. " - скачать  Relative clauses, clause of purpose
Relative clauses, clause of purpose To be Present Simple
To be Present Simple Amazing creatures
Amazing creatures Презентация к уроку английского языка "Edinburgh (Эдинбург)" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Edinburgh (Эдинбург)" - скачать  London landmarks
London landmarks