Содержание
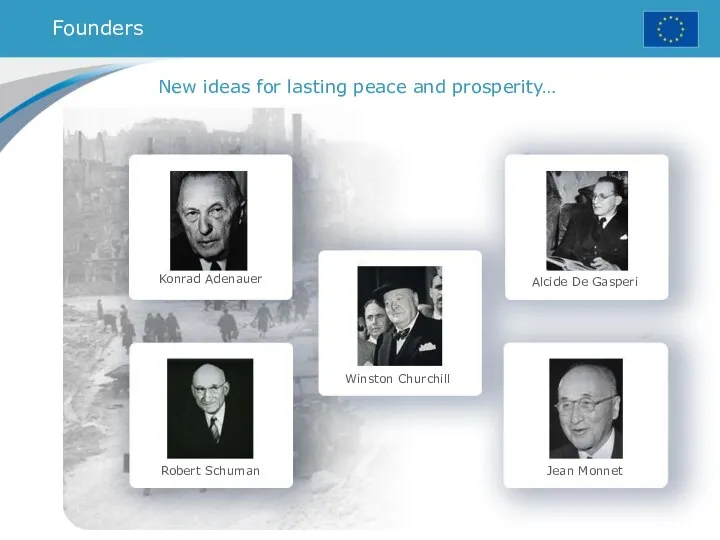
- 2. Konrad Adenauer Robert Schuman Winston Churchill Alcide De Gasperi Jean Monnet New ideas for lasting peace
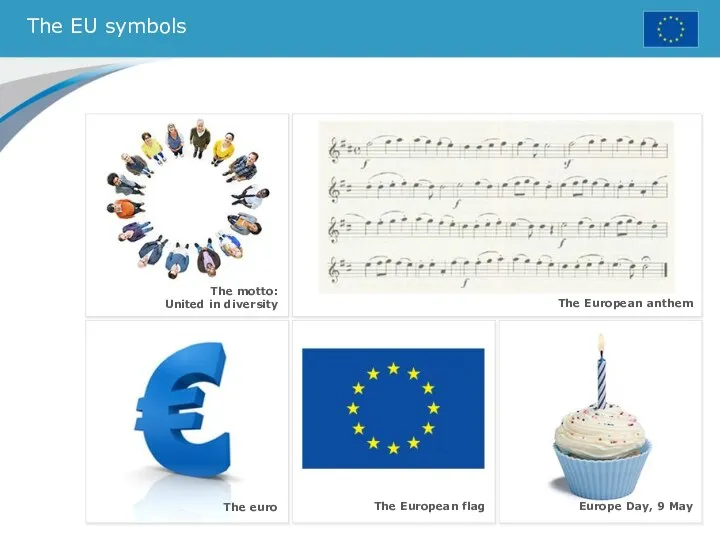
- 3. The EU symbols The European flag The European anthem The euro Europe Day, 9 May The
- 4. 24 official languages Български Čeština dansk Deutsch eesti keel Ελληνικά English español français Gaeilge hrvatski Italiano
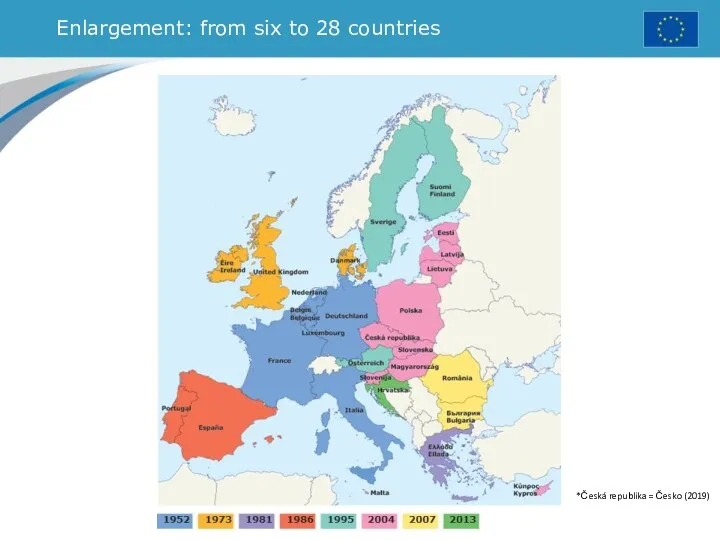
- 5. Enlargement: from six to 28 countries *Česká republika = Česko (2019)
- 6. The big enlargement: uniting east and west Fall of Berlin Wall – end of Communism EU
- 7. Candidate countries and potential candidates
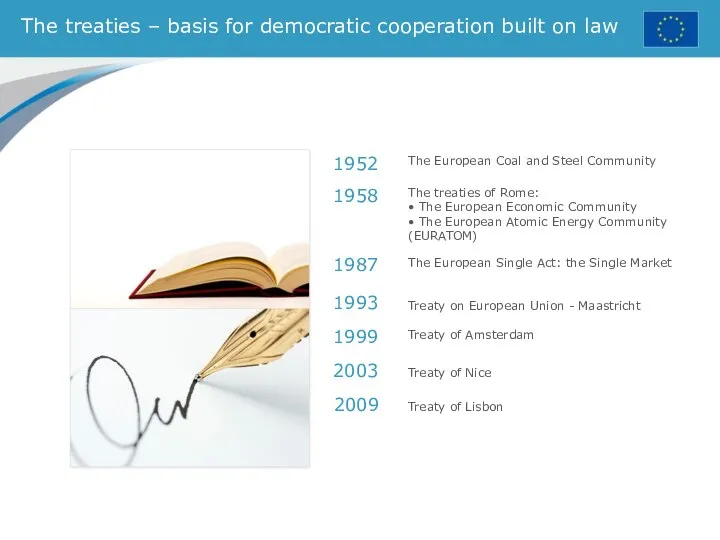
- 8. The treaties – basis for democratic cooperation built on law The European Coal and Steel Community
- 9. The EU Charter of Fundamental Rights Binding for all the EU's activities 54 articles under 6
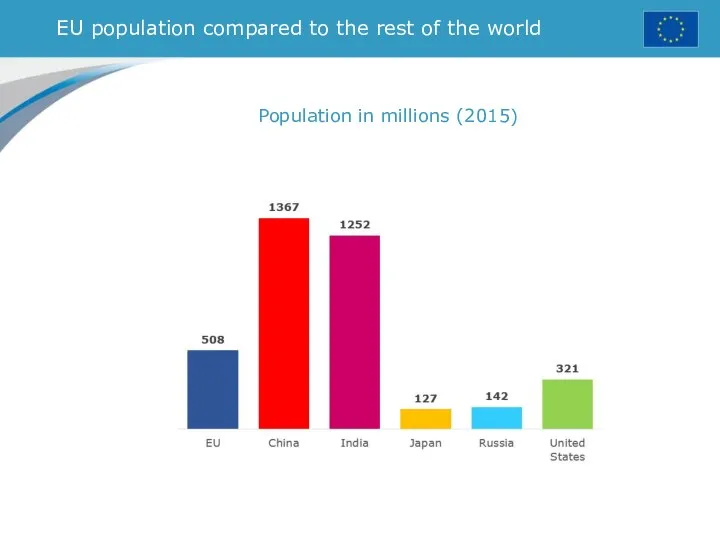
- 10. EU population compared to the rest of the world Population in millions (2015)
- 11. EU surface area compared to the rest of the world Surface area (x 1000 km²)
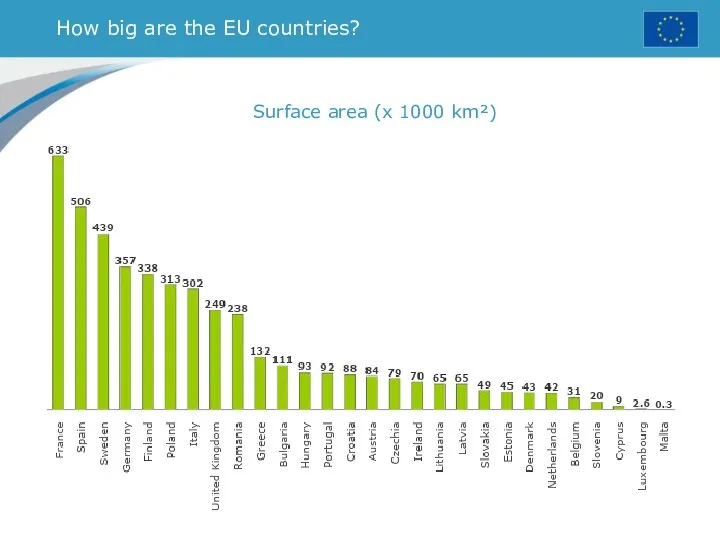
- 12. How big are the EU countries? Surface area (x 1000 km²)
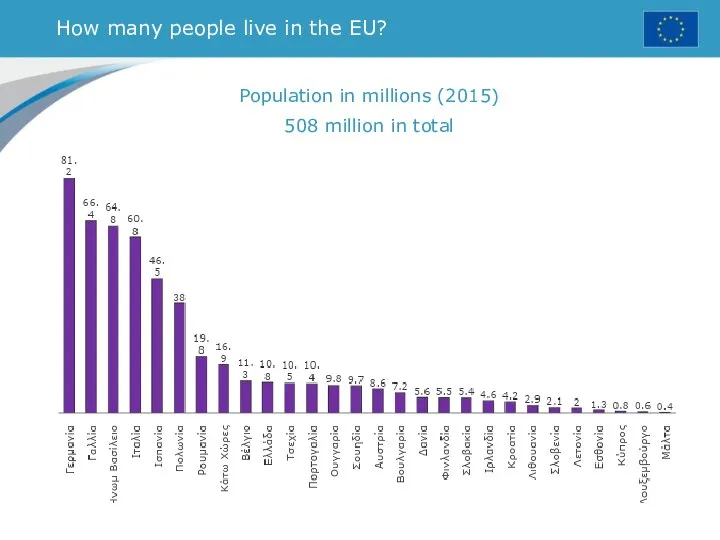
- 13. How many people live in the EU? Population in millions (2015) 508 million in total
- 14. The European economy: stronger together 2008: Worldwide financial crisis starts in the United States. Coordinated response
- 15. Ten priorities for Europe The European Commission of President Jean-Claude Juncker focuses on: The investment plan:
- 16. An investment plan for Europe The European Fund for Strategic Investments 2015: Europe’s economy begins to
- 17. Banking union: safe and reliable banks The EU’s response to the financial crisis: Rulebook: New laws
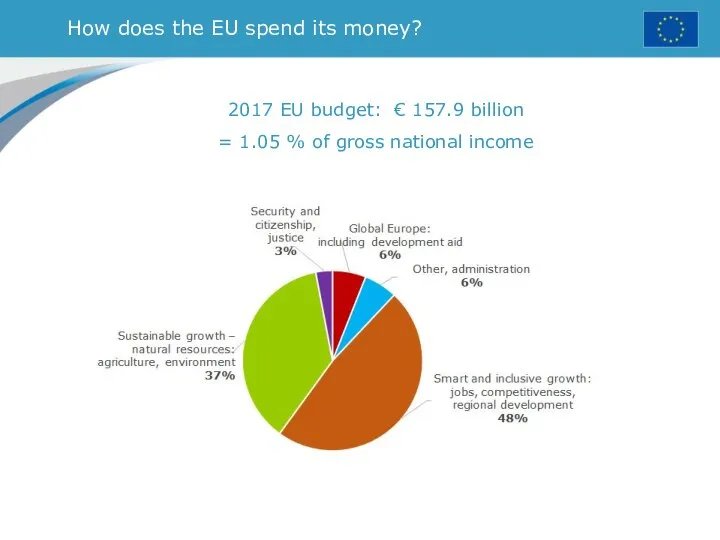
- 18. How does the EU spend its money? 2017 EU budget: € 157.9 billion = 1.05 %
- 19. Climate change – a global challenge reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 40 % by 2030, compared
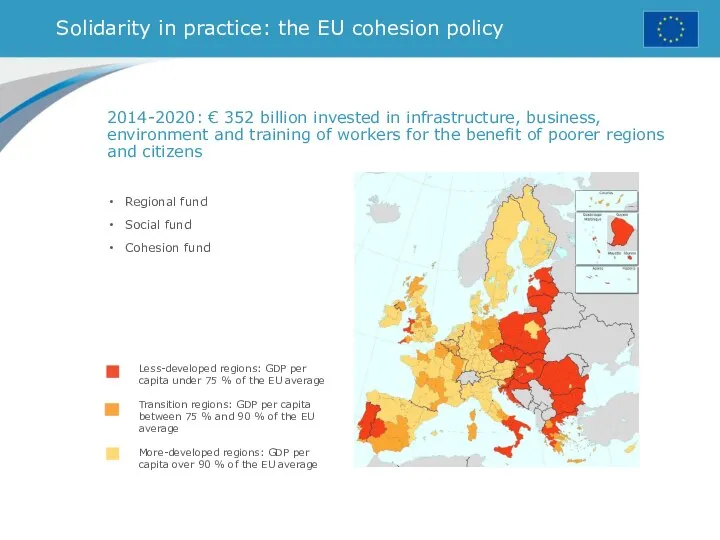
- 20. Solidarity in practice: the EU cohesion policy Regional fund Social fund Cohesion fund Less-developed regions: GDP
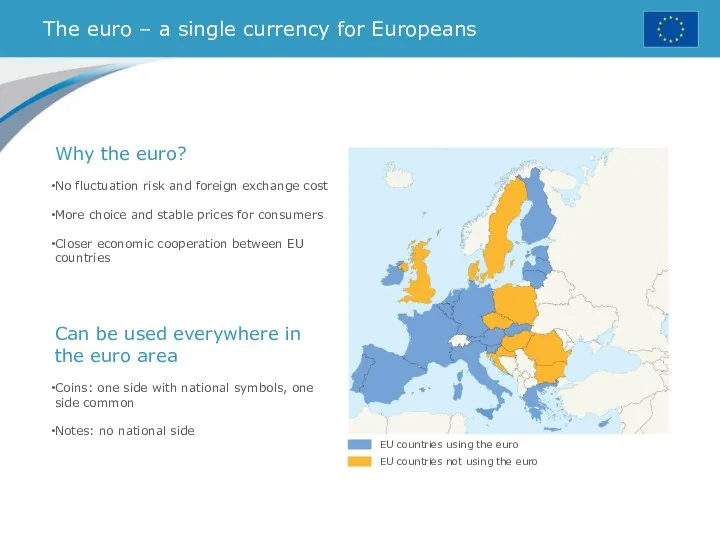
- 21. The euro – a single currency for Europeans EU countries using the euro EU countries not
- 22. The single market: freedom of choice The single market has led to: significant reductions in the
- 23. Free to move ‘Schengen’ No police or customs checks at borders between most EU countries Controls
- 24. Going abroad to learn Erasmus+ Every year, more than 400 000 young people study or pursue
- 25. Improving health and the environment EU action has helped bring about: cleaner bathing water much less
- 26. An area of freedom, security and justice EU Charter of Fundamental Rights Joint fight against terrorism
- 27. The EU: an exporter of peace and prosperity World trade rules Common foreign and security policy
- 28. Protecting consumers' rights Clear labelling Health and safety standards Unfair practice in contracts prohibited Passengers’ rights,
- 29. Three key players The European Parliament - voice of the people Antonio Tajani, President of the
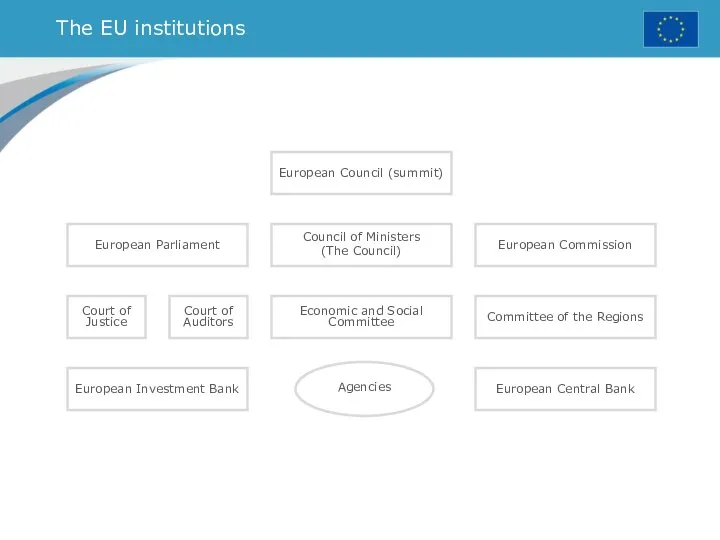
- 30. The EU institutions European Parliament Court of Justice Court of Auditors Economic and Social Committee Committee
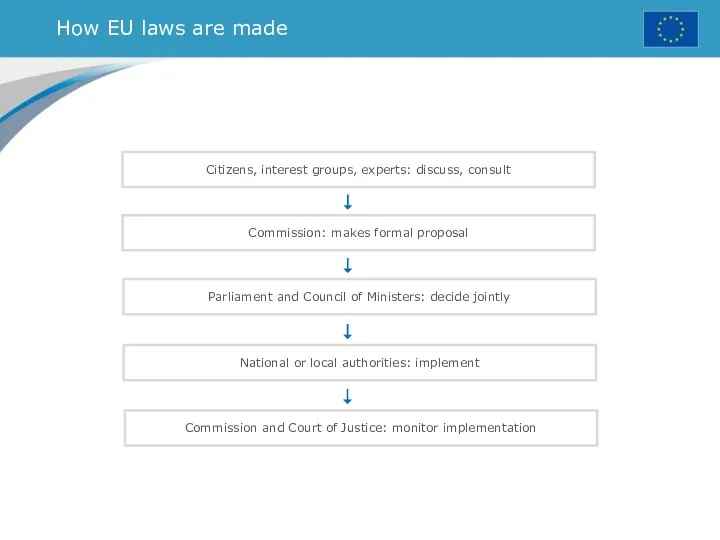
- 31. How EU laws are made Citizens, interest groups, experts: discuss, consult Commission: makes formal proposal Parliament
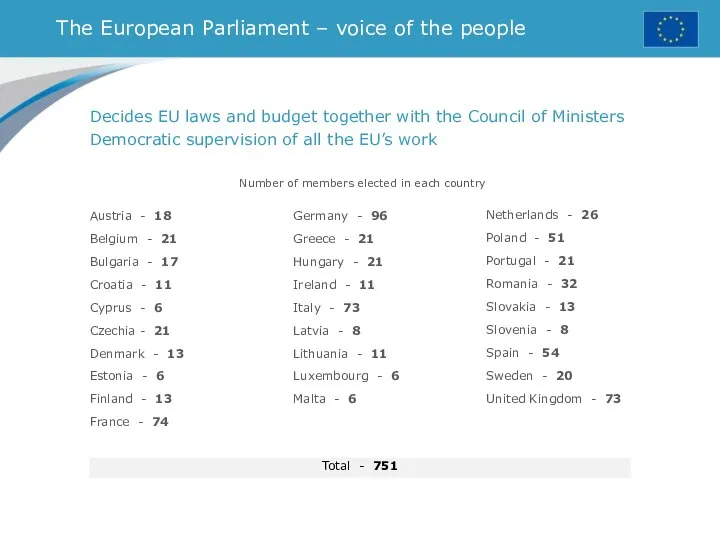
- 32. The European Parliament – voice of the people Number of members elected in each country Decides
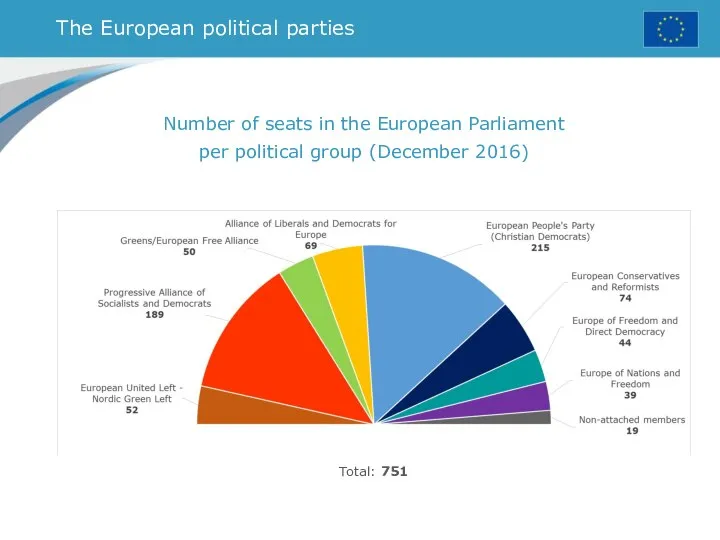
- 33. The European political parties Number of seats in the European Parliament per political group (December 2016)
- 34. Council of Ministers – voice of the Member States One minister from each EU country Presidency:
- 35. Council of Ministers – how they vote Most decisions in the Council are taken by ‘double
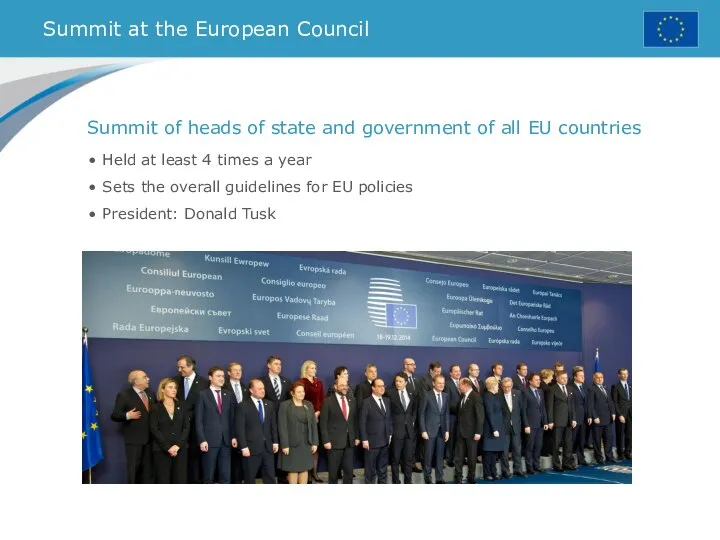
- 36. Summit at the European Council Held at least 4 times a year Sets the overall guidelines
- 37. A high representative for foreign affairs and security Double role: chairs meetings of the Foreign Affairs
- 38. The European Commission – promoting the common interest 28 independent members, one from each EU country
- 39. The Court of Justice – upholding the law 28 independent judges, one from each EU country
- 40. The European Ombudsman Emily O’Reilly The European Ombudsman Investigates complaints about poor or failed administration by
- 41. The European Court of Auditors: getting value for your money 28 independent members Checks that EU
- 42. Ensures price stability Controls money supply and decides interest rates Supervises that banks are safe Works
- 43. The European Economic and Social Committee: voice of civil society Represents trade unions, employers, farmers, consumers
- 44. The Committee of the Regions: voice of local government Represents cities and regions Advises on new
- 46. Скачать презентацию




























 Классическая школа
Классическая школа Министерство Российской Федерации по развитию Дальнего Востока
Министерство Российской Федерации по развитию Дальнего Востока Инфляция
Инфляция Рынок страховых услуг
Рынок страховых услуг Несостоятельность рынка и пути ее преодоления
Несостоятельность рынка и пути ее преодоления Салықтардың экономикалық мәні және мазмұны
Салықтардың экономикалық мәні және мазмұны Экономика отрасли инфокоммуникаций
Экономика отрасли инфокоммуникаций Критический анализ модели «кейнсианского креста». Рецессионный и инфляционный разрыв
Критический анализ модели «кейнсианского креста». Рецессионный и инфляционный разрыв Концепция гегемонии А. Грамши
Концепция гегемонии А. Грамши Сущность розничных торговых сетей в регионе. Понятие розничные торговые сети
Сущность розничных торговых сетей в регионе. Понятие розничные торговые сети Русский мир
Русский мир Региональная политика государства
Региональная политика государства Управленческий риск
Управленческий риск Анализ приоритетных направлений наукоёмких технологий в РФ и других странах
Анализ приоритетных направлений наукоёмких технологий в РФ и других странах Последствия Великих географических открытий
Последствия Великих географических открытий Качественные и количественные методы экономических исследований
Качественные и количественные методы экономических исследований Ўзбекистон ва жаҳон ҳамжамияти
Ўзбекистон ва жаҳон ҳамжамияти Модель совместного равновесия товарного и денежного рынков
Модель совместного равновесия товарного и денежного рынков Программа "Мастера жизни"
Программа "Мастера жизни" Участие России в интеграционных процессах
Участие России в интеграционных процессах Пространственная организация экономики регионов
Пространственная организация экономики регионов Презентация Экономический рост и развитие
Презентация Экономический рост и развитие  Основные фонды предприятия
Основные фонды предприятия Політична економія як фундаментальна суспільна наука
Політична економія як фундаментальна суспільна наука Система национальных счетов. Основные макроэкономические показатели. (Тема 10)
Система национальных счетов. Основные макроэкономические показатели. (Тема 10) Рынок труда
Рынок труда Проблема развития моногородов
Проблема развития моногородов Экономические потребности, блага и ресурсы. Лекция 1
Экономические потребности, блага и ресурсы. Лекция 1