Содержание
- 2. Computer Network Evolution 1960s: Terminals access shared host computer SAGE; SABRE airline reservation system Tree-topology terminal-oriented
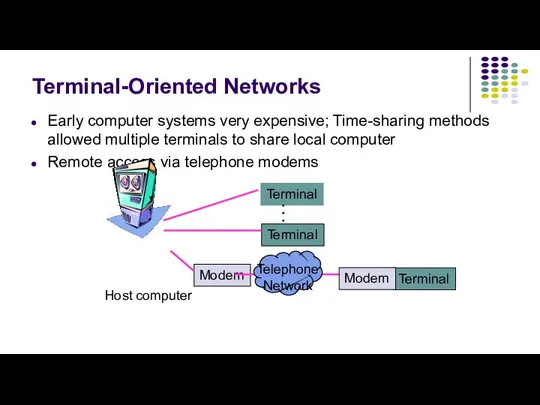
- 3. Terminal-Oriented Networks Early computer systems very expensive; Time-sharing methods allowed multiple terminals to share local computer
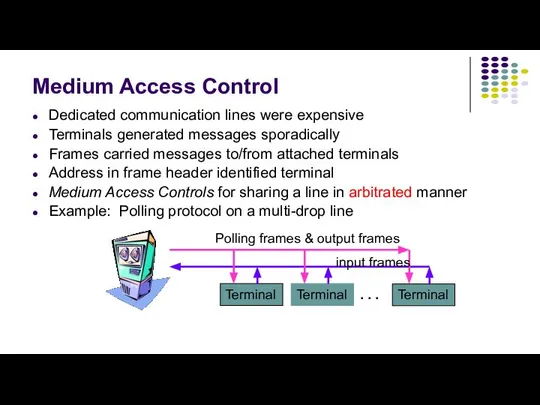
- 4. Dedicated communication lines were expensive Terminals generated messages sporadically Frames carried messages to/from attached terminals Address
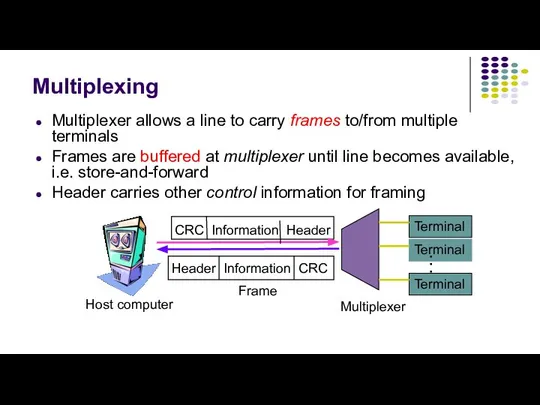
- 5. Multiplexing Multiplexer allows a line to carry frames to/from multiple terminals Frames are buffered at multiplexer
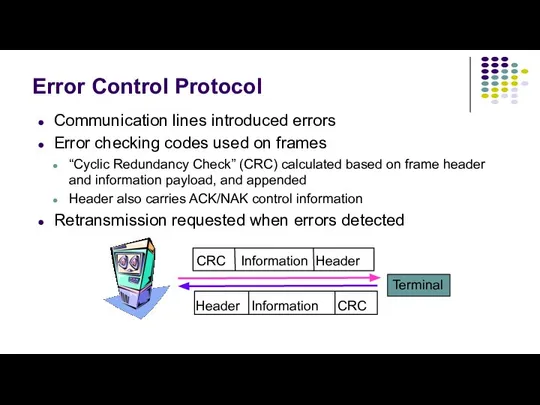
- 6. Error Control Protocol Communication lines introduced errors Error checking codes used on frames “Cyclic Redundancy Check”
- 7. Computer-to-Computer Networks As cost of computing dropped, terminal-oriented networks viewed as too inflexible and costly Need
- 8. Packet Switching Network should support multiple applications Transfer arbitrary message size Low delay for interactive applications
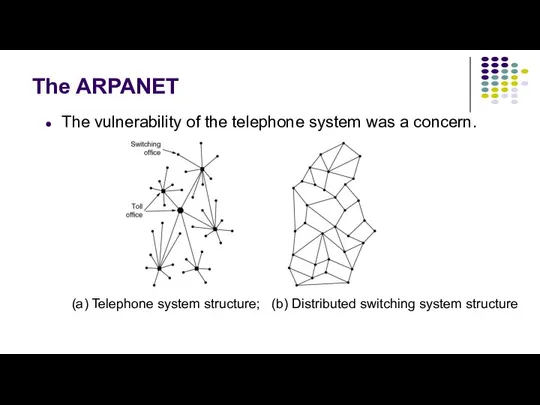
- 9. The ARPANET The vulnerability of the telephone system was a concern. (a) Telephone system structure; (b)
- 10. The ARPANET Design Connection-less packet transmission Packets are encapsulated in frames Error control uses check bits
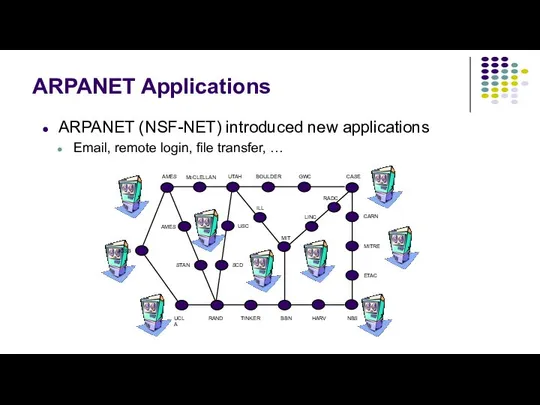
- 11. ARPANET Applications ARPANET (NSF-NET) introduced new applications Email, remote login, file transfer, …
- 12. Ethernet Local Area Network In 1980s, affordable workstations available Need for low-cost, low error rate, high-speed
- 14. Скачать презентацию


 Текстовые редакторы
Текстовые редакторы Серия семинаров и/или тренингов в дистанционной форме по теме «Как эффективно использовать сервисы Веб 2.0 для создания учебного п
Серия семинаров и/или тренингов в дистанционной форме по теме «Как эффективно использовать сервисы Веб 2.0 для создания учебного п Презентация на тему Алгоритм. Свойства алгоритма.
Презентация на тему Алгоритм. Свойства алгоритма. Международный день защиты информации
Международный день защиты информации Проектирование баз данных. Метод ER-диаграмм. Основы программирования и базы данных
Проектирование баз данных. Метод ER-диаграмм. Основы программирования и базы данных Разработка АИС для учета передвижения продукции
Разработка АИС для учета передвижения продукции Кодирование информации. В мире кодов
Кодирование информации. В мире кодов История операционных систем
История операционных систем Электронные таблицы
Электронные таблицы Памятка по проверке документов из Росреестра
Памятка по проверке документов из Росреестра Устройства хранения информации. Внешняя память компьютера. Накопители
Устройства хранения информации. Внешняя память компьютера. Накопители Призначення браузерів. (9 клас)
Призначення браузерів. (9 клас) Моделирование, формализация, визуализация
Моделирование, формализация, визуализация Windows приложения. Компоненты формы. Многооконные приложения
Windows приложения. Компоненты формы. Многооконные приложения Профессия таргетолога и SMM-специалиста с нуля до первых проектов
Профессия таргетолога и SMM-специалиста с нуля до первых проектов Роль SMS-сообщений в жизни человека
Роль SMS-сообщений в жизни человека Правовая информатика Конспект лекций в слайдах
Правовая информатика Конспект лекций в слайдах  Dressage Training Tips from Experts
Dressage Training Tips from Experts Презентация по информатике Кодирование информации
Презентация по информатике Кодирование информации Путешествие по клавишам
Путешествие по клавишам Основные этапы моделирования Цель моделирования.
Основные этапы моделирования Цель моделирования. Обработка событий в AWT. Классы-обертки (Java)
Обработка событий в AWT. Классы-обертки (Java) Формы представления информационных моделей. Построение словесной модели в среде текстового редактора
Формы представления информационных моделей. Построение словесной модели в среде текстового редактора Основные устройства компьютера
Основные устройства компьютера Киберспорт в жизни тинейджеров
Киберспорт в жизни тинейджеров Кейс по созданию сайта математических статей
Кейс по созданию сайта математических статей Средства информационных и коммуникационных технологий. Защита информации
Средства информационных и коммуникационных технологий. Защита информации Аквариум
Аквариум