Содержание
- 2. The evidence for evolution
- 3. learning Objective analyze the evidence for evolution
- 4. Success criteria 1. Name at least three examples which are evolution evidences and comment two examples
- 5. Terminology Microevolution, macroevolution, population, fossil record, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, comparative biochemistry, molecular embryology, biogeography, homologous
- 6. Evolution … In biology, evolution is the change in the characteristics of a species over several
- 7. What is natural selection? Individuals with characteristics best suited to their environment are more likely to
- 8. Natural selection in action: the Peppered moth
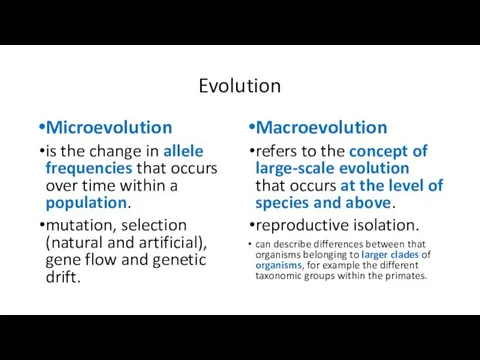
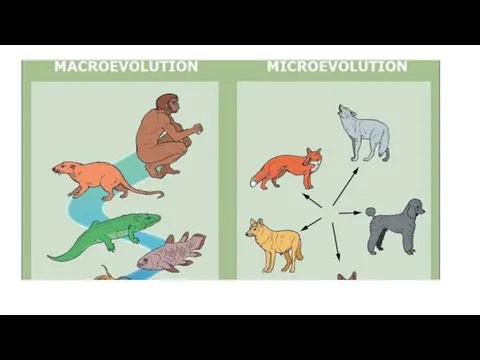
- 9. Evolution Microevolution is the change in allele frequencies that occurs over time within a population. mutation,
- 11. Evidence of Evolution fossil record, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, comparative biochemistry, molecular biology, biogeography
- 14. Fossil record The fossil reveals the existence of species that have become extinct or have evolved
- 15. Fossil record -Transitional fossils
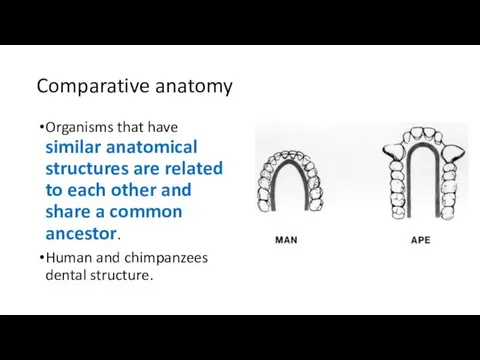
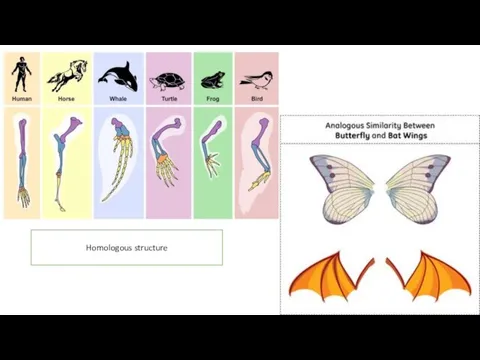
- 16. Comparative anatomy Organisms that have similar anatomical structures are related to each other and share a
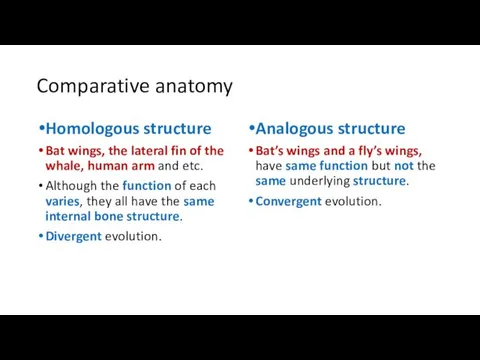
- 17. Comparative anatomy Homologous structure Bat wings, the lateral fin of the whale, human arm and etc.
- 18. Homologous structure
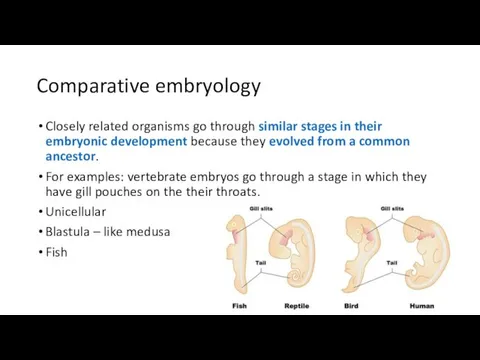
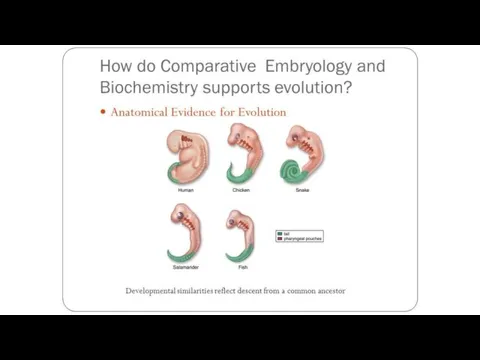
- 19. Comparative embryology Closely related organisms go through similar stages in their embryonic development because they evolved
- 21. Molecular biology (DNA, protein and enzyme system) Since all aerobic organisms contain cells that carry out
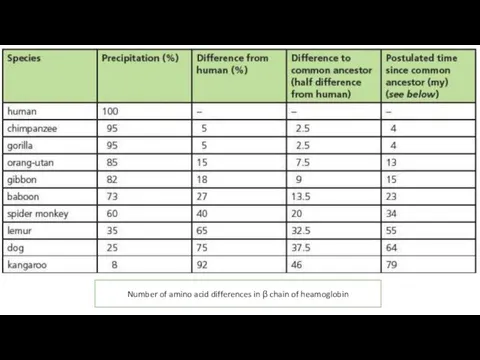
- 22. Number of amino acid differences in β chain of heamoglobin
- 23. Comparative biochemistry Organisms that have a common ancestor will have common biochemical pathway. The more closely
- 24. Biogeography The theory of continental drift (Pangaea). Supercontinent Pangaea slowly separated into 7 continents. Isolation (most
- 26. Скачать презентацию














 Северный олень. 8 класс
Северный олень. 8 класс Биоритмы и сновидения
Биоритмы и сновидения Методы лучевого исследования опорно-двигательной системы. Рентгеноанатомия костей и суставов
Методы лучевого исследования опорно-двигательной системы. Рентгеноанатомия костей и суставов Разнообразие животных.
Разнообразие животных. Животные смешанных и лиственных лесов. Заповедники
Животные смешанных и лиственных лесов. Заповедники Презентация на тему Новые виды
Презентация на тему Новые виды
 Презентация на тему ХИМИЧЕСКИЙ СОСТАВ РАСТЕНИЙ Презентация по биологии 6 класс
Презентация на тему ХИМИЧЕСКИЙ СОСТАВ РАСТЕНИЙ Презентация по биологии 6 класс Ко- агглютинация и латекс -агглютинация
Ко- агглютинация и латекс -агглютинация Тема урока: «Бесполое и половое размножение организмов»
Тема урока: «Бесполое и половое размножение организмов» Электрический ток
Электрический ток Сухие плоды. Семена
Сухие плоды. Семена ЭМ биологических ресурсов Основные понятия ЭМ растительных ресурсов ЭМ животных ресурсов
ЭМ биологических ресурсов Основные понятия ЭМ растительных ресурсов ЭМ животных ресурсов Вещества клетки. Неорганические. Органические
Вещества клетки. Неорганические. Органические Самые удивительные растения мира Растительный мир очень красив и многообразен. Сегодня существует около 360.000 различных видов
Самые удивительные растения мира Растительный мир очень красив и многообразен. Сегодня существует около 360.000 различных видов  Живая и неживая природа. Растения
Живая и неживая природа. Растения Головной мозг
Головной мозг Современные биобанки
Современные биобанки Веселые синички
Веселые синички Еволюція екосистем
Еволюція екосистем Презентация на тему "Молочнокислые бактерии" - скачать бесплатно презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Молочнокислые бактерии" - скачать бесплатно презентации по Биологии Биологические задачи
Биологические задачи Аптека на подоконнике
Аптека на подоконнике Презентация на тему "Биологический аукцион «Простейшие»" - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Биологический аукцион «Простейшие»" - скачать презентации по Биологии Строение клетки
Строение клетки Тип кишечнополостные
Тип кишечнополостные Генетически модифицированные организмы - презентация_
Генетически модифицированные организмы - презентация_ Як змінюється життя комах і риб восени?
Як змінюється життя комах і риб восени?