Содержание
- 2. LECTURE No. 4 PROPERTIES OF NANOSTRUCTURED MATERIALS
- 3. INTRODUCTION Physical-chemistry of solid-state nanostructures is a bridge between: Atomic Physics Physical chemistry of the concentrated
- 4. INTRODUCTION What is Nonotechnology? What is Nonoscience? Stability: Kinetic Thermodynamic factors
- 5. OBJECTIVES To analyse physico-chemical properties of nanostructured materials. To explain size effect of nanoparticles on the
- 6. OUTLINE Physico-chemical properties of nanostructured materials. Size effect of nanoparticles on the chemical and thermodynamic properties.
- 7. Factors, influencing the properties of nanostructured materials (with decreasing of size of nanoparticles): A change in
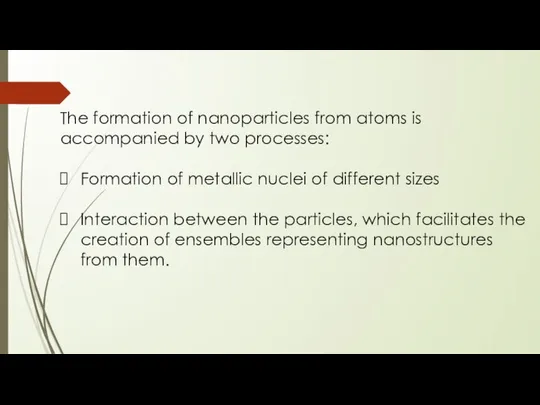
- 8. The formation of nanoparticles from atoms is accompanied by two processes: Formation of metallic nuclei of
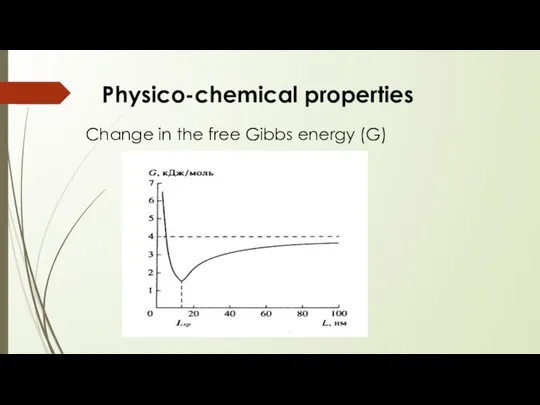
- 9. Change in the free Gibbs energy (G) Physico-chemical properties
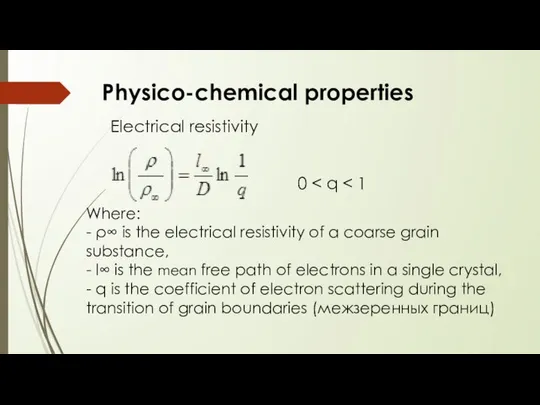
- 10. Electrical resistivity Physico-chemical properties Where: - ρ∞ is the electrical resistivity of a coarse grain substance,
- 11. Physico-chemical properties Mechanical properties Tensile strength and hardness: Where: - is strength of a single crystal,
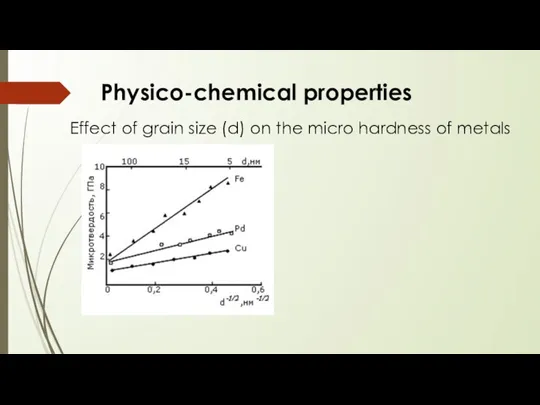
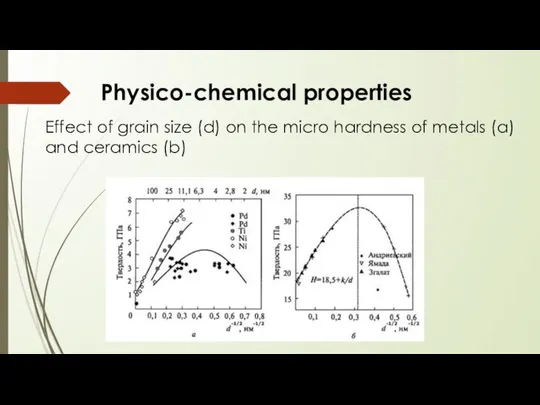
- 12. Physico-chemical properties Effect of grain size (d) on the micro hardness of metals
- 13. Physico-chemical properties Effect of grain size (d) on the micro hardness of metals (a) and ceramics
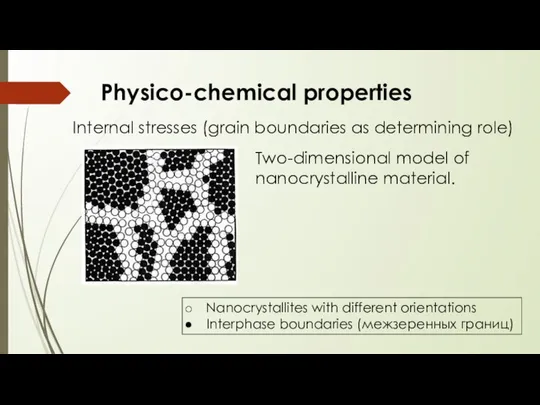
- 14. Physico-chemical properties Two-dimensional model of nanocrystalline material. Nanocrystallites with different orientations Interphase boundaries (межзеренных границ) Internal
- 15. Physico-chemical properties The study of experimental data and reactions of atoms, clusters and nanoparticles of various
- 16. Types of size effects Internal: associated with specific changes in the volume and surface properties of
- 17. Types of size effects The study of internal dimensional effects is aimed on the studying of:
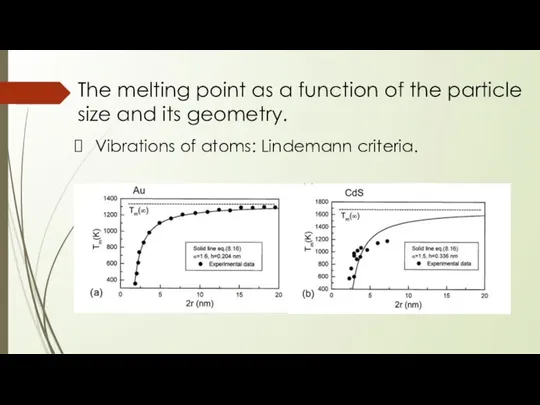
- 18. The melting point as a function of the particle size and its geometry. Thermodynamic representations Where:
- 19. The melting point as a function of the particle size and its geometry. Vibrations of atoms:
- 20. The melting point as a function of the particle size and its geometry. Vibrations of atoms:
- 21. The melting point as a function of the particle size and its geometry. Vibrations of atoms:
- 22. Control questions 1. What are the main factors that influence in the properties of nanomaterials?. 2.
- 24. Скачать презентацию














 Шкала электромагнитных волн
Шкала электромагнитных волн Презентация по физике "Реостаты" - скачать
Презентация по физике "Реостаты" - скачать  Доклад по микро- и оптоэлектронике. Студентки гр.21305 Васильевой Е.А.
Доклад по микро- и оптоэлектронике. Студентки гр.21305 Васильевой Е.А. Внутренняя энергия и способы ее изменения. Тест
Внутренняя энергия и способы ее изменения. Тест Тесты по МЕХАНИКЕ группа А (первый уровень)
Тесты по МЕХАНИКЕ группа А (первый уровень) Кристаллы и их выращивание в домашних условиях Работу выполнила: Мельникова Алина, ученица 10 класса МАОУ «Гимназия «Исток» Руков
Кристаллы и их выращивание в домашних условиях Работу выполнила: Мельникова Алина, ученица 10 класса МАОУ «Гимназия «Исток» Руков Закон Архимеда. Действие жидкости и газа на погруженное в них тело. Билет 24
Закон Архимеда. Действие жидкости и газа на погруженное в них тело. Билет 24 Демонстрационный эксперимент по геометрической оптике Выполнил: Ригачев Илья Ученик 9 «А» класса Научный руководитель: Федот
Демонстрационный эксперимент по геометрической оптике Выполнил: Ригачев Илья Ученик 9 «А» класса Научный руководитель: Федот Введение в тепломассообмен
Введение в тепломассообмен Трансформатор
Трансформатор Топливно-энергетические ресурсы. Способы получения, преобразования и использования энергии
Топливно-энергетические ресурсы. Способы получения, преобразования и использования энергии Жазыќ механизмдерді кинематикалыќ зерттеу. (Дјріс 3)
Жазыќ механизмдерді кинематикалыќ зерттеу. (Дјріс 3) Релаксаційні процеси у феритових структурах
Релаксаційні процеси у феритових структурах Презентация по физике "Радиолокация" - скачать
Презентация по физике "Радиолокация" - скачать  Автоматизированный электрический привод
Автоматизированный электрический привод Метод эквивалентного генератора
Метод эквивалентного генератора Теплові двигуни
Теплові двигуни Трансформатор. Принцип действия
Трансформатор. Принцип действия Общие теоремы динамики точки
Общие теоремы динамики точки Воздействие электрического тока на человека
Воздействие электрического тока на человека Напряжения. Связь внутренних усилий и напряжений
Напряжения. Связь внутренних усилий и напряжений Проверочная работа №1
Проверочная работа №1 Модели атома. Атом Резерфорда - Бора
Модели атома. Атом Резерфорда - Бора Испарение и конденсация. Насыщенные и ненасыщенные пары. Влажность воздуха
Испарение и конденсация. Насыщенные и ненасыщенные пары. Влажность воздуха Выдающиеся ученые-физики
Выдающиеся ученые-физики Приборы радиационной и химической разведки и дозиметрического контроля
Приборы радиационной и химической разведки и дозиметрического контроля Самоиндукция. Индуктивность. Часть 4
Самоиндукция. Индуктивность. Часть 4 Оптические приборы
Оптические приборы