Содержание
- 2. Outline Auctions Common value auctions All-pay auctions Review of seminar 2 Revision slides
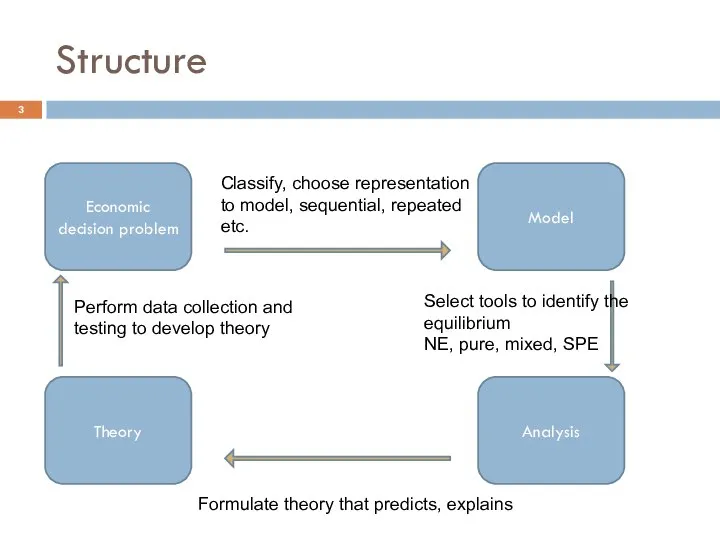
- 3. Structure Economic decision problem Model Analysis Theory Classify, choose representation to model, sequential, repeated etc. Select
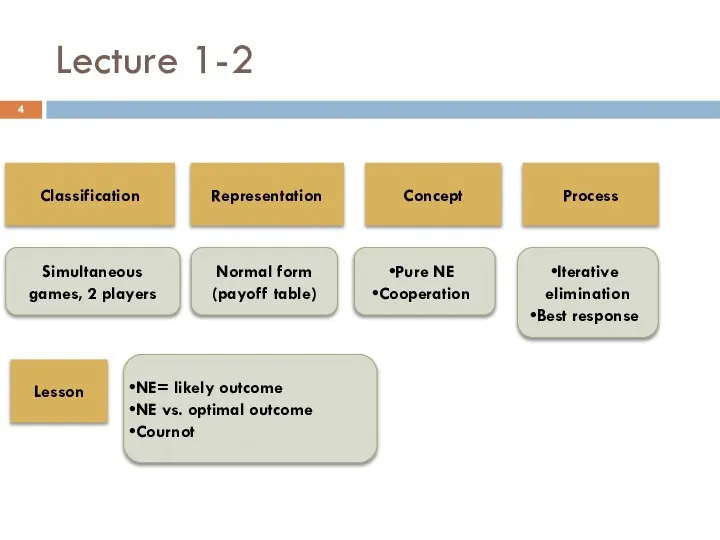
- 4. Lecture 1-2 Classification Simultaneous games, 2 players Representation Concept Process Lesson Normal form (payoff table) Pure
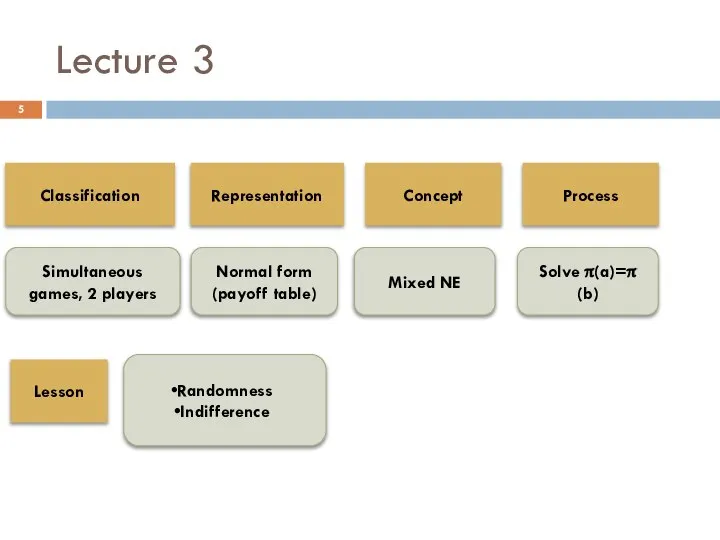
- 5. Lecture 3 Classification Simultaneous games, 2 players Representation Concept Process Lesson Normal form (payoff table) Mixed
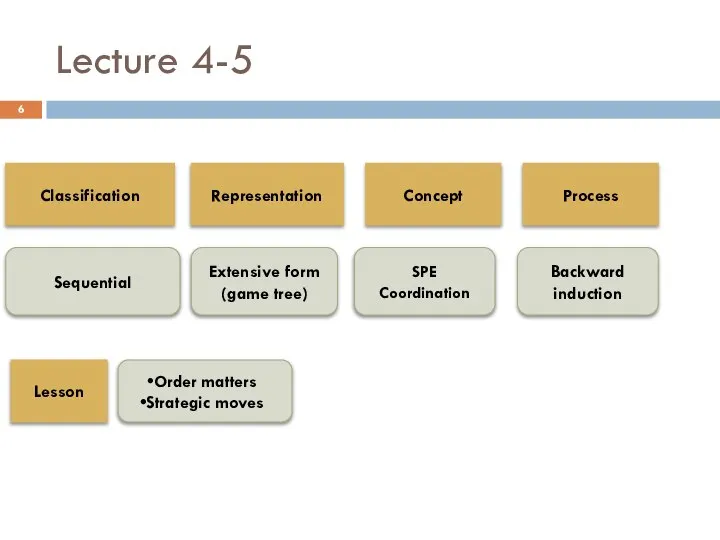
- 6. Lecture 4-5 Classification Sequential Representation Concept Process Lesson Extensive form (game tree) SPE Coordination Order matters
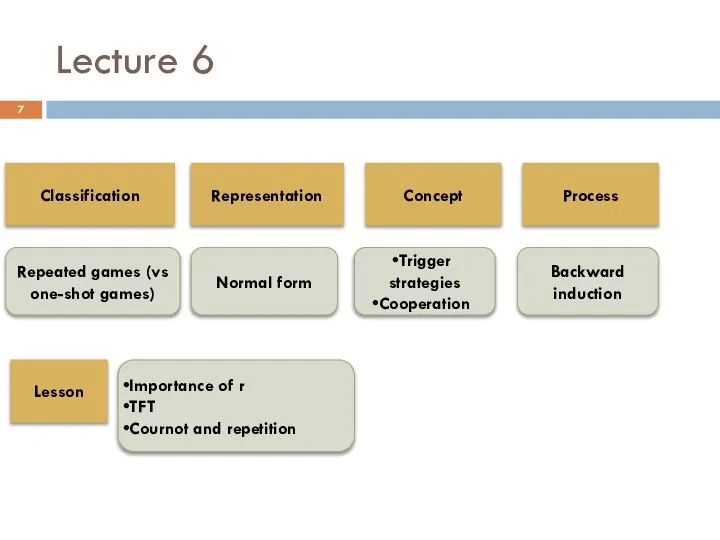
- 7. Lecture 6 Classification Repeated games (vs one-shot games) Representation Concept Process Lesson Normal form Trigger strategies
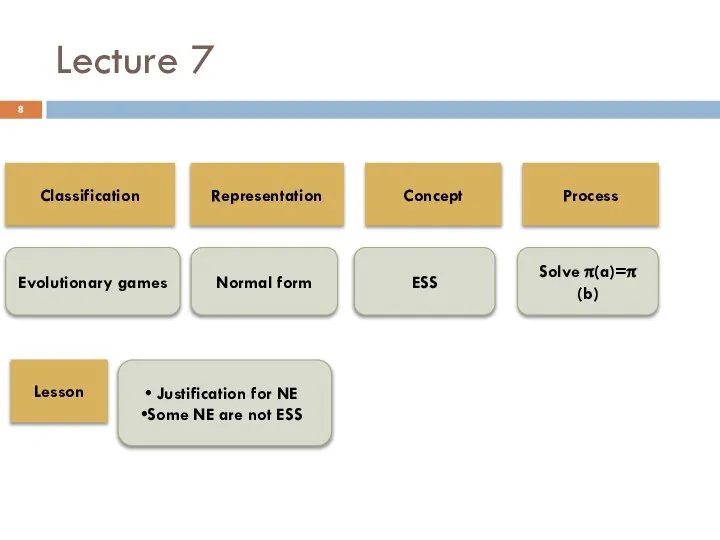
- 8. Lecture 7 Classification Evolutionary games Representation Concept Process Lesson Normal form ESS Justification for NE Some
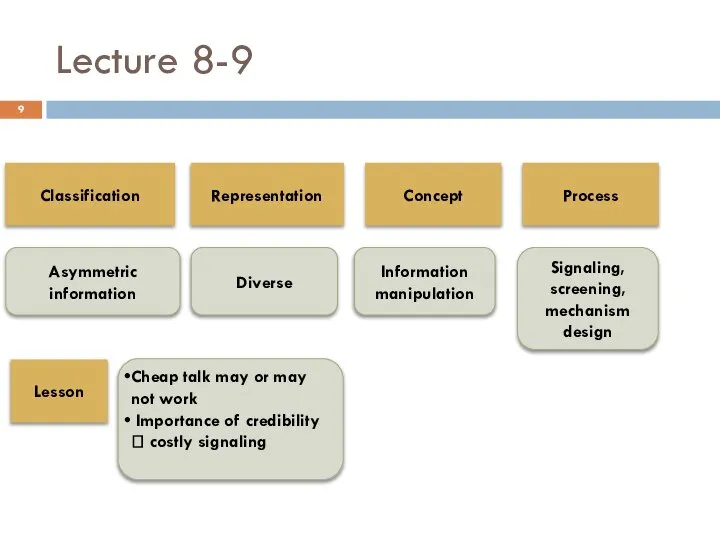
- 9. Lecture 8-9 Classification Asymmetric information Representation Concept Process Lesson Diverse Information manipulation Cheap talk may or
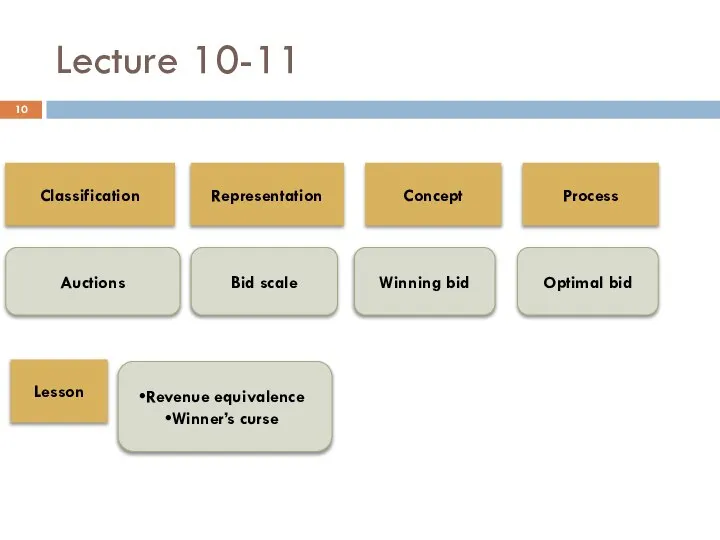
- 10. Lecture 10-11 Classification Auctions Representation Concept Process Lesson Bid scale Winning bid Revenue equivalence Winner’s curse
- 11. Exam Section A: 5 compulsory questions, at most 3 "mathematical/analytical" questions. (10 marks each) Section B:
- 12. Past paper (2014-15) 6. In games of cooperation, explain how the repetition of play may affect
- 13. Section A 1 conceptual question: e.g. explain the meaning of mixed strategies in evolutionary game theory...
- 15. Скачать презентацию




 Структура мировой экономики
Структура мировой экономики Доходы от использования и продажи государственного имущества
Доходы от использования и продажи государственного имущества Өндіріс факторларынан түске табыс
Өндіріс факторларынан түске табыс Демографическая политика Китая: последствия для экономики в прошлом и в будущем
Демографическая политика Китая: последствия для экономики в прошлом и в будущем Economic and Information mechanisms of activity of banks in Ukraine
Economic and Information mechanisms of activity of banks in Ukraine Показатели производственных мощностей предприятий
Показатели производственных мощностей предприятий Макроэкономическая нестабильность. Инфляция и безработица
Макроэкономическая нестабильность. Инфляция и безработица Самые популярные профессии Ростова-на-Дону
Самые популярные профессии Ростова-на-Дону Введение в экономику общественного сектора. Государство и рынки. (Тема 1)
Введение в экономику общественного сектора. Государство и рынки. (Тема 1) Международные валютные рынки и риски
Международные валютные рынки и риски Статистика национального богатства
Статистика национального богатства Институционализм. Основные идеи
Институционализм. Основные идеи Государственная программа Российской Федерации «Комплексное развитие сельских территорий»
Государственная программа Российской Федерации «Комплексное развитие сельских территорий» Предприятие в условиях рыночной экономики. (Тема 1)
Предприятие в условиях рыночной экономики. (Тема 1) Спрос и предложение на рынке труда
Спрос и предложение на рынке труда Государственные органы управления в системе регулирования ВЭД РФ
Государственные органы управления в системе регулирования ВЭД РФ Проблемы Развития внешнеэкономических связей в Сэз
Проблемы Развития внешнеэкономических связей в Сэз Внешнеторговая политика. Валютный рынок
Внешнеторговая политика. Валютный рынок Производственная свободная экономическая зона. Село Гыска
Производственная свободная экономическая зона. Село Гыска Спрос на деньги. Понятие, функции денежного спроса в различных экономических школах
Спрос на деньги. Понятие, функции денежного спроса в различных экономических школах Метод экспертных оценок
Метод экспертных оценок Система показателей и анализ хозяйственных результатов производства
Система показателей и анализ хозяйственных результатов производства Хочу весь мир и еще 5%
Хочу весь мир и еще 5% Национальная безопасность России
Национальная безопасность России Стратегии выхода на зарубежные рынки
Стратегии выхода на зарубежные рынки Государство как частная собственность инсайдеров на примере госкорпораций
Государство как частная собственность инсайдеров на примере госкорпораций Курсовая работа по экономической теории: технология написания
Курсовая работа по экономической теории: технология написания Практика ВТО (Всемирная торговая организация) по вопросам применения санитарных и фитосанитарных мер
Практика ВТО (Всемирная торговая организация) по вопросам применения санитарных и фитосанитарных мер