Содержание
- 2. Chemistry is a science that studies the properties of substances and how substances react with each
- 3. Who uses chemistry? Many people use chemistry as part of their work. Cooks use chemistry all
- 4. Where do the chemists work? People who have trained as chemists work in hospital laboratories, in
- 5. MATTER and states of matter Matter is anything that has mass and takes up a space.
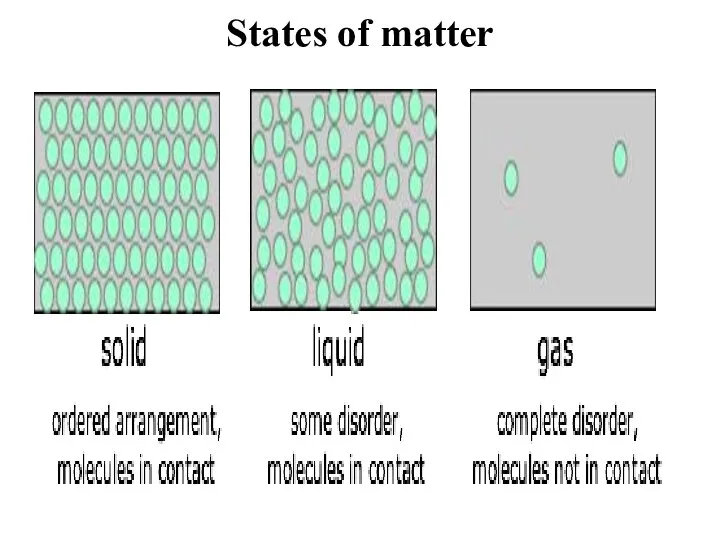
- 6. States of matter Matter exists in three different states: solid, liquid and gas. If the whole
- 7. States of matter
- 8. ‘substances’ Scientist also use the word ‘substances’. This means a particular type of matter, which you
- 9. ELEMENTS An element is one of a group of fundamental substances that cannot be broken down
- 10. Symbolic representations Later on symbols were used because of the difficulty for finding names to excessive
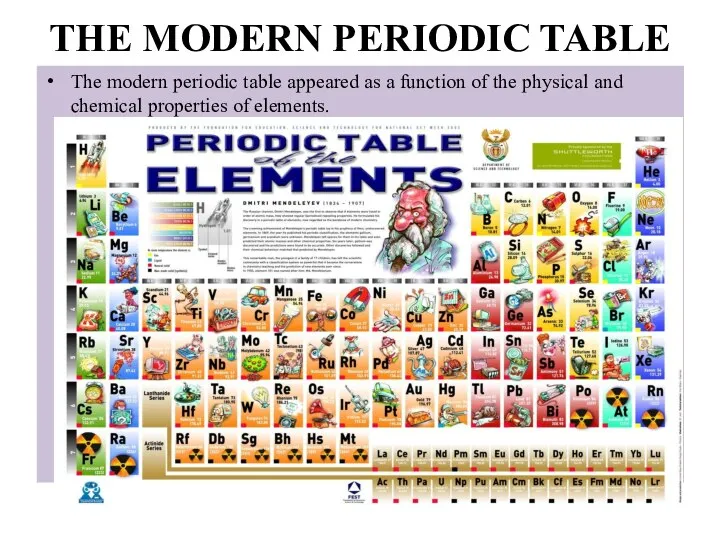
- 11. THE MODERN PERIODIC TABLE The modern periodic table appeared as a function of the physical and
- 12. USAGE OF SOME ELEMENTS Hydrogen: A rocket fuel Production of hydrogen bomb Being the lightest of
- 13. Sodium: Production of electricity in nuclear reactors by transferring excess heat to the vapor turbines Its
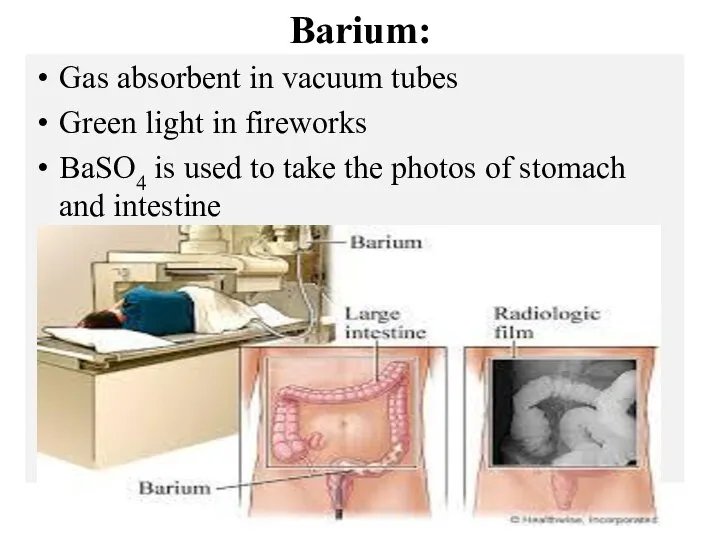
- 14. Barium: Gas absorbent in vacuum tubes Green light in fireworks BaSO4 is used to take the
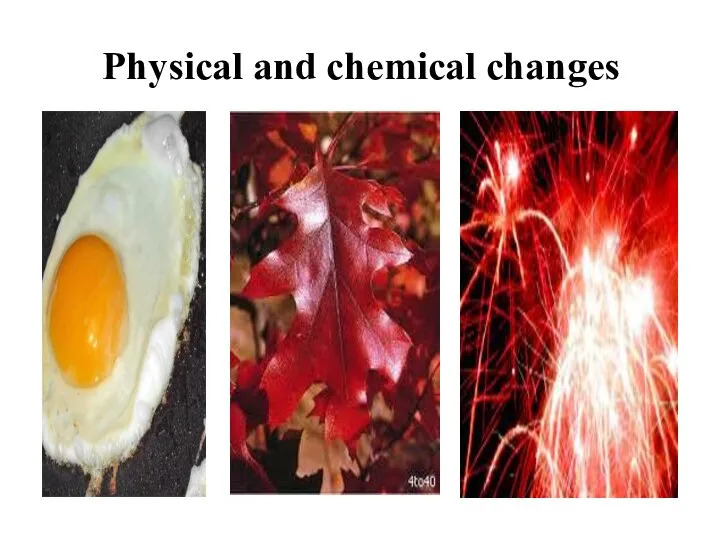
- 15. Physical and chemical changes When we look around, in the world we live, we see some
- 16. Physical and chemical changes
- 17. chemical changes Changes in the molecular structure of substances are called chemical changes. baking of cake
- 18. physical changes Evaporation of water, melting ice, dissolving of sugar in water, powdering marble, breaking of
- 20. Скачать презентацию













 What the weather will be tomorrow
What the weather will be tomorrow Презентация к уроку английского языка "Sand drawing" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Sand drawing" - скачать бесплатно Словарный состав английского языка. (Лекция 3)
Словарный состав английского языка. (Лекция 3) Презентация к уроку английского языка "American Holidays" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "American Holidays" - скачать  Скачать Формы прощания
Скачать Формы прощания Lesson 47 УМК М.З. Биболетовой Enjoy English -3
Lesson 47 УМК М.З. Биболетовой Enjoy English -3 Презентация к уроку английского языка "Chloroplast evolution" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Chloroplast evolution" - скачать бесплатно Management styles
Management styles Visit to Britain
Visit to Britain My family duties
My family duties Little Red Riding Hood
Little Red Riding Hood Великобритания
Великобритания Subjunctive mood Сослагательное наклонение
Subjunctive mood Сослагательное наклонение Plans for the weekend
Plans for the weekend  Smoking. Drugs. Alcohol. Проблемы молодежи
Smoking. Drugs. Alcohol. Проблемы молодежи  My Home
My Home Significant events and famous people of Ireland
Significant events and famous people of Ireland  Учитель английского языка Халоша Лидия Николаевна
Учитель английского языка Халоша Лидия Николаевна  Презентация к уроку английского языка "American inventors" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "American inventors" - скачать бесплатно Презентация к уроку английского языка "Scouting in the World / Скаутинг в мире" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Scouting in the World / Скаутинг в мире" - скачать бесплатно Project
Project Kilt in different countries
Kilt in different countries Презентация Англицизмы в русском языке
Презентация Англицизмы в русском языке Эссе на основе таблиц и диаграмм
Эссе на основе таблиц и диаграмм Презентация к уроку английского языка "Различия в слогоделении в английском и русском" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Различия в слогоделении в английском и русском" - скачать бесплатно Настоящее длительное время
Настоящее длительное время The singular and plural (el singular y el plural)
The singular and plural (el singular y el plural) Неопределенные местоимения. 5 класс
Неопределенные местоимения. 5 класс