Содержание
- 2. Economic Integration Globalisation about growing economic interdependence of countries as well as the rapid diffusion of
- 3. The case FOR government intervention Political arguments: “protecting jobs and industries” “protecting industries vital for national
- 4. Barriers to Trade Tariff Barriers Official constraints on the import of certain goods. Non Tariff Barriers:
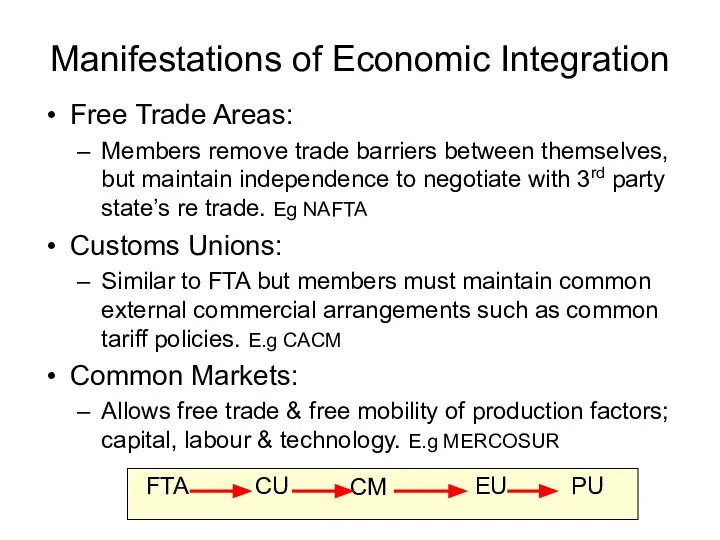
- 5. Manifestations of Economic Integration Free Trade Areas: Members remove trade barriers between themselves, but maintain independence
- 6. Instruments of Global Integration GATT: 8 rounds 1947 to 1994. Early stages concerned with removal of
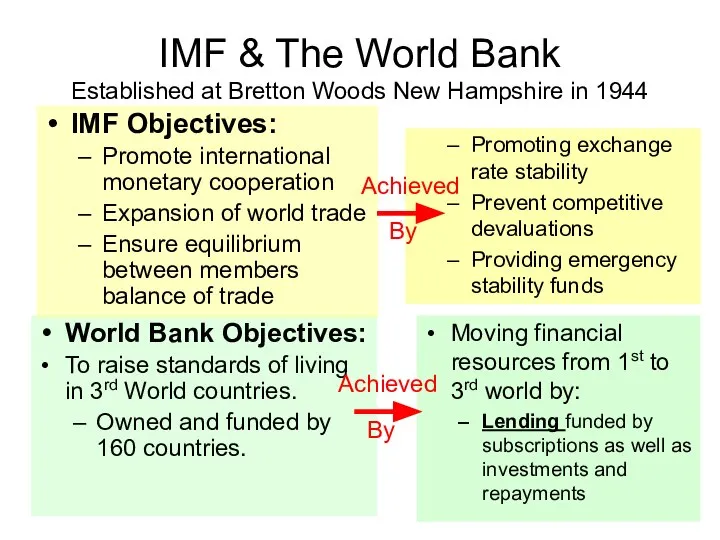
- 7. World Bank Objectives: To raise standards of living in 3rd World countries. Owned and funded by
- 8. Key Issues The WTO, The IMF and The World Bank: The key organisations concerned with global
- 9. Multinational Enterprises (MNE) MNE Vs International Firm: An MNE any firm that with (FDI) Foreign Direct
- 10. Are MNE’s Trans-national? MNE’s no longer have allegiance to a single country? Increasingly difficult to pinpoint
- 11. The Free Trade Debate For: Generally trade theories show the benefit of free trade particularly absolute
- 13. Скачать презентацию








 Труд. Рынок труда. Безработица
Труд. Рынок труда. Безработица Основные этапы развития экономической теории
Основные этапы развития экономической теории Презентация Генетическая социология и теория прогресса по М.М. Ковалевскому
Презентация Генетическая социология и теория прогресса по М.М. Ковалевскому Экономическая жизнь общества. Экономика как наука и хозяйство
Экономическая жизнь общества. Экономика как наука и хозяйство «Школьная лига Роснано». Разговор второй. Ловушки развития: институты как они есть
«Школьная лига Роснано». Разговор второй. Ловушки развития: институты как они есть Зовнішнє середовище підприємства
Зовнішнє середовище підприємства Економіка охорони здоров’я, як наука і практика. Ринок послуг охорони здоров’я
Економіка охорони здоров’я, як наука і практика. Ринок послуг охорони здоров’я Dichloromethane. Import in Russia
Dichloromethane. Import in Russia Стратегия экономического и социального развития Санкт-Петербурга до 2030 года
Стратегия экономического и социального развития Санкт-Петербурга до 2030 года Финансовая сфера экономики. Деньги, банки, налоги. (11 класс)
Финансовая сфера экономики. Деньги, банки, налоги. (11 класс) Государсвенно регулирование экономики в условях кризиса РФ
Государсвенно регулирование экономики в условях кризиса РФ Економічний механізм функціонування ринку. Ринкова інфраструктура
Економічний механізм функціонування ринку. Ринкова інфраструктура Negative Externalities
Negative Externalities Механизм саморегуляции рынка
Механизм саморегуляции рынка SMED. Быстрая переналадка
SMED. Быстрая переналадка Demand and Supply
Demand and Supply Город Жуковский в Московской области России
Город Жуковский в Московской области России Программа пребывания делегации из Швеции в России , г. Грозный
Программа пребывания делегации из Швеции в России , г. Грозный Трендвотчер\форсайтер
Трендвотчер\форсайтер Generating electric power from the atmosphere
Generating electric power from the atmosphere Презентация ФИНАНСОВОЕ ПРОГНОЗИРОВАНИЕ И ПЛАНИРОВАНИЕ
Презентация ФИНАНСОВОЕ ПРОГНОЗИРОВАНИЕ И ПЛАНИРОВАНИЕ Вопросы для повторения Форма государственного устройства, ее виды. Унитарное государство, признаки, особенности, виды Федера
Вопросы для повторения Форма государственного устройства, ее виды. Унитарное государство, признаки, особенности, виды Федера Проекты в современном мире. Цель, задачи, проблемы. Тема 3
Проекты в современном мире. Цель, задачи, проблемы. Тема 3 Тест по экономике
Тест по экономике Статистические таблицы
Статистические таблицы Региональная политика: мезоуровень
Региональная политика: мезоуровень Еколого-економічне обґрунтування структури угідь та організації сівозмін фермерського господарства
Еколого-економічне обґрунтування структури угідь та організації сівозмін фермерського господарства Бережливое производство. История бережливого производства
Бережливое производство. История бережливого производства