Содержание
- 2. Sect. 1 What is Refrigeration?
- 3. Sect. 1 DEFINITION ‘Refrigeration’… …is the transfer of heat from a place where it is ‘not
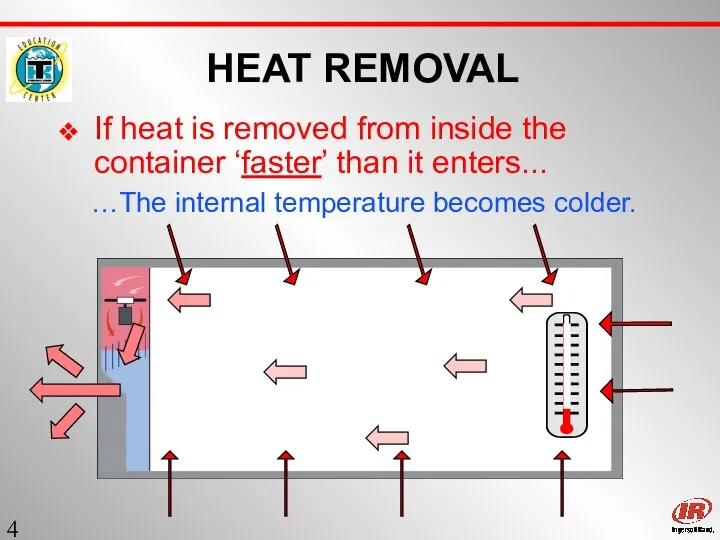
- 4. Sect. 1 HEAT REMOVAL If heat is removed from inside the container ‘faster’ than it enters...
- 5. Sect. 1 WHAT IS HEAT? A Form of Energy It Exists ‘Everywhere’ It Exists at ‘All
- 6. Sect. 1 WHAT ARE REEFERS? Machines that ‘Move Heat’
- 7. Sect. 1 ‘HOW’ DOES HEAT MOVE? Warmer ⇒ Colder - ALWAYS!!!!!!! Heat Heat Heat ‘Faster’ with
- 8. Sect. 1 ‘HOW’ DOES IT MOVE? Heat can move three (3) ways…. 1. Conduction 2. Convection
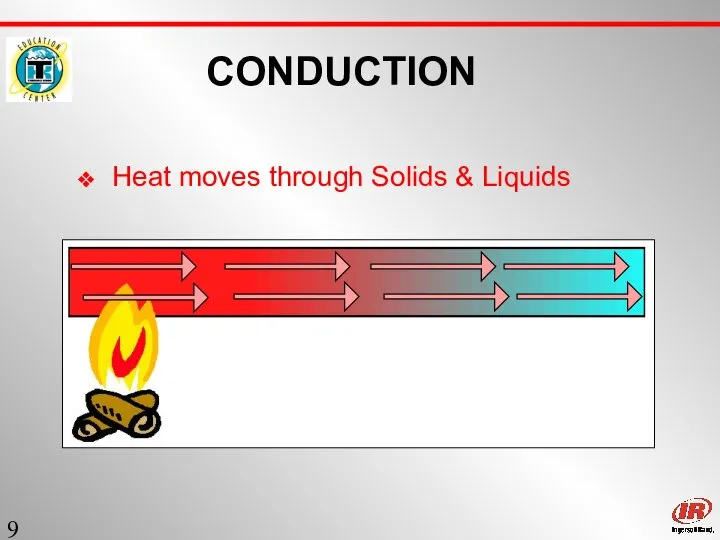
- 9. Sect. 1 CONDUCTION Heat moves through Solids & Liquids
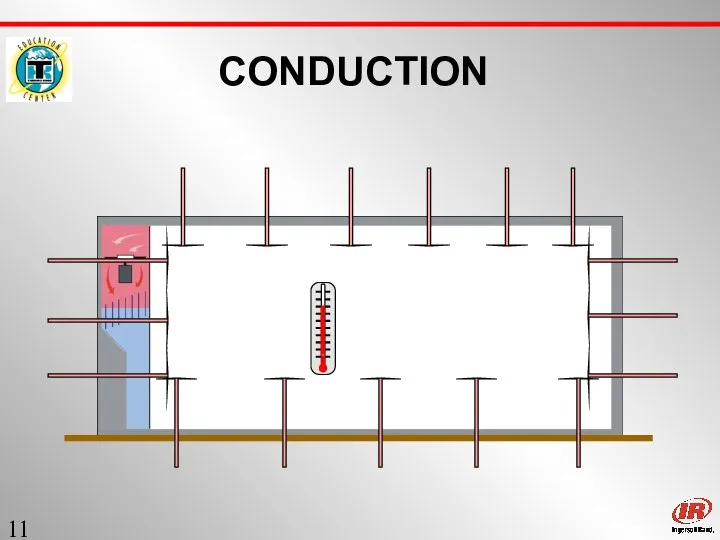
- 10. Sect. 1 CONDUCTION Heat will move Between Solids and / or Fluids in direct contact with
- 11. Sect. 1 CONDUCTION
- 12. Sect. 1 Any other Examples of Conduction?
- 13. Sect. 1 CONVECTION Definition - Heat transfers via the circulation (movement) of a fluid. i.e….. Air
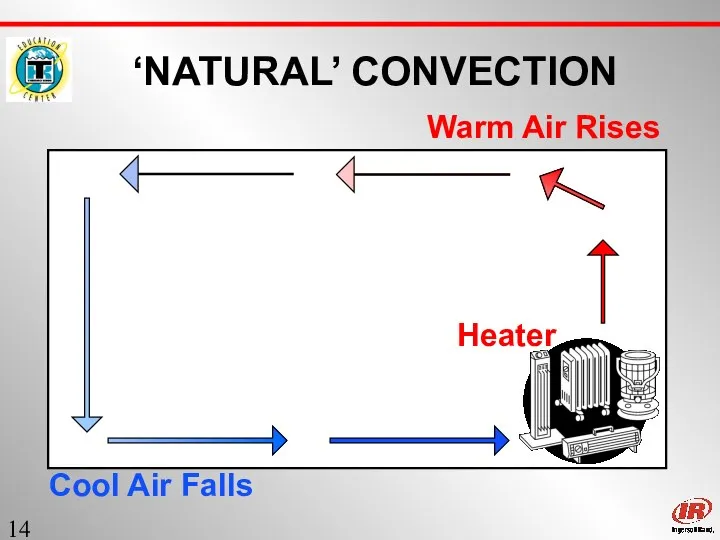
- 14. Sect. 1 ‘NATURAL’ CONVECTION Warm Air Rises Cool Air Falls Heater
- 15. Sect. 1 ‘NATURAL’ CONVECTION
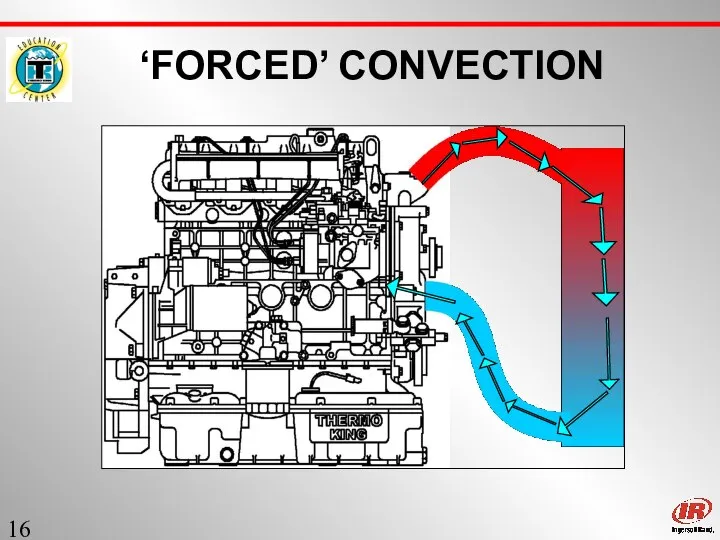
- 16. Sect. 1 ‘FORCED’ CONVECTION
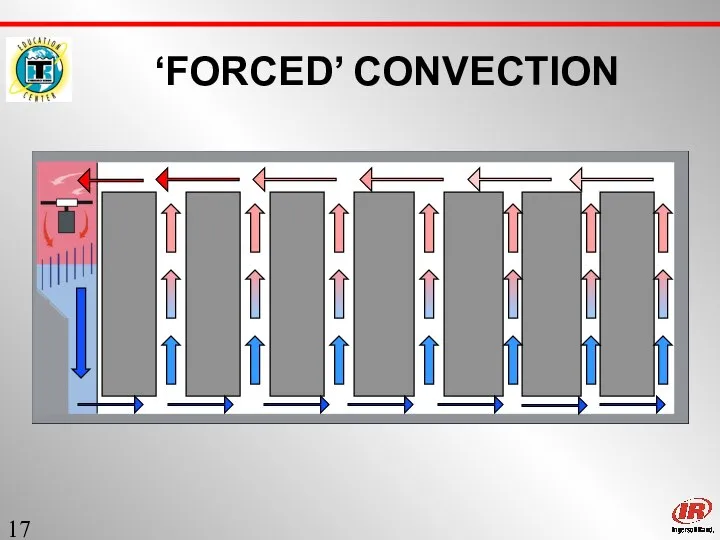
- 17. Sect. 1 ‘FORCED’ CONVECTION
- 18. Sect. 1 Any other Examples of Convection?
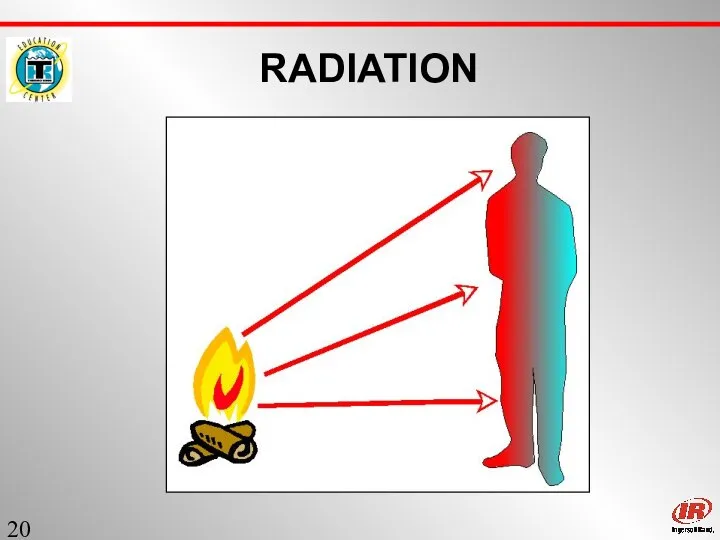
- 19. Sect. 1 RADIATION Moves in Straight Lines… like light Does not heat the air it passes
- 20. Sect. 1 RADIATION
- 21. Sect. 1 RADIATION
- 22. Sect. 1 Any other Examples of Radiation?
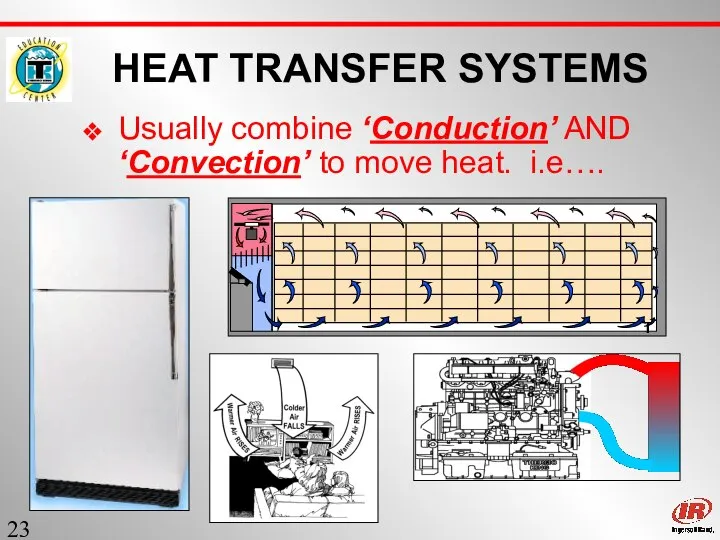
- 23. Sect. 1 HEAT TRANSFER SYSTEMS Usually combine ‘Conduction’ AND ‘Convection’ to move heat. i.e….
- 24. Sect. 1 TERMS TO REMEMBER Refrigeration Heat Box Conduction Convection Radiation
- 25. Sect. 1 HOW IS HEAT ‘MEASURED’? Four (4) Ways…. Temperature Sensible Heat British Thermal Unit (BTU)
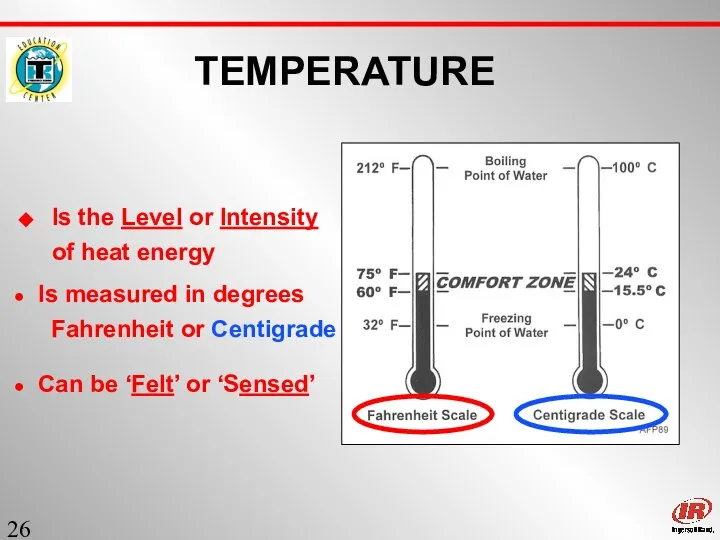
- 26. Sect. 1 TEMPERATURE Is the Level or Intensity of heat energy Is measured in degrees Fahrenheit
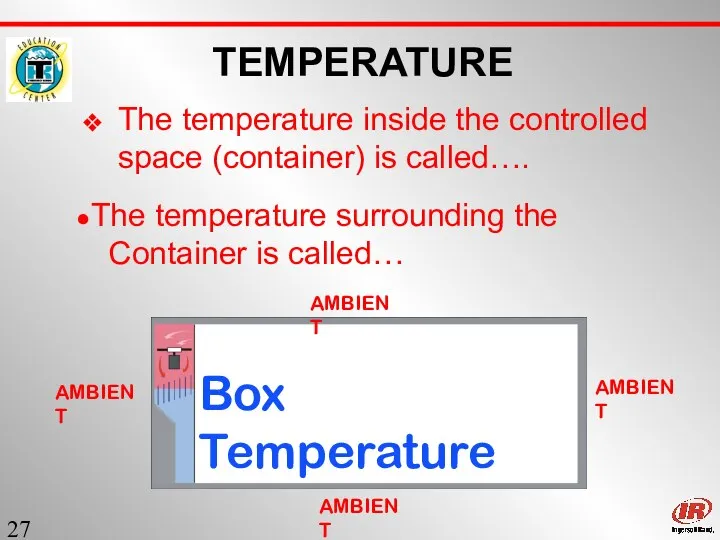
- 27. Sect. 1 TEMPERATURE The temperature inside the controlled space (container) is called…. Box Temperature AMBIENT AMBIENT
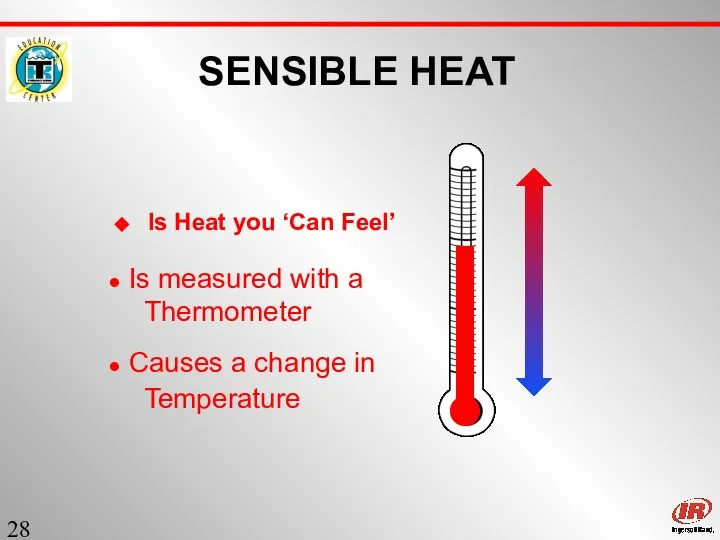
- 28. Sect. 1 SENSIBLE HEAT Is Heat you ‘Can Feel’ Is measured with a Thermometer Causes a
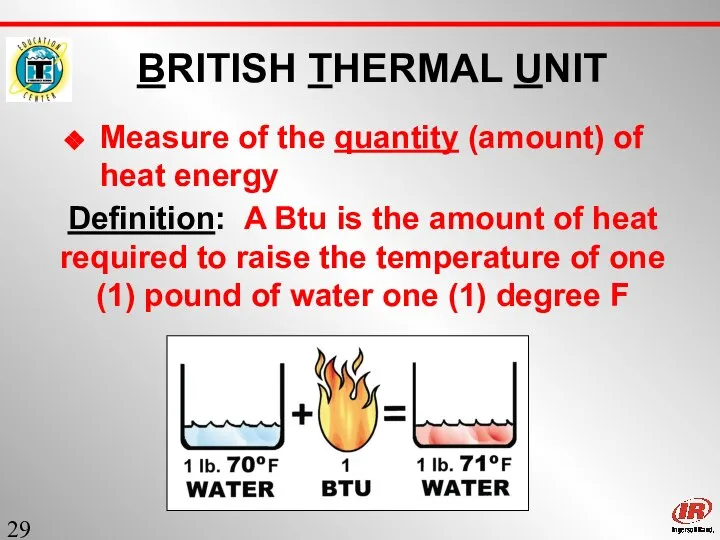
- 29. Sect. 1 BRITISH THERMAL UNIT Measure of the quantity (amount) of heat energy Definition: A Btu
- 30. Sect. 1 SPECIFIC HEAT Amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one (1) pound
- 31. Sect. 1 SPECIFIC HEAT EXAMPLES Water - 1.0 Aluminum - .22 Honey - .35 Cheese -
- 32. Sect. 1 TERMS TO REMEMBER Temperature Box Temperature Ambient Temperature Sensible Heat Btu Specific Heat
- 34. Скачать презентацию



















 Презентация по физике "тест " закон всемирного тяготения"" - скачать
Презентация по физике "тест " закон всемирного тяготения"" - скачать  Основы теории антенн. Лекция № 5. АФУ
Основы теории антенн. Лекция № 5. АФУ Оптическая активность
Оптическая активность Условие равновесия рычагов. Правило моментов
Условие равновесия рычагов. Правило моментов Основы электротехники
Основы электротехники Теплопроводность
Теплопроводность Электромагнитные излучения небесных тел
Электромагнитные излучения небесных тел Геометрические характеристики поперечных сечений
Геометрические характеристики поперечных сечений Устройство автомобиля
Устройство автомобиля Магнитный поток. Решение задач
Магнитный поток. Решение задач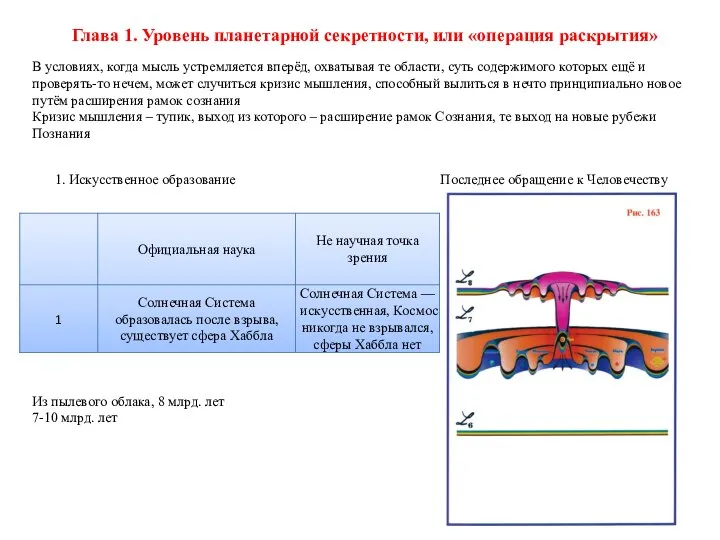 Уровень планетарной секретности, или операция раскрытия
Уровень планетарной секретности, или операция раскрытия Система контроля качества турбинного масла
Система контроля качества турбинного масла "Работа и мощность электрического тока
"Работа и мощность электрического тока Элементы квантовой физики. Гипотеза Планка
Элементы квантовой физики. Гипотеза Планка Електростатика Електричний заряд. Закон збереження електричного заряду
Електростатика Електричний заряд. Закон збереження електричного заряду  Презентация Электромагнитное поле
Презентация Электромагнитное поле Преломление света (11 класс)
Преломление света (11 класс) Ядерные технологии
Ядерные технологии Учебный курс «Термодинамика и теплопередача». Практическое занятие 2
Учебный курс «Термодинамика и теплопередача». Практическое занятие 2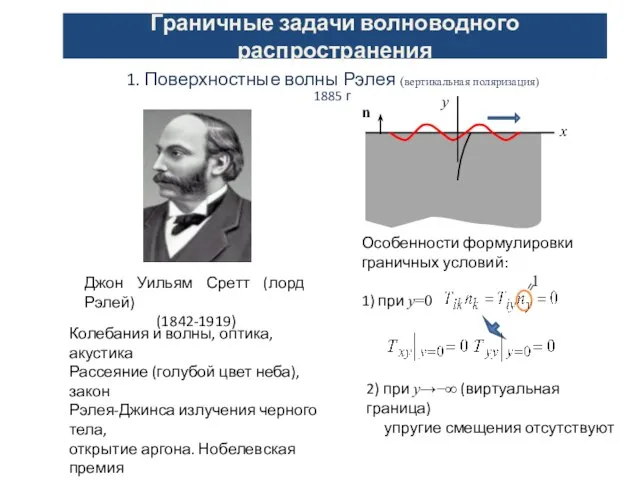 Граничные задачи волноводного распространения
Граничные задачи волноводного распространения Атомно-молекулярное учение
Атомно-молекулярное учение Лекция 6
Лекция 6  Расчет теплообменных аппаратов
Расчет теплообменных аппаратов Явление электромагнитной индукции. (лекция 3б)
Явление электромагнитной индукции. (лекция 3б) Принципы симметрии Категории симметрии, асимметрии.
Принципы симметрии Категории симметрии, асимметрии. Элементы строения вещества
Элементы строения вещества Закон Кулона
Закон Кулона Поле в диэлектрике
Поле в диэлектрике