Содержание
- 2. The immune system consist of two interconnected arms Innate immunity Detect molecular components shared with all
- 3. Innate immunity
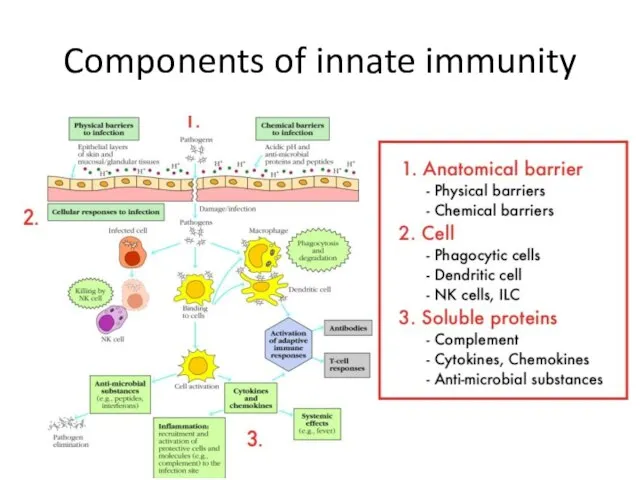
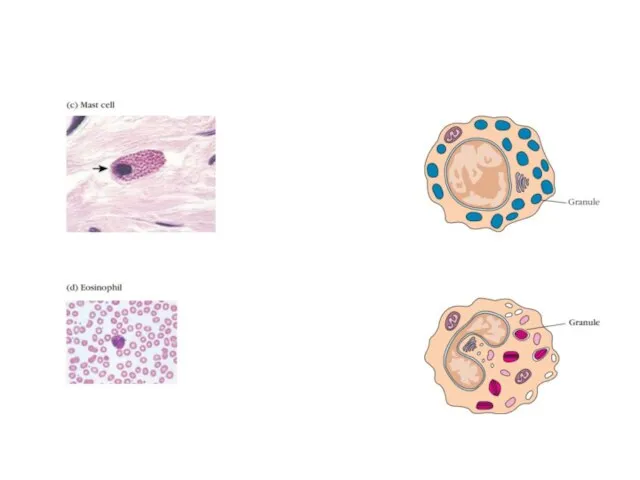
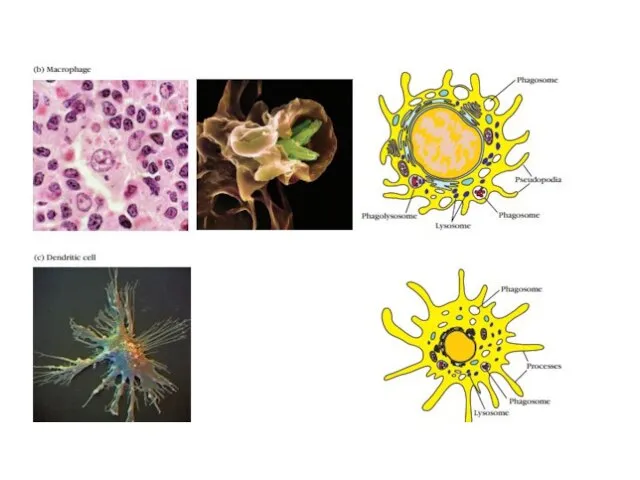
- 4. Components of innate immunity
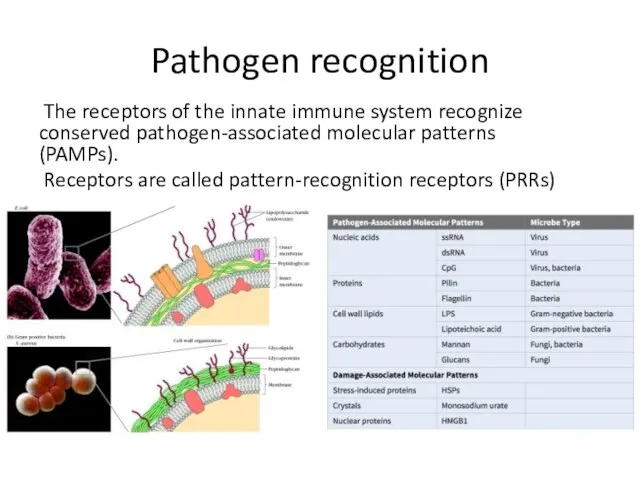
- 8. Pathogen recognition The receptors of the innate immune system recognize conserved pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). Receptors
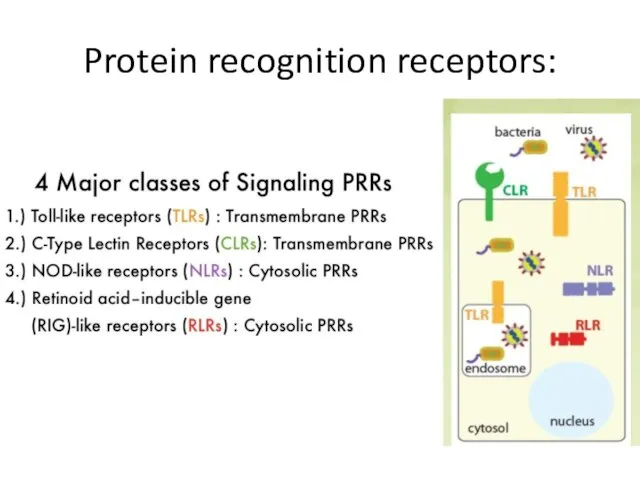
- 9. Protein recognition receptors:
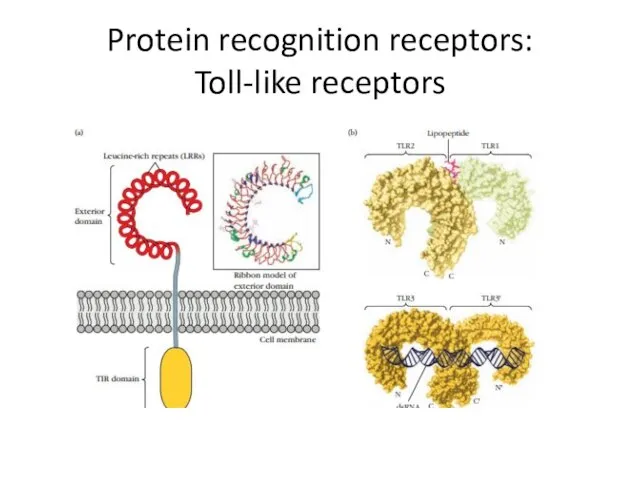
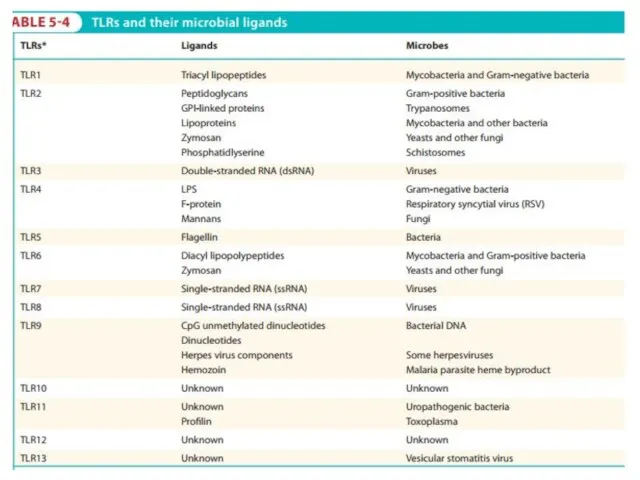
- 10. Protein recognition receptors: Toll-like receptors
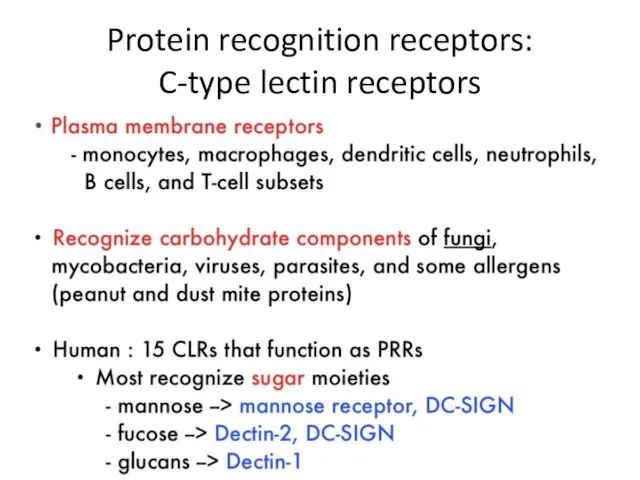
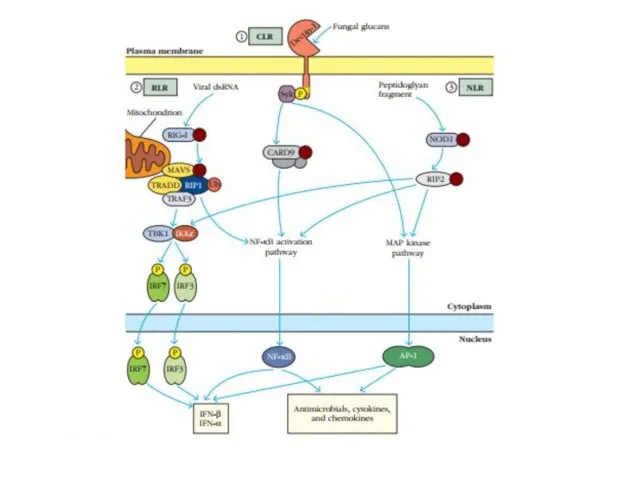
- 12. Protein recognition receptors: C-type lectin receptors
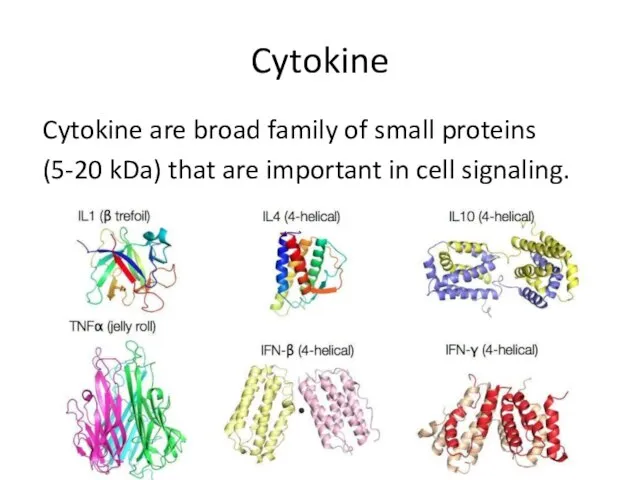
- 14. Cytokine Cytokine are broad family of small proteins (5-20 kDa) that are important in cell signaling.
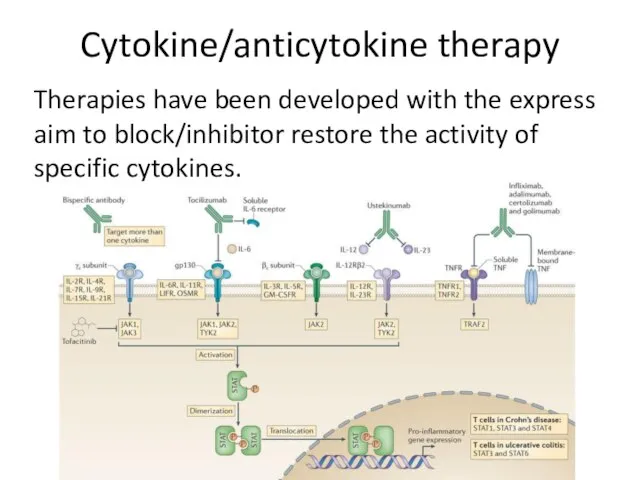
- 17. Cytokine/anticytokine therapy Therapies have been developed with the express aim to block/inhibitor restore the activity of
- 18. Adaptive immune system
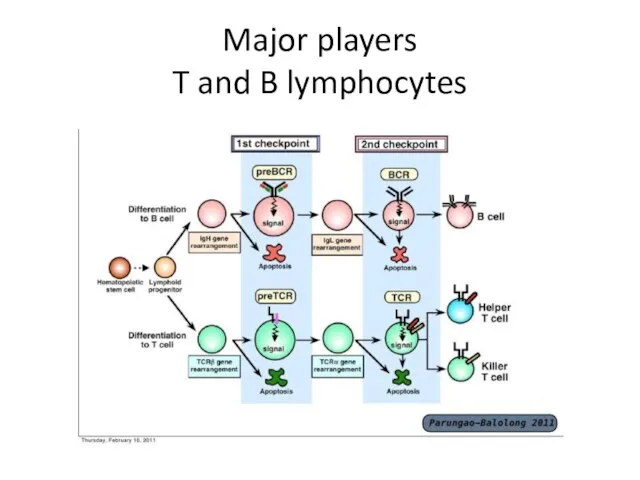
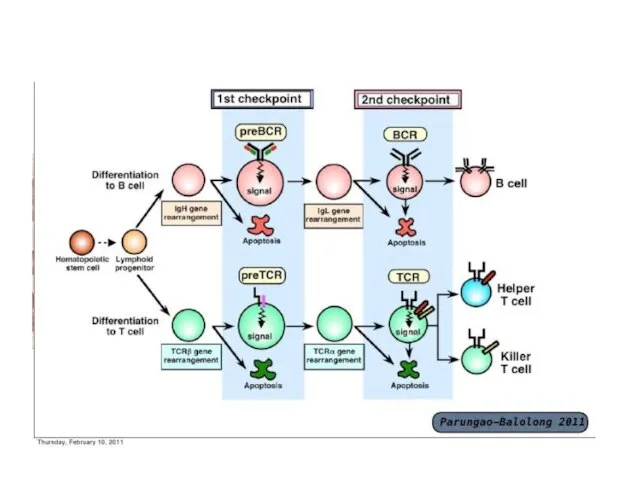
- 19. Major players T and B lymphocytes
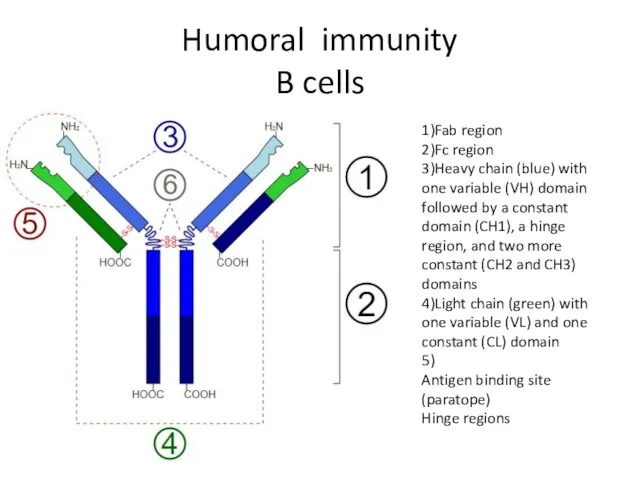
- 22. Humoral immunity B cells 1)Fab region 2)Fc region 3)Heavy chain (blue) with one variable (VH) domain
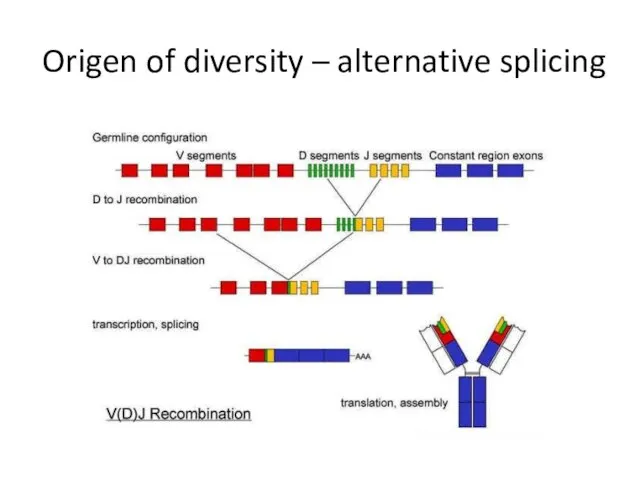
- 23. Origen of diversity – alternative splicing
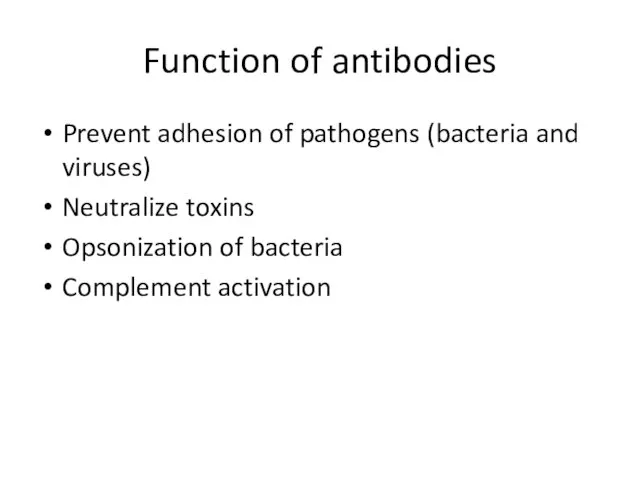
- 25. Function of antibodies Prevent adhesion of pathogens (bacteria and viruses) Neutralize toxins Opsonization of bacteria Complement
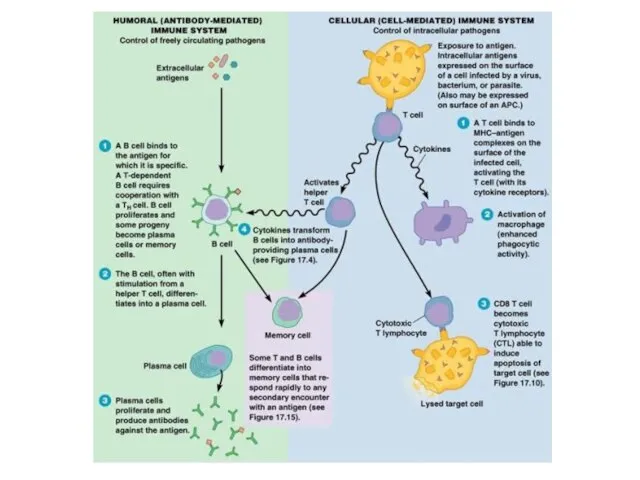
- 26. Adaptive immune system Cellular immunity
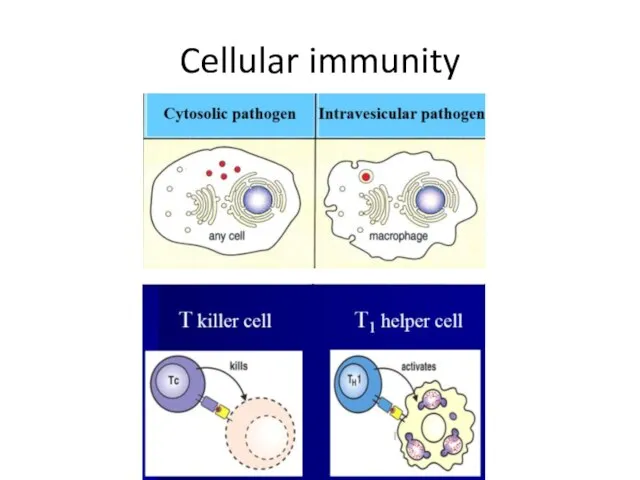
- 27. Cellular immunity
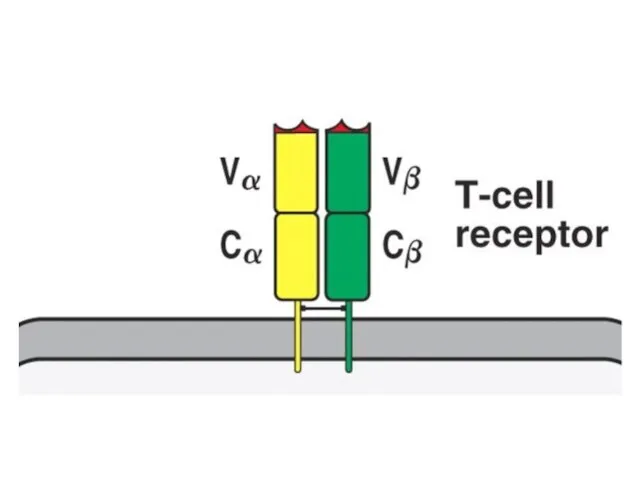
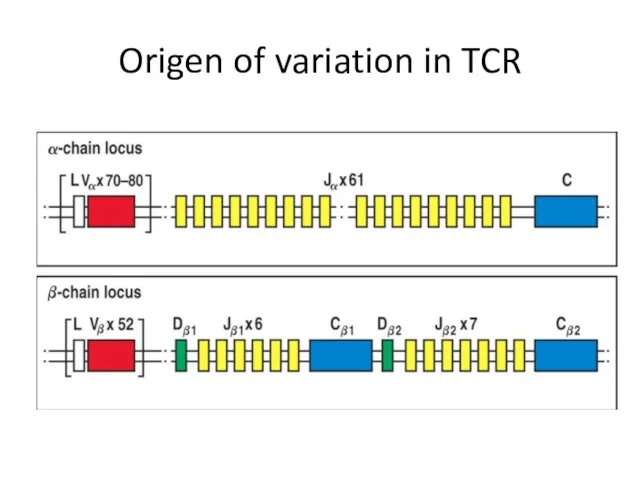
- 29. Origen of variation in TCR
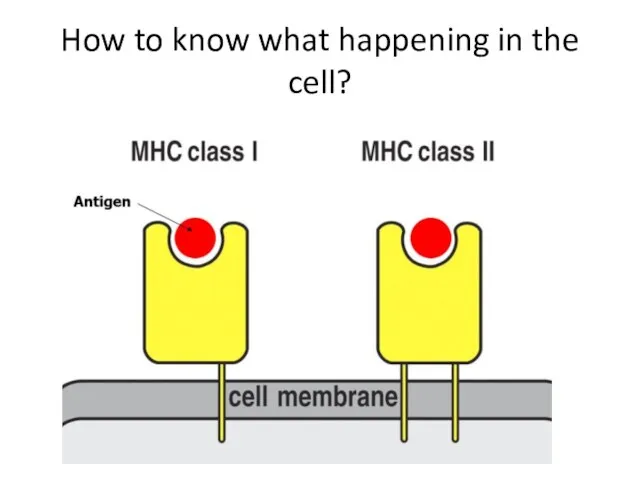
- 30. How to know what happening in the cell?
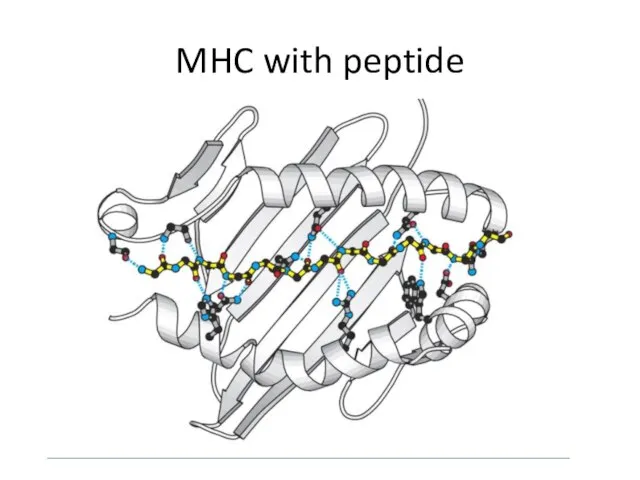
- 31. MHC with peptide
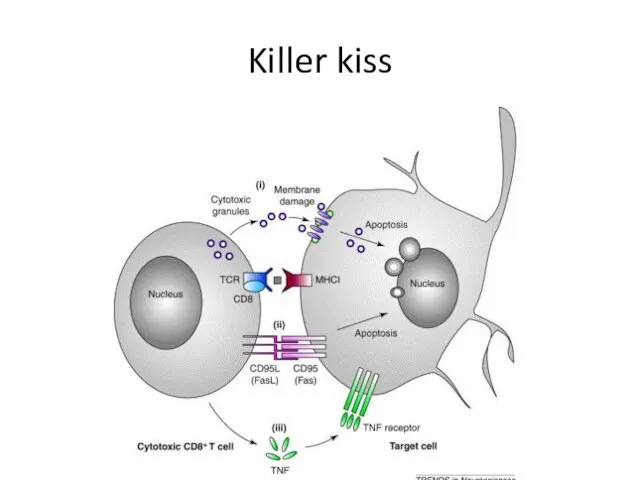
- 32. Killer kiss
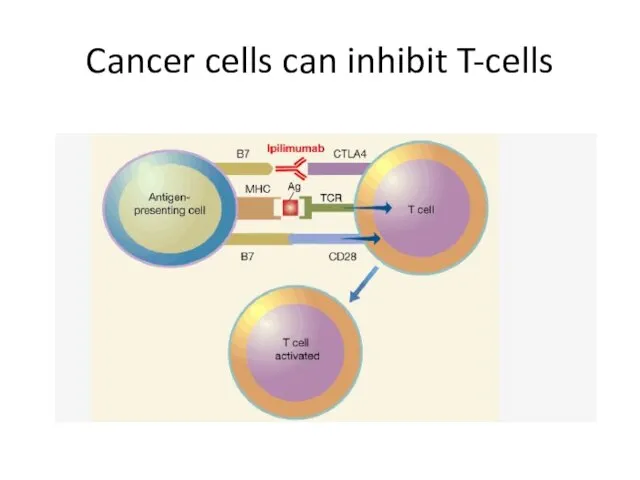
- 33. Cancer cells can inhibit T-cells
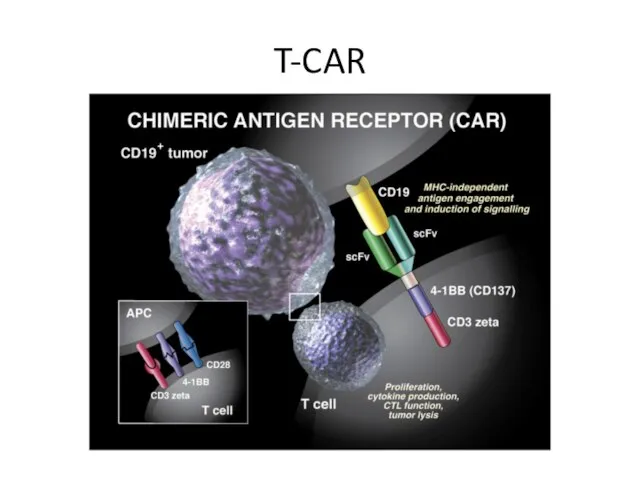
- 34. T-CAR
- 36. Скачать презентацию







 Введение в обмен веществ
Введение в обмен веществ БЕЛКИ, ИХ СТРОЕНИЕ,СВОЙСТВА, БИОЛОГИЧЕСКИЕ ФУНКЦИИ (УРОК-ПРАКТИКУМ) Балыбина Светлана Николаевна учитель химии и биологии МБОУ С
БЕЛКИ, ИХ СТРОЕНИЕ,СВОЙСТВА, БИОЛОГИЧЕСКИЕ ФУНКЦИИ (УРОК-ПРАКТИКУМ) Балыбина Светлана Николаевна учитель химии и биологии МБОУ С Көбею. Жынысты және жыныссыз көбеюдің түрлері
Көбею. Жынысты және жыныссыз көбеюдің түрлері Тема проекта: «Летят перелётные птицы»
Тема проекта: «Летят перелётные птицы» Как сохранить зубы здоровыми?
Как сохранить зубы здоровыми? Регуляция активности ферментов. Множественные формы ферментов. Введение в клиническую энзимологию. (Лекция 7)
Регуляция активности ферментов. Множественные формы ферментов. Введение в клиническую энзимологию. (Лекция 7) Семейство Пасленовые
Семейство Пасленовые Микроэлементы в организме человека
Микроэлементы в организме человека Морфология бактерий. Методы окраски. Занятие 1
Морфология бактерий. Методы окраски. Занятие 1 Презентация на тему "Сожительство растений с грибами и бактериями" - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Сожительство растений с грибами и бактериями" - скачать презентации по Биологии Физиология мозгового ствола. Продолговатый и средний мозг. Мозжечок
Физиология мозгового ствола. Продолговатый и средний мозг. Мозжечок Предмет и задачи медицинской микробиологии и иммунологии
Предмет и задачи медицинской микробиологии и иммунологии Радиоактивность
Радиоактивность Презентация на тему "Биоритмы человека" - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Биоритмы человека" - скачать презентации по Биологии Пресмыкающиеся, или Рептилии (Reptilia)
Пресмыкающиеся, или Рептилии (Reptilia) Черепно-мозговые нервы
Черепно-мозговые нервы Шиншилла домашний питомец
Шиншилла домашний питомец Примитивные организмы
Примитивные организмы Учитель биологии: Галковская И.И. 8 класс
Учитель биологии: Галковская И.И. 8 класс  Презентация на тему "Грибная поляна" - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Грибная поляна" - скачать презентации по Биологии Сон і цікаві факти про нього
Сон і цікаві факти про нього  Криоконсервация – контролируемая пауза в развитии
Криоконсервация – контролируемая пауза в развитии Клеточная инженерия
Клеточная инженерия Палеодемографические исследования паразитарных заболеваний человека
Палеодемографические исследования паразитарных заболеваний человека Нейрофизиологические основы памяти и обучения
Нейрофизиологические основы памяти и обучения Задачи: Изучить особенности строения, функции и гигиену кожи
Задачи: Изучить особенности строения, функции и гигиену кожи Сцепленное задачи
Сцепленное задачи Изучение природы
Изучение природы