Содержание
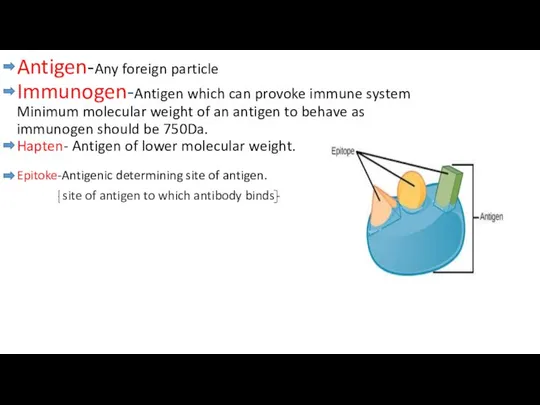
- 2. Antigen-Any foreign particle Immunogen-Antigen which can provoke immune system Minimum molecular weight of an antigen to
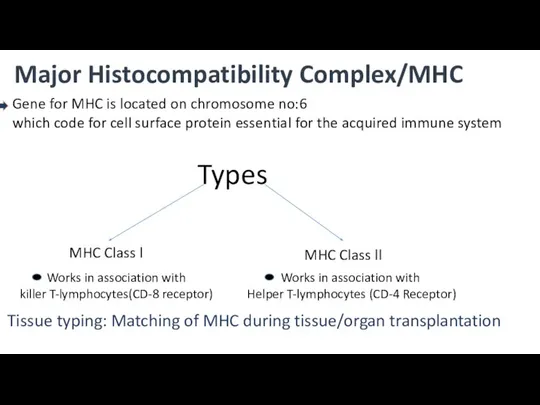
- 3. Major Histocompatibility Complex/MHC Gene for MHC is located on chromosome no:6 which code for cell surface
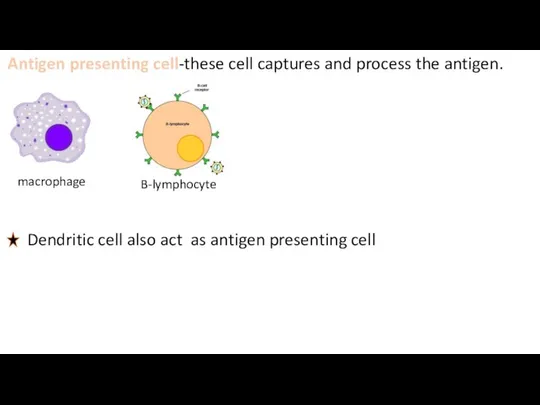
- 4. Antigen presenting cell-these cell captures and process the antigen. macrophage B-lymphocyte Dendritic cell also act as
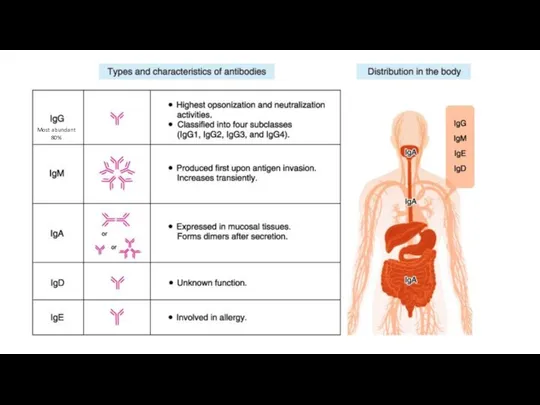
- 7. Most abundant 80%
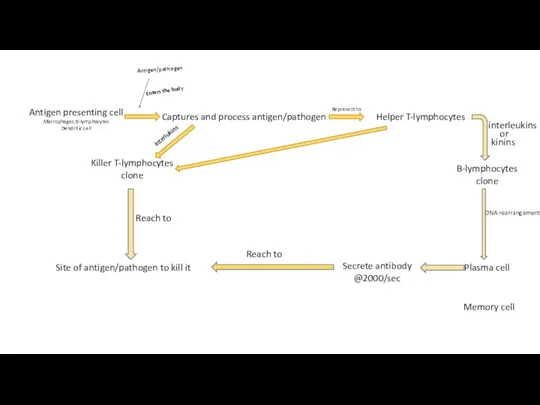
- 8. Antigen presenting cell Macrophages,B-lymphocytes Dendritic cell Antigen/pathogen Enters the body Captures and process antigen/pathogen Represent to
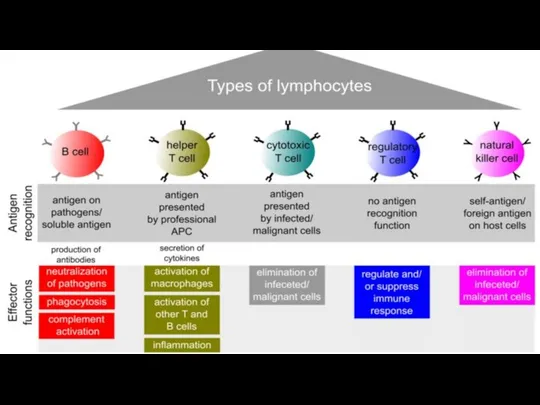
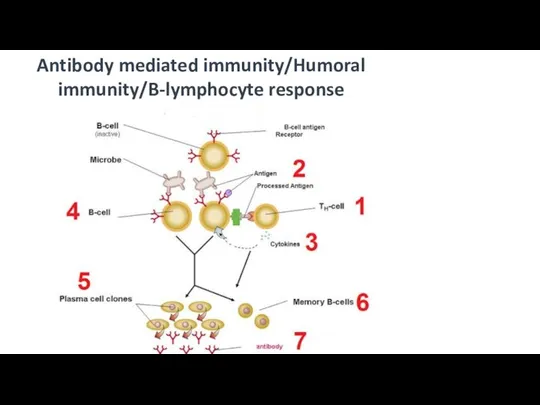
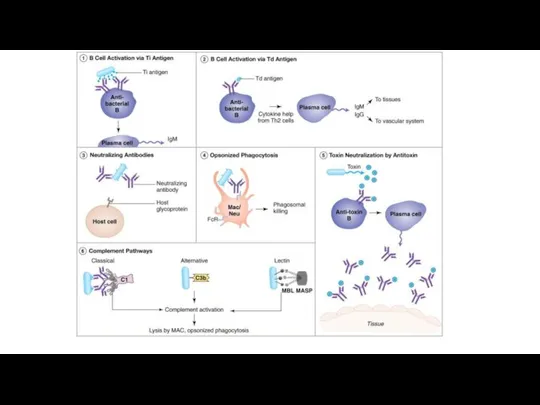
- 9. Antibody mediated immunity/Humoral immunity/B-lymphocyte response
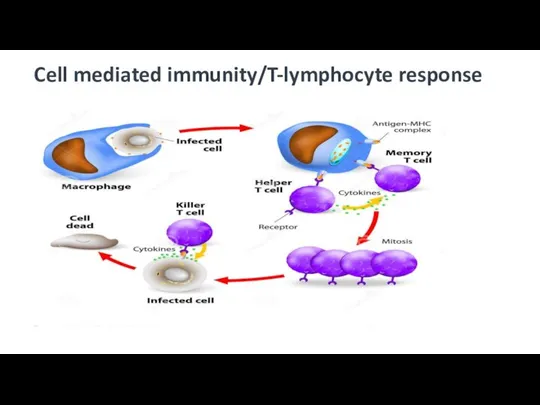
- 10. Cell mediated immunity/T-lymphocyte response
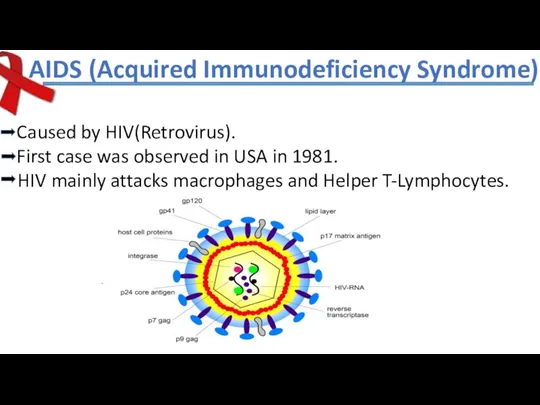
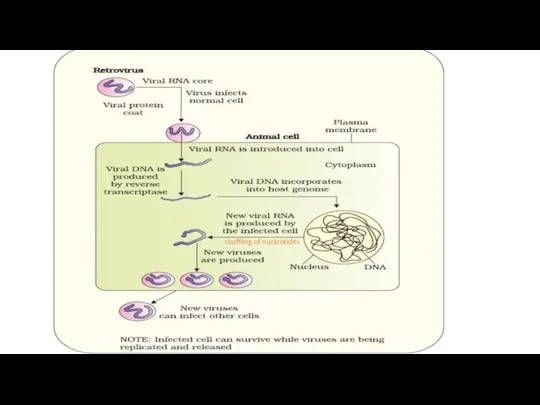
- 12. AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) Caused by HIV(Retrovirus). First case was observed in USA in 1981. HIV
- 13. shuffling of nucleotides
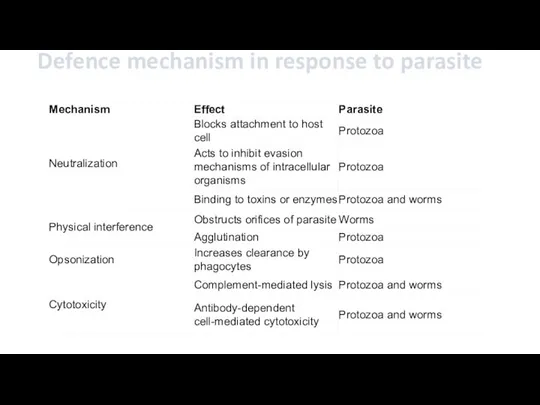
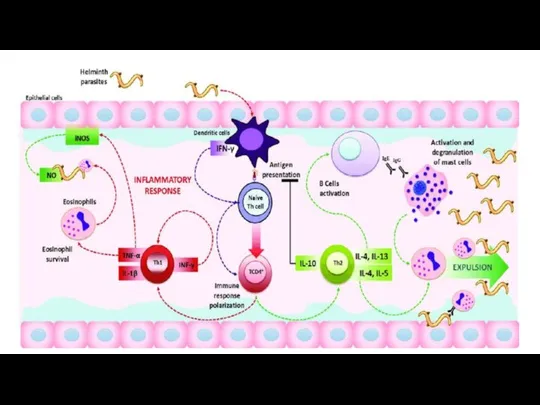
- 15. Defence mechanism in response to parasite
- 17. Protozoa activate quite distinct specific immune responses, which are different from the responses to fungi, bacteria
- 18. IMMUNE EVASION MECHANISMS OF PROTOZOA: Different protozoa have developed remarkably effective ways of resisting specific immunity:
- 19. T cells are essential for providing complete protection against T. gondii, which is confirmed by the
- 23. Скачать презентацию







 Строение мышц. Биология, 8 класс
Строение мышц. Биология, 8 класс Рёбра. Анатомия грудной клетки
Рёбра. Анатомия грудной клетки Международный день птиц
Международный день птиц Ряд Соколоподібні Птахи, занесені до Червоної книги України
Ряд Соколоподібні Птахи, занесені до Червоної книги України Молекулярная биология изучает механизмы хранения и передачи наследственной информации. Задачи по молекулярной биол
Молекулярная биология изучает механизмы хранения и передачи наследственной информации. Задачи по молекулярной биол «Вода, у тебя нет ни вкуса, ни цвета, ни запаха, тобой наслаждаются, не ведая, что ты такое. Нельзя сказать, что необходима для жизни; ты - сама жизнь…» (Антуан де Сент-Экзюпери
«Вода, у тебя нет ни вкуса, ни цвета, ни запаха, тобой наслаждаются, не ведая, что ты такое. Нельзя сказать, что необходима для жизни; ты - сама жизнь…» (Антуан де Сент-Экзюпери Какие бывают растения
Какие бывают растения Кожа. Дерматология как наука
Кожа. Дерматология как наука Нейруляция и дифференцировка нейроэктодермы
Нейруляция и дифференцировка нейроэктодермы ЧТО? ГДЕ? КОГДА? «Занимательная биология и химия»
ЧТО? ГДЕ? КОГДА? «Занимательная биология и химия»  Атеросклероз – распространённое хроническое заболевание артерий эластического и мышечно-эластического типа (крупного и среднег
Атеросклероз – распространённое хроническое заболевание артерий эластического и мышечно-эластического типа (крупного и среднег Белка-летяга
Белка-летяга Общая характеристика класса Млекопитающие
Общая характеристика класса Млекопитающие МОУ «Куровская средняя общеобразовательная школа № 6» МОУ «Куровская средняя общеобразовательная школа № 6» Р
МОУ «Куровская средняя общеобразовательная школа № 6» МОУ «Куровская средняя общеобразовательная школа № 6» Р Самое интересное о жуках
Самое интересное о жуках Догляд за кімнатними рослинами
Догляд за кімнатними рослинами Структуры и функции биополимеров (ДНК, РНК, белки) Введение в молекулярную биологию (как часть введения в биоинформатику) БиБ
Структуры и функции биополимеров (ДНК, РНК, белки) Введение в молекулярную биологию (как часть введения в биоинформатику) БиБ Витамины и их значение
Витамины и их значение Көмірсулар
Көмірсулар КИШЕЧНОПОЛОСТНЫЕ
КИШЕЧНОПОЛОСТНЫЕ  Закон гомологических рядов в наследственной изменчивости. (11 класс)
Закон гомологических рядов в наследственной изменчивости. (11 класс) Растения - реликты Крыма
Растения - реликты Крыма Презентация на тему Зелёная аптека
Презентация на тему Зелёная аптека Деление клетки. Митоз и мейоз
Деление клетки. Митоз и мейоз Полость рта. (Cavitas oris)
Полость рта. (Cavitas oris) Животные - ОБИТАТЕЛИ ЖИЛИЩА ЧЕЛОВЕКА.
Животные - ОБИТАТЕЛИ ЖИЛИЩА ЧЕЛОВЕКА. Доказательства эволюционного происхождения человека
Доказательства эволюционного происхождения человека Селекция зеброида
Селекция зеброида