Содержание
- 2. A problem AUA average power consumption rate is: 75 kW. Large Auditorium Lighting ONLY takes: 120
- 3. Solution Answer: 75 kW? 120 kW? 195 kW? Or? Answer: Solve an optimization problem.
- 4. Capacity & Demand Investment is needed to add the physical Stock of Capital. Capital Stock =
- 5. Capacity & Demand Power shortage means: Peak demand > Installed capacity Energy shortage means: Not enough
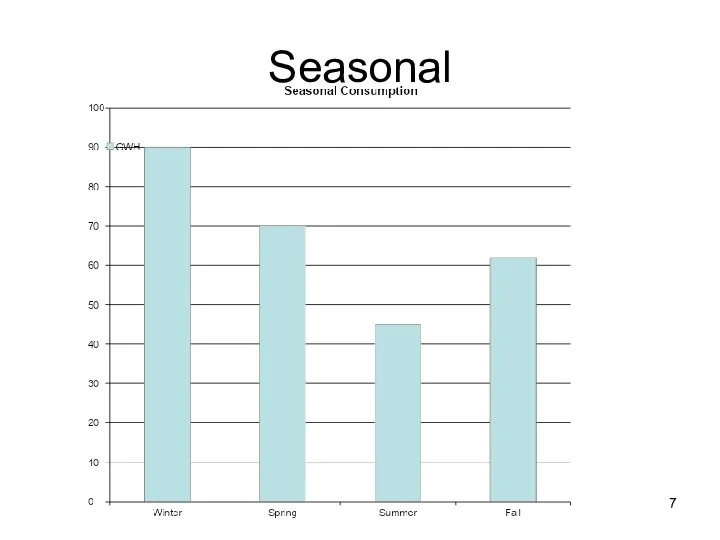
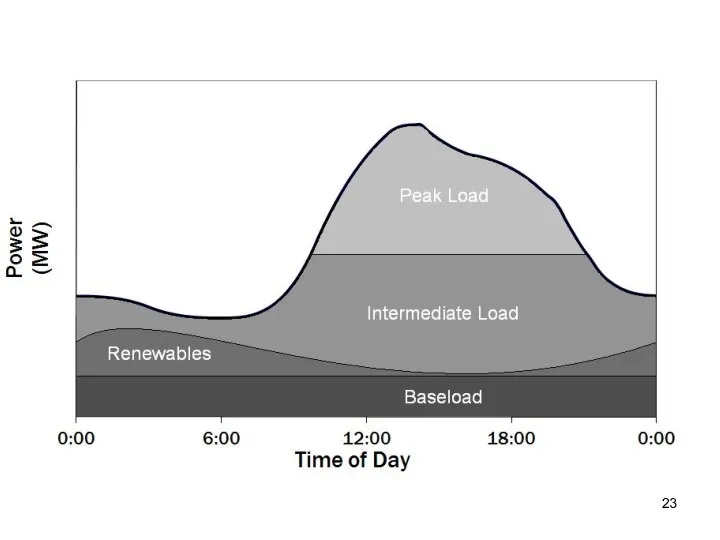
- 6. Load curves Electric power demand = load Load curves, regular (periodic): Daily Weekly Seasonal Per shift,
- 7. Seasonal
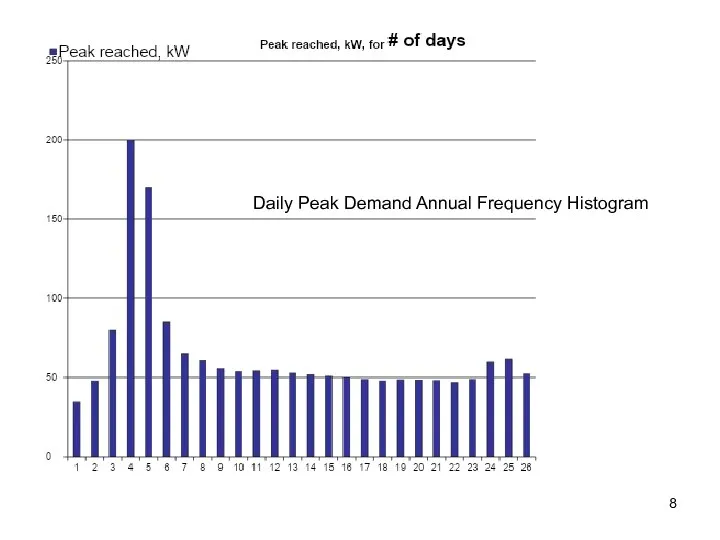
- 8. Daily Peak Demand Annual Frequency Histogram
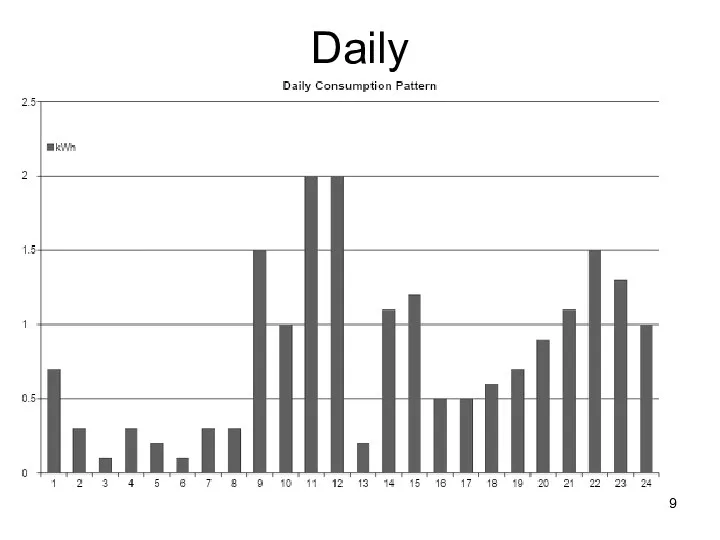
- 9. Daily
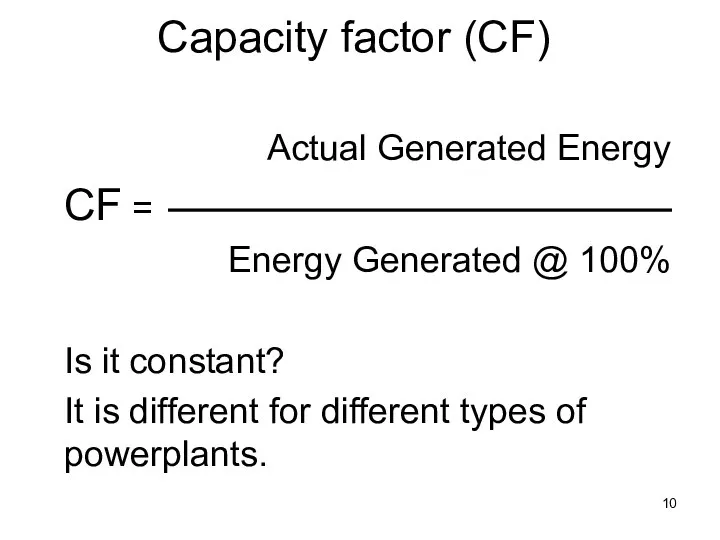
- 10. Capacity factor (CF) Actual Generated Energy CF = Energy Generated @ 100% Is it constant? It
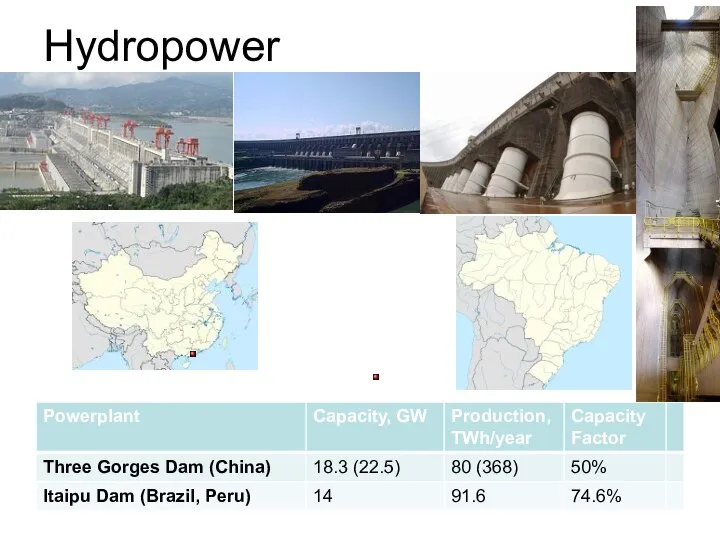
- 11. Hydropower
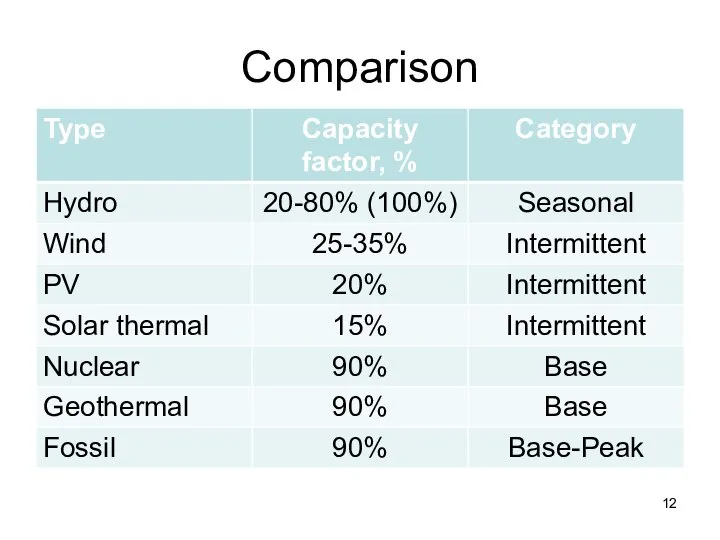
- 12. Comparison
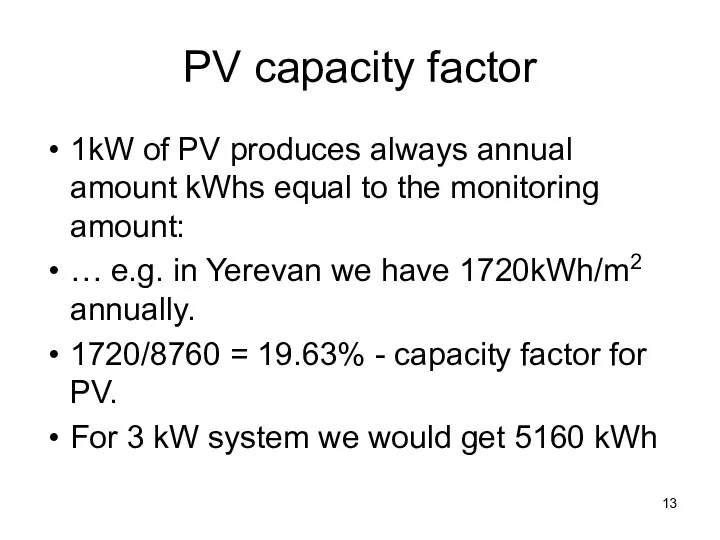
- 13. PV capacity factor 1kW of PV produces always annual amount kWhs equal to the monitoring amount:
- 14. Energy Shortage: Two Approaches Construction of new capacities - supply side. Conservation, Load leveling – demand
- 15. Peak vs. Average vs. Base AUA peak is: 75 kW? 120 kW? 195 kW? Or? Average
- 16. Countrywise Peak Average Base
- 17. Peak All powerplants, all generation capacities are operating. We are going to extreme measures: ALLOWING TO
- 18. Base Consumption never goes below certain amount Metsamor NPP is providing the base power.
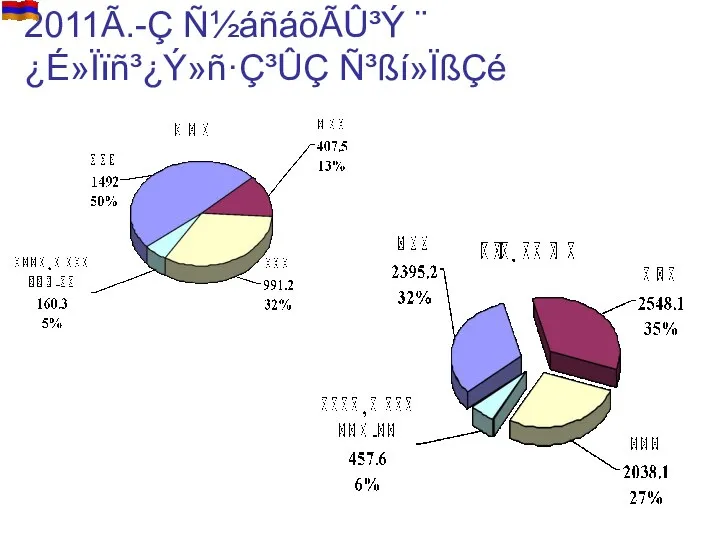
- 20. 2011Ã.-Ç Ñ½áñáõÃÛ³Ý ¨ ¿É»Ïïñ³¿Ý»ñ·Ç³ÛÇ Ñ³ßí»ÏßÇé
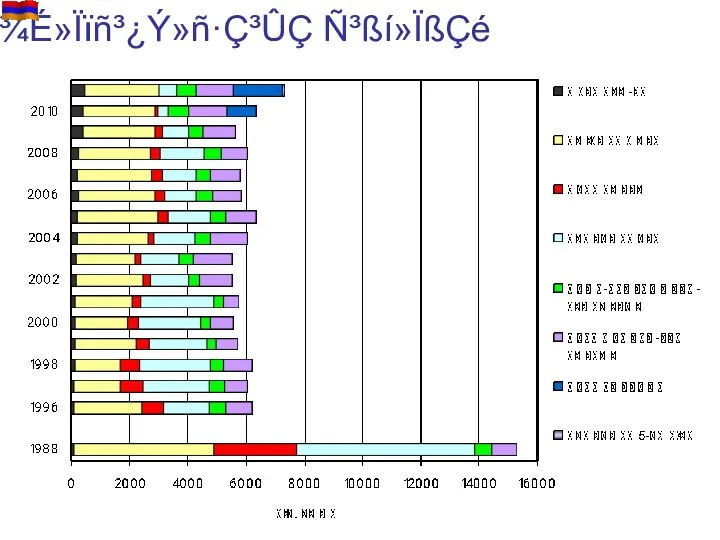
- 21. ¾É»Ïïñ³¿Ý»ñ·Ç³ÛÇ Ñ³ßí»ÏßÇé
- 22. Average is in Between! Thus one needs: BASE, stabile, powerplants, e.g. Nuclear, Coal. CF > 90%;
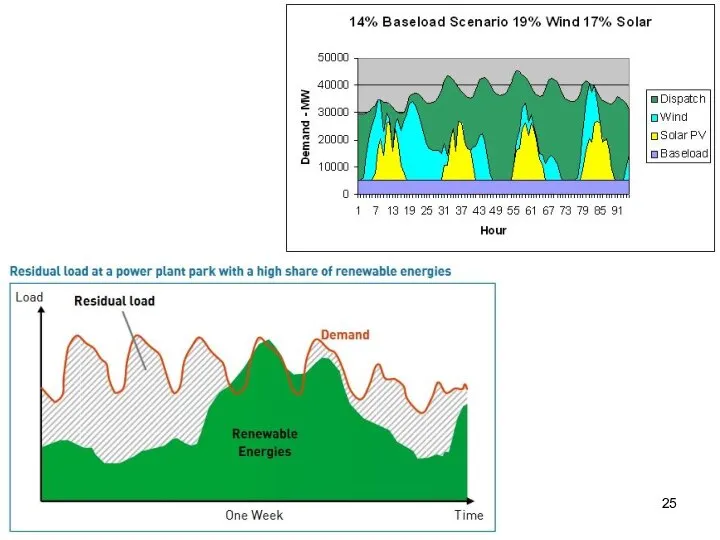
- 24. Renewable Wind (CF Solar (CF
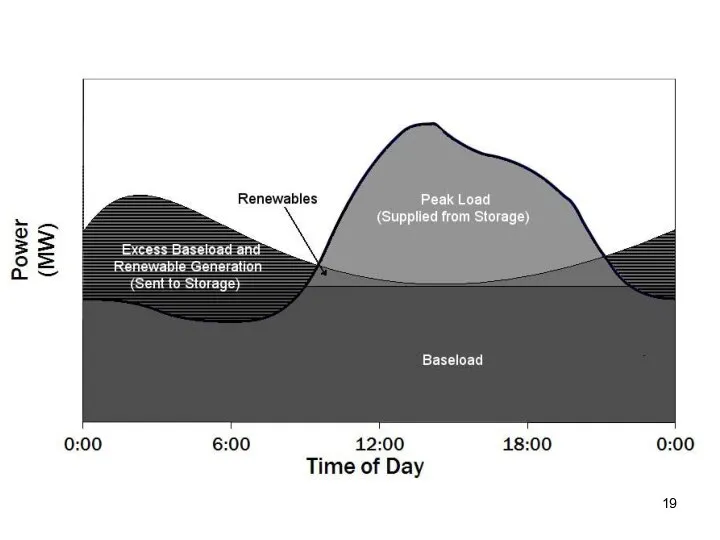
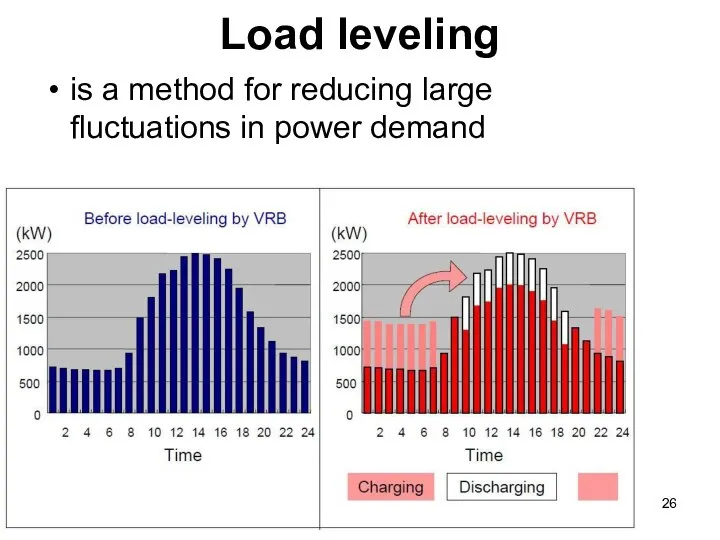
- 26. Load leveling is a method for reducing large fluctuations in power demand
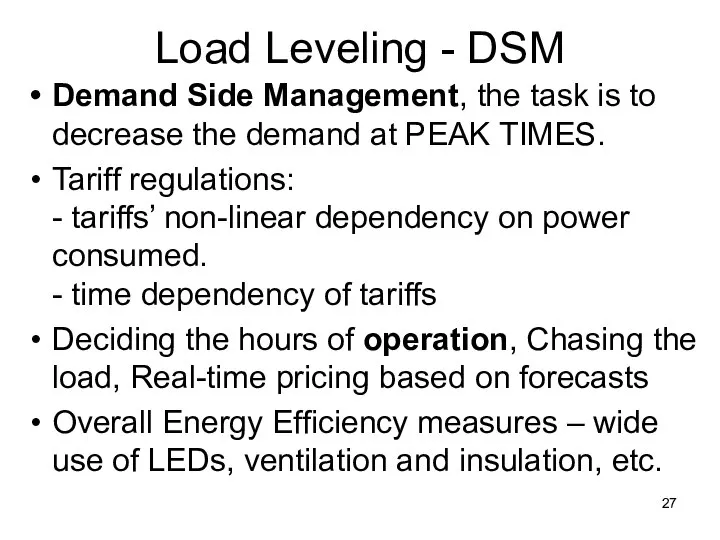
- 27. Load Leveling - DSM Demand Side Management, the task is to decrease the demand at PEAK
- 28. Elasticity % Demand Change E(d) = % of Price Change
- 29. Load Leveling - SSM Supply Side Management, the task is to organize capacities to meet the
- 30. European policy In 2007, the EU was importing 82% of its oil and 57% of its
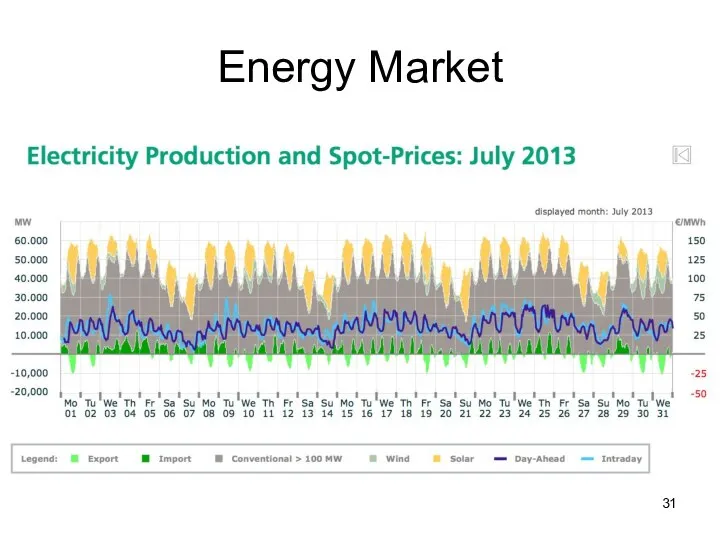
- 31. Energy Market
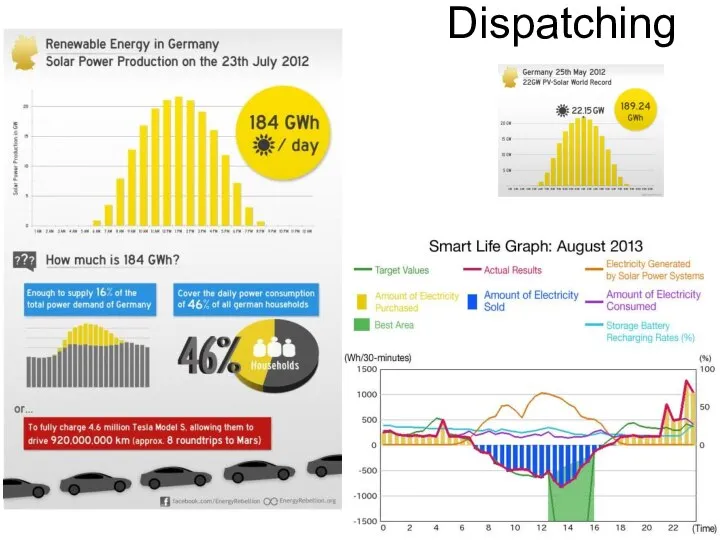
- 32. Dispatching
- 33. Storage Hydro-Pump Natural gas Thermal Hydrogen
- 34. Storage
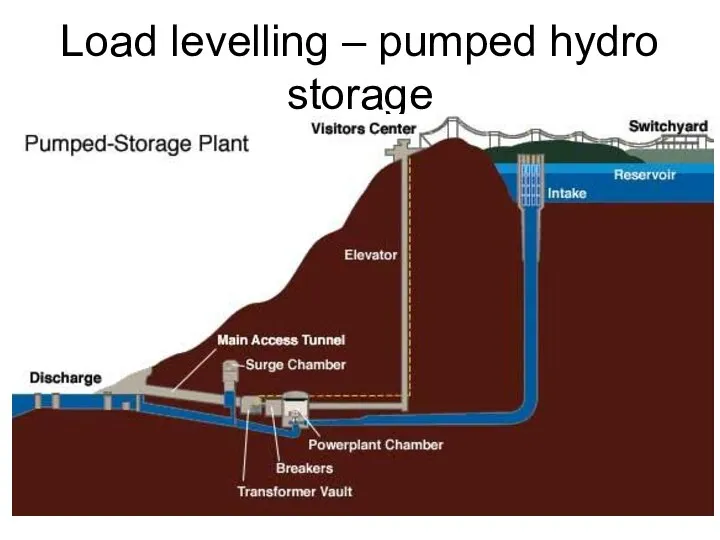
- 35. Load levelling – pumped hydro storage
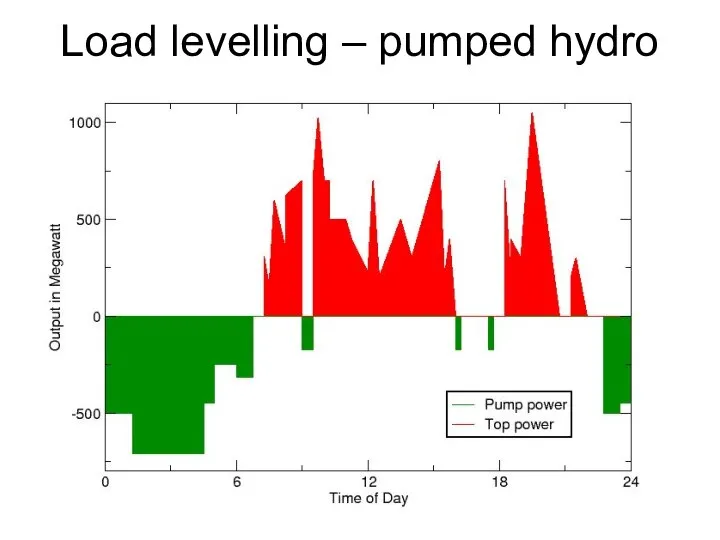
- 36. Load levelling – pumped hydro storage
- 37. RA gasification level ~94% Length of the main pipelines 14 050 km Number of gasified communities
- 38. Load levelling – EV fleet
- 40. Скачать презентацию



















 Предмет макроэкономики и методы макроэкономического анализа
Предмет макроэкономики и методы макроэкономического анализа Экономикалық теорияның пәні және зерттеу әдістері
Экономикалық теорияның пәні және зерттеу әдістері Общая характеристика рыночной экономики
Общая характеристика рыночной экономики Сервисная деятельность как форма удовлетворения потребностей
Сервисная деятельность как форма удовлетворения потребностей Экономика и её основные участники
Экономика и её основные участники Экономический эффект базовых рабочих мест в технопарках
Экономический эффект базовых рабочих мест в технопарках Инфраструктурный комплекс
Инфраструктурный комплекс Классификация видов, моделей, сегментов рынка труда
Классификация видов, моделей, сегментов рынка труда Особенности стратегического анализа: PEST анализ
Особенности стратегического анализа: PEST анализ Основы программного и проектного управления в развитии регионов
Основы программного и проектного управления в развитии регионов Proiecte. Fonduri ne/rambursabile. Granturi. (Curs 5)
Proiecte. Fonduri ne/rambursabile. Granturi. (Curs 5) Экономика предприятия
Экономика предприятия Оценка эффективности инновационных проектов. Пример
Оценка эффективности инновационных проектов. Пример Организмический подход в экономике
Организмический подход в экономике Концепции макроэкономического равновесия
Концепции макроэкономического равновесия Отраслевая структура машиностроения
Отраслевая структура машиностроения Модели макрорегиональной интеграции
Модели макрорегиональной интеграции Бережливое производство
Бережливое производство Установление тарифов на использование объектов инженерной инфраструктуры, сетей водоснабжения и водоотведения
Установление тарифов на использование объектов инженерной инфраструктуры, сетей водоснабжения и водоотведения Инвестиционный потенциал Кемеровской области
Инвестиционный потенциал Кемеровской области Основные средства
Основные средства Бюджетные отношения и основы бюджетной политики
Бюджетные отношения и основы бюджетной политики Приоритетные направления инновационного развития
Приоритетные направления инновационного развития Рыночные структуры и конкуренция
Рыночные структуры и конкуренция Составление экономико-географической характеристики одной из отраслей промышленности мира. Практическая работа
Составление экономико-географической характеристики одной из отраслей промышленности мира. Практическая работа Пример списания косвенных расходов на основное и вспомогательное производство организации
Пример списания косвенных расходов на основное и вспомогательное производство организации Прогнозирование и планирование трудовых ресурсов и занятости населения
Прогнозирование и планирование трудовых ресурсов и занятости населения Роль государства в регулировании экономических процессов
Роль государства в регулировании экономических процессов