Содержание
- 2. Topic 2. General equilibrium in the open (trading) economy 2.1. General equilibrium conditions in the open
- 3. (2.1.) Formulation of the general equilibrium model for small open economy What is small economy? Demand
- 4. (2.1.) Formulation of the general equilibrium model for small open economy (continued) (2) Endogenous parameters of
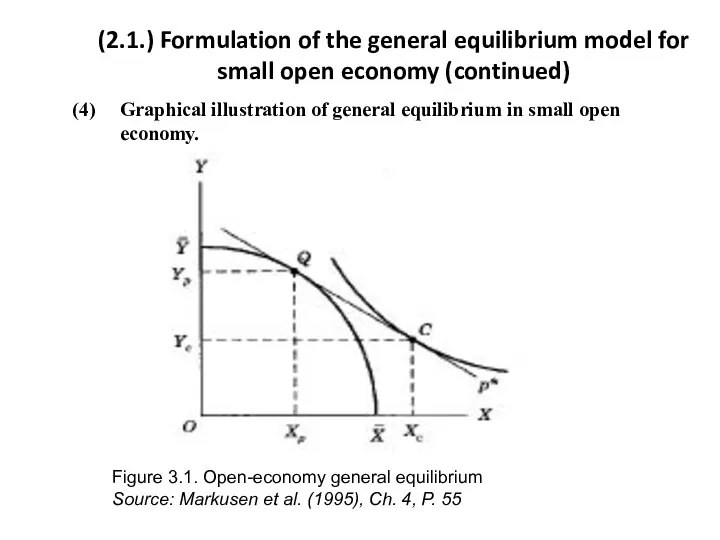
- 5. (2.1.) Formulation of the general equilibrium model for small open economy (continued) (4) Graphical illustration of
- 6. (2.2.) The concept of the excess demand function Definition (general): The excess demand function: relates the
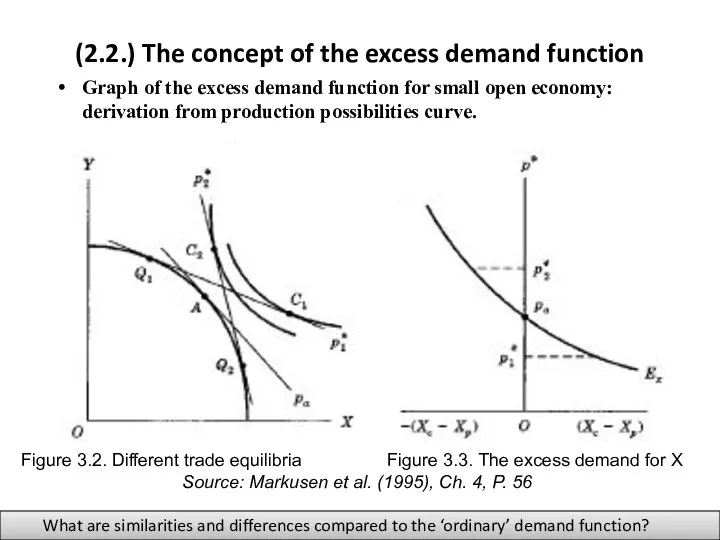
- 7. (2.2.) The concept of the excess demand function Graph of the excess demand function for small
- 8. (2.2.) The concept of the excess demand function Graph of the excess demand function for small
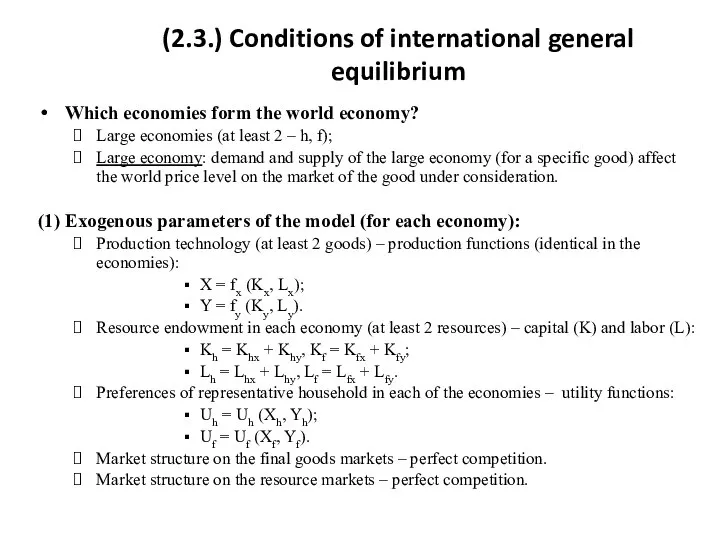
- 9. (2.3.) Conditions of international general equilibrium Which economies form the world economy? Large economies (at least
- 10. (2.3.) Conditions of international general equilibrium (continued) (2) Endogenous parameters of the model: Equilibrium production of
- 11. (2.3.) Conditions of international general equilibrium (continued) (4) Graphical illustration of general equilibrium in the world
- 12. (2.3.) Conditions of international general equilibrium (continued) (4) Graphical illustration of general equilibrium in the world
- 13. Exercise session 2 (2) Think about topics for reports during exercise sessions and work on a
- 15. Скачать презентацию







 Экономическая эффективность природоохранной деятельности
Экономическая эффективность природоохранной деятельности Қоғамдық өндіріс негіздері
Қоғамдық өндіріс негіздері Инновации и инновационная деятельность
Инновации и инновационная деятельность Человеческий капитал ТЭК. Роль ТЭК в экономике страны
Человеческий капитал ТЭК. Роль ТЭК в экономике страны Системный анализ в экономике. Предмет, содержание и задачи курса. Система и ее свойства
Системный анализ в экономике. Предмет, содержание и задачи курса. Система и ее свойства Развитие неоклассической теории (микроэкономика) в 20 – 40 годы ХХ века
Развитие неоклассической теории (микроэкономика) в 20 – 40 годы ХХ века Рыноктық механизмді
Рыноктық механизмді Предложение. Закон предложения
Предложение. Закон предложения Безробіття в Україні
Безробіття в Україні Теория потребительского поведения
Теория потребительского поведения Дефлятор ВВП як показник рівня цін
Дефлятор ВВП як показник рівня цін Міжнародна безпека. Лекція 5. Економічна безпека та її роль в розвитку світового господарства та МЕВ
Міжнародна безпека. Лекція 5. Економічна безпека та її роль в розвитку світового господарства та МЕВ Экономика. Часть 2. Задачи
Экономика. Часть 2. Задачи Петрозаводск - исполнение поручений
Петрозаводск - исполнение поручений Эконометрика, начальный курс
Эконометрика, начальный курс Кредитный потребительский кооператив
Кредитный потребительский кооператив Спрос. Закон спроса. Эластичность спроса
Спрос. Закон спроса. Эластичность спроса Құрылыстың сметалық құны
Құрылыстың сметалық құны Экономикалық дамудың үлгілері
Экономикалық дамудың үлгілері Теория организации. Предприятие в рыночной экономике. Предприятие и его место в системе народного хозяйства. (Часть 2.1.1)
Теория организации. Предприятие в рыночной экономике. Предприятие и его место в системе народного хозяйства. (Часть 2.1.1) Проблемы эффективного формирования и использования капитала фирмы
Проблемы эффективного формирования и использования капитала фирмы Методология неоклассической школы
Методология неоклассической школы Состояние и обзор качества товарной продукции, поступившей из КНР на территорию Республики Хакасия
Состояние и обзор качества товарной продукции, поступившей из КНР на территорию Республики Хакасия Валютное регулирование и валютный контроль. Лекция 3 - Роль валютного регулирования в микро- и макроэкономике
Валютное регулирование и валютный контроль. Лекция 3 - Роль валютного регулирования в микро- и макроэкономике Концепція розвитку велосипедної інфраструктури міста Южноукраїнська
Концепція розвитку велосипедної інфраструктури міста Южноукраїнська Марксистская (материалистическая) теория
Марксистская (материалистическая) теория Корпоративная социальная ответственность
Корпоративная социальная ответственность Використання електричної енергії в Україні
Використання електричної енергії в Україні