Содержание
- 2. Just: people treated the way they deserve Effective: producing greatest good at least cost What is
- 3. What is just? Substantive justice Treat people as they deserve Treat everyone equally Contribute more, get
- 4. Procedural justice Arbitrary action vs. due process Special basic rights (which ones?) Overriding social needs: do
- 5. Effectiveness Are gains greater than costs? Is it as efficient as can possibly be? Any unanticipated
- 6. FOR DISCUSSION The Mayor of Ozzville decides to help parents raise their children. There will be
- 7. Market vs. Government Market: the “invisible hand” Government authority: rules, laws, etc. Government can tweak markets
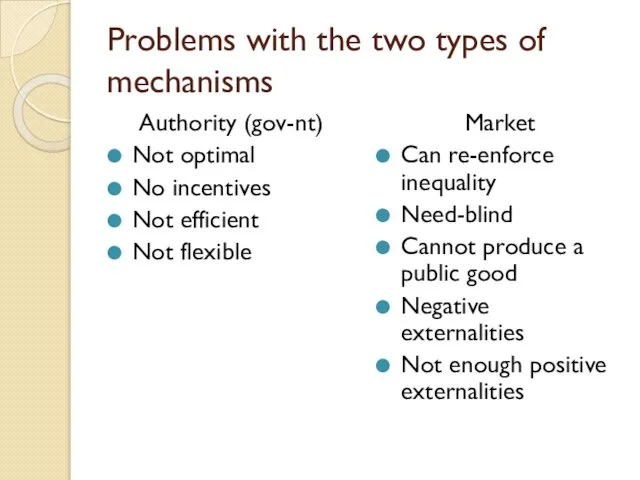
- 8. Problems with the two types of mechanisms Authority (gov-nt) Not optimal No incentives Not efficient Not
- 10. Скачать презентацию






 Политические партии и движения в политической системе
Политические партии и движения в политической системе Государственная политика в сфере занятости
Государственная политика в сфере занятости Политика и политическая власть
Политика и политическая власть Международные конфликты: причины и сущность
Международные конфликты: причины и сущность Суспільно-політичне та економічне життя України у 2005—2010 рр
Суспільно-політичне та економічне життя України у 2005—2010 рр Propaganda
Propaganda Региональная власть в системе политических сетей
Региональная власть в системе политических сетей Гадаад бодлогын зорилго
Гадаад бодлогын зорилго Классические концепции политических элит. Теории элит Г. Моски, В. Парето, Р. Михельса
Классические концепции политических элит. Теории элит Г. Моски, В. Парето, Р. Михельса Допомога Бельгії Україні
Допомога Бельгії Україні Разновидности политических режимов
Разновидности политических режимов Политический режим
Политический режим Юридическая техника в Венесуэле
Юридическая техника в Венесуэле Королевство Саудовская Аравия. Особенности конституционной истории и общественного строя
Королевство Саудовская Аравия. Особенности конституционной истории и общественного строя Политические партии и движения
Политические партии и движения Поликультурное образование в Республике Казахстан
Поликультурное образование в Республике Казахстан Влияние образов прошлого на современную региональную политическую культуру
Влияние образов прошлого на современную региональную политическую культуру 9 ноября - Международный день против фашизма, расизма и антисемитизма
9 ноября - Международный день против фашизма, расизма и антисемитизма Демократия. Народовластие
Демократия. Народовластие Позитивистский подход в типологии обществ
Позитивистский подход в типологии обществ Договор о дальнейшем сокращении и ограничении стратегических наступательных вооружений СНВ II
Договор о дальнейшем сокращении и ограничении стратегических наступательных вооружений СНВ II Политические партии
Политические партии Исламский радикализм
Исламский радикализм Политические партии России
Политические партии России Кандидат президента МБОУ СОШ №11
Кандидат президента МБОУ СОШ №11 Демократия
Демократия Футуристические концепции культуры
Футуристические концепции культуры Государство как основной механизм управления общественными процессами
Государство как основной механизм управления общественными процессами