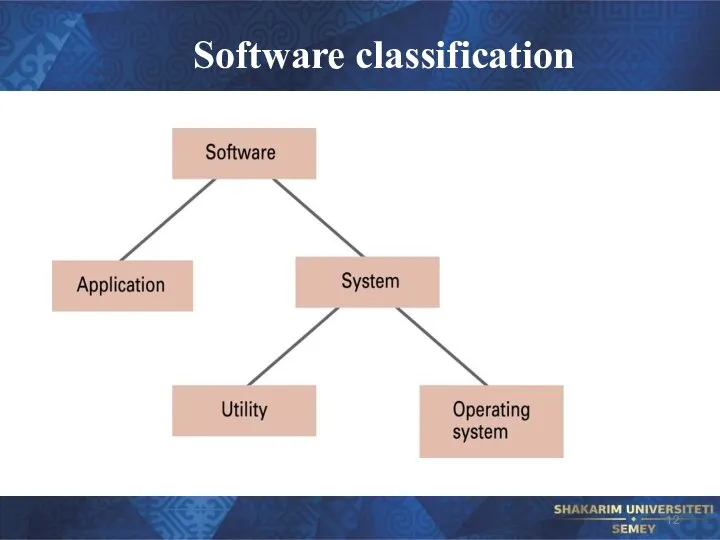
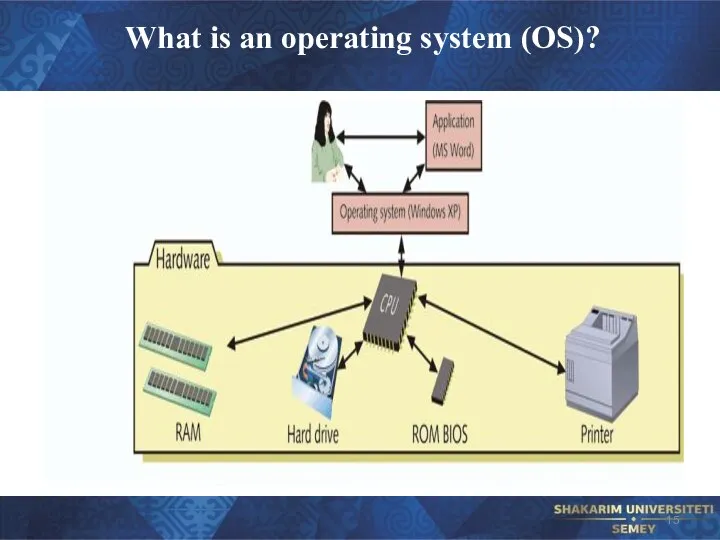
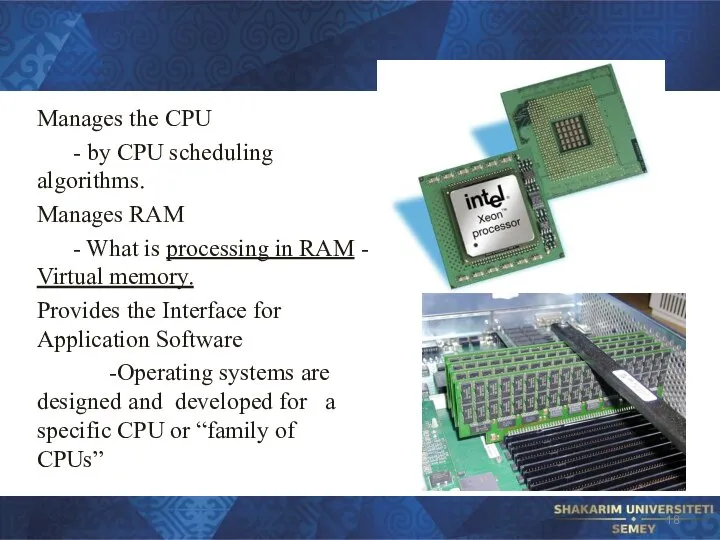
Слайд 9

Classification of operating systems.
Handheld operating systems are much smaller and less capable
than desktop operating systems, so that they can fit into the limited memory of handheld devices. Barcode scanners, PDA’s, are examples of such systems. Currently, the PDA world is witnessing an operating system battle between several players (Microsoft Windows, iPAQ, etc.)
Real time operating systems (RTOS) are designed to respond to events that happen in real time. Computers using such operating systems may run ongoing processes in a factory, emergency room systems, air traffic control systems or power stations. The operating systems are classified according to the response time they need to deal with: seconds, milliseconds, micro-seconds. They are also classified according to whether or not they involve systems where failure can result in loss of life. As in the case of supercomputers, there are no such systems in Lebanon today. However, given the way the technology is growing, it may be possible to use them in the future.
Embedded systems are combinations of processors and special software that are inside another device, such as contents switches or Network Attached Storage devices.
Smart Card Operating Systems are the smallest Operating Systems of all. Some handle only a single function, such as electronic payments, others handle multiple functions. Often these OS are proprietary systems but we are seeing more and more smart cards that are Java oriented.
Specialized Operating systems, like Database Computers are dedicated high performance data warehousing servers.
The above Operating Systems are commonly found in government agencies and private industries.






















 Компьютер, как исполнитель команд
Компьютер, как исполнитель команд Представление графической информации. Виды графики
Представление графической информации. Виды графики Сравнение и анализ методов присвоения значений управляющих сигналов RLO в языке FBD
Сравнение и анализ методов присвоения значений управляющих сигналов RLO в языке FBD Cloud computing (облачные технологии)
Cloud computing (облачные технологии) Презентация по информатике Компьютерная графика
Презентация по информатике Компьютерная графика  Основные операторы. Лекция 2 по алгоритмизации и программированию
Основные операторы. Лекция 2 по алгоритмизации и программированию Презентацию подготовила Машкина Татьяна Анатольевна, учитель информатики МБОУ «СОШ №92»
Презентацию подготовила Машкина Татьяна Анатольевна, учитель информатики МБОУ «СОШ №92»  Двоичное кодирование. Информация и информационные процессы
Двоичное кодирование. Информация и информационные процессы История Turbo Pascal
История Turbo Pascal Әдеби мәліметтер көздерінің критикалық анализі. Плагиат және антиплагиат
Әдеби мәліметтер көздерінің критикалық анализі. Плагиат және антиплагиат Обзор основных возможностей Kali Linux
Обзор основных возможностей Kali Linux Enstella systems data recovery
Enstella systems data recovery Классификация задач конструкторского проектирования (лекция 2)
Классификация задач конструкторского проектирования (лекция 2)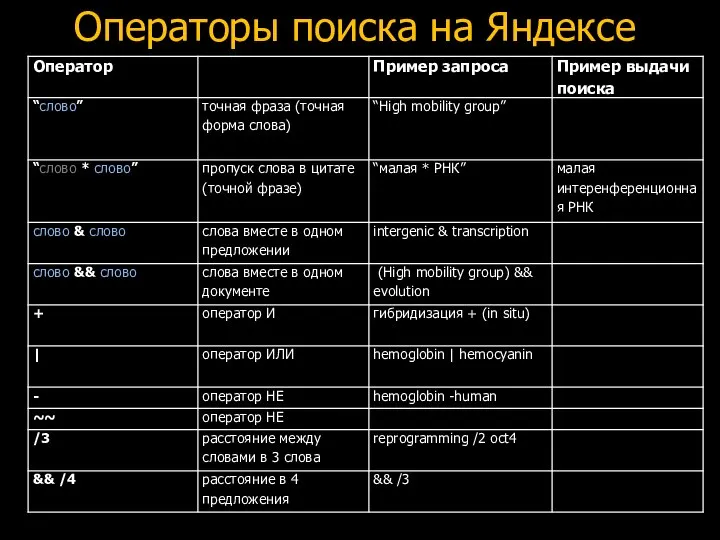 Операторы поиска на Яндексе
Операторы поиска на Яндексе Алгоритм. Свойства и формы
Алгоритм. Свойства и формы З Україною в серці
З Україною в серці Основы HTML
Основы HTML CALS/ИПИ как основная стратегия выживания в условиях рыночной экономики
CALS/ИПИ как основная стратегия выживания в условиях рыночной экономики Системы счисления
Системы счисления UT Inc, Universal Technologies Incorporated. Умный холодильник
UT Inc, Universal Technologies Incorporated. Умный холодильник Как составить резюме, сопроводительное и мотивационное письмо
Как составить резюме, сопроводительное и мотивационное письмо Прекрасное и безобразное на примере дизайна сайтов. Описание по критериям формы
Прекрасное и безобразное на примере дизайна сайтов. Описание по критериям формы Гаджимурадова Жанна Магомедовна учитель информатики МБОУ «СОШ №11» г. Чебоксары Всероссийский сетевой педагогический проект: «А
Гаджимурадова Жанна Магомедовна учитель информатики МБОУ «СОШ №11» г. Чебоксары Всероссийский сетевой педагогический проект: «А Сообщества ОК. SS socialjet
Сообщества ОК. SS socialjet Каскадные таблицы стилей CSS
Каскадные таблицы стилей CSS Вычислительная система (ВС)
Вычислительная система (ВС) SQL. Ռելացիոն բազայի կառուցվածքը
SQL. Ռելացիոն բազայի կառուցվածքը Стадии жизненного цикла ИС. (Лекция 3)
Стадии жизненного цикла ИС. (Лекция 3)