Содержание
- 2. Agenda Basic Information How to include JS Code into HTML Comments Variables Data Types Type Casting
- 3. Basic information JavaScript - dynamic computer programming language. It is most commonly used as part of
- 4. 1. Inline JavaScript: 2. Internal tag : alert('Hello!'); 3. External file: How to add JavaScript to
- 5. Comments Comments - part of the program text which will be ignored by language interpreter The
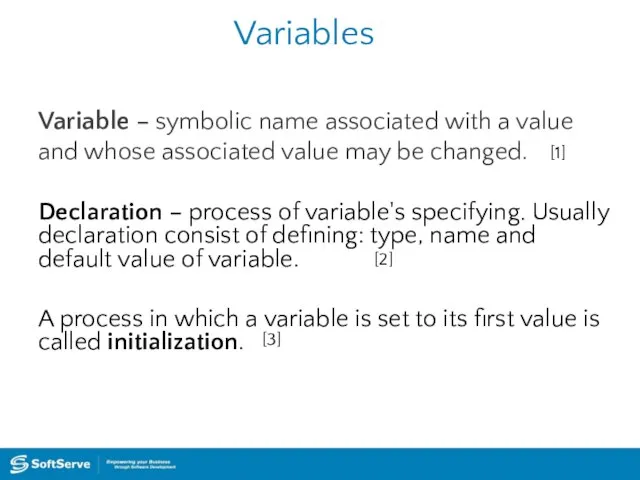
- 6. Variables Variable – symbolic name associated with a value and whose associated value may be changed.
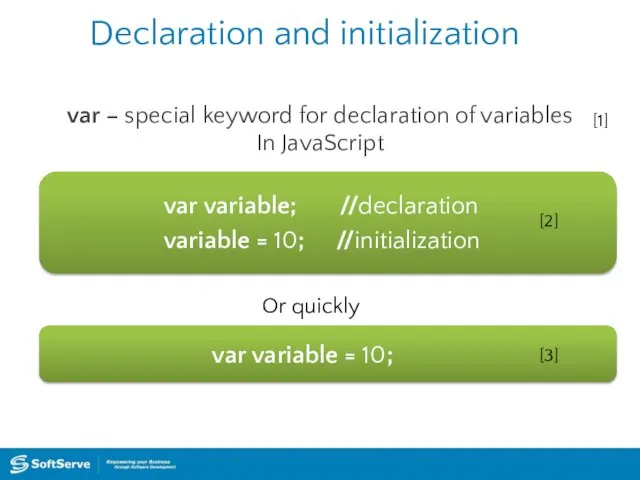
- 7. Declaration and initialization var – special keyword for declaration of variables In JavaScript var variable; //declaration
- 8. Global and local JavaScript has two types of variables: global - exist in memory and is
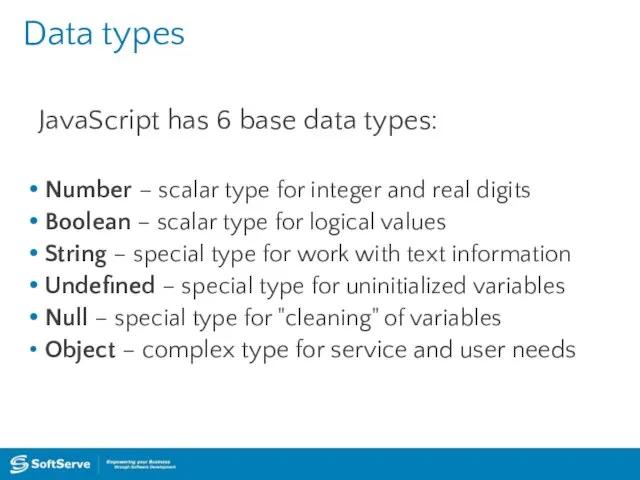
- 9. Data types JavaScript has 6 base data types: Number – scalar type for integer and real
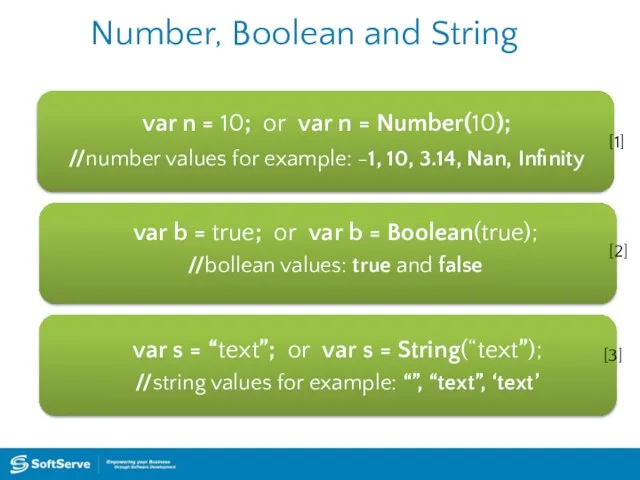
- 10. Number, Boolean and String var n = 10; or var n = Number(10); //number values for
- 11. Null and Undefined var n = null; //null variables can have only null value var u;
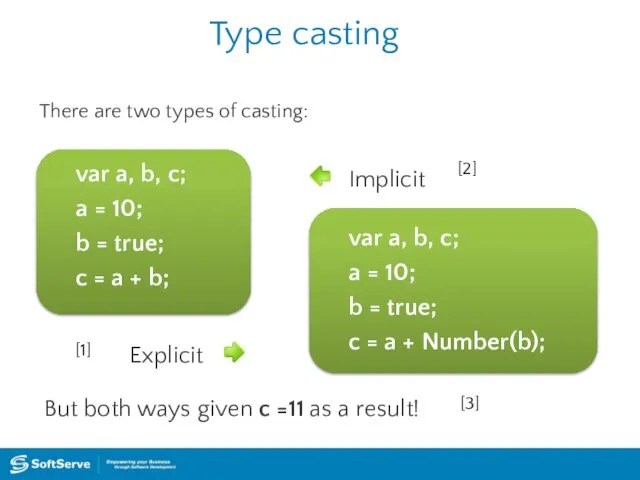
- 12. Type casting var a, b, c; a = 10; b = true; c = a +
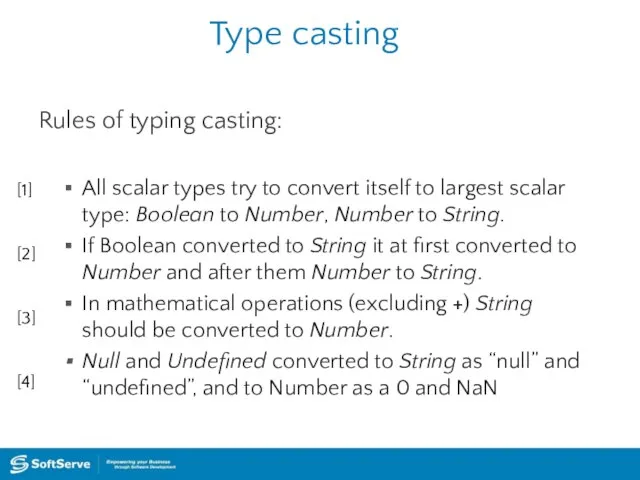
- 13. Type casting Rules of typing casting: All scalar types try to convert itself to largest scalar
- 14. Functions In mathematics: In classical programming [3] Function is a relation between a set of inputs
- 15. Example var i, base, power, result; base = 2; power = 2; result = 1; for(i
- 16. Function Declaration function name (a, b) { return a + b; } [1] * you can
- 17. Function call Call - operation for execution of function. ( ) – operator for this action.
- 18. Example var out; out = pow(2, 2); console.log(out); out = pow(3, 4); console.log(out); function pow (base,
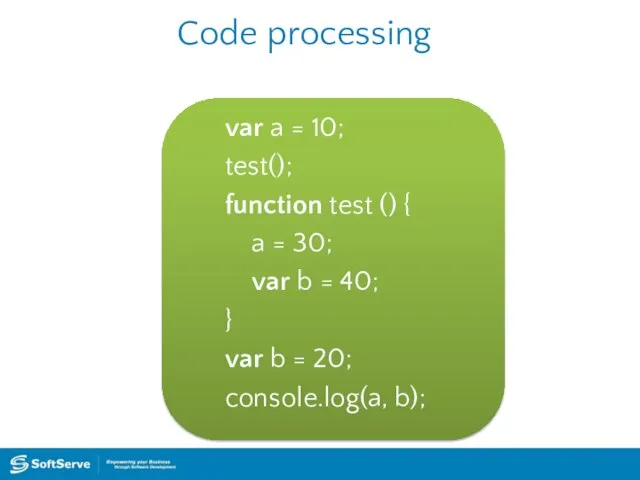
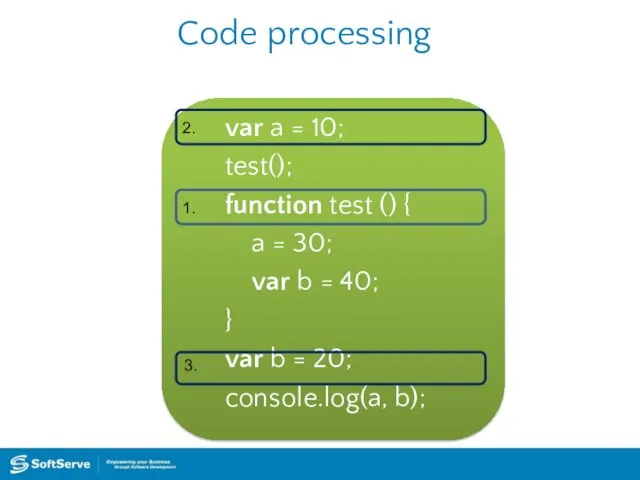
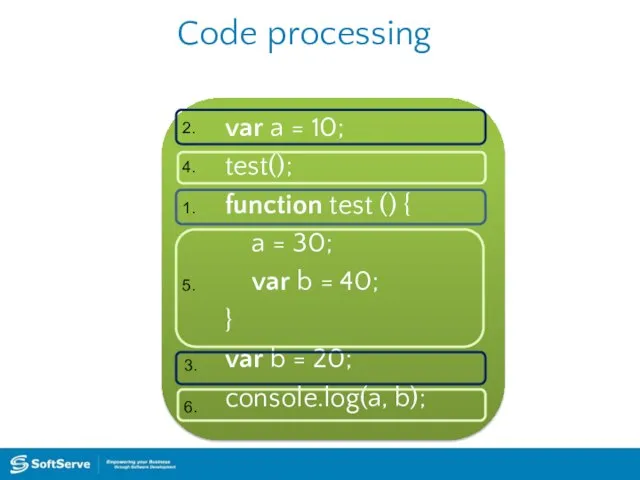
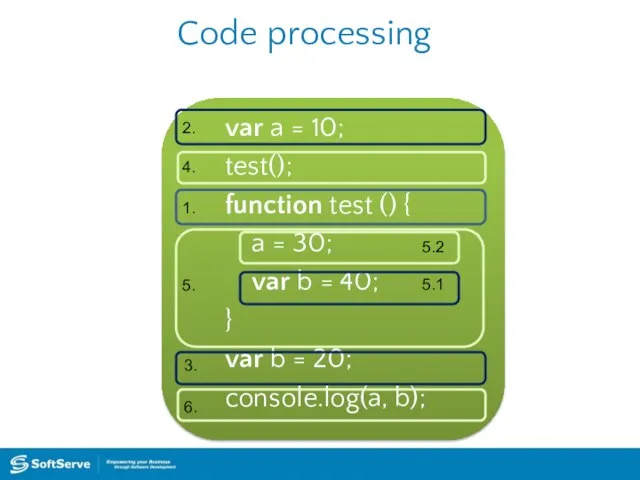
- 19. Code processing var a = 10; test(); function test () { a = 30; var b
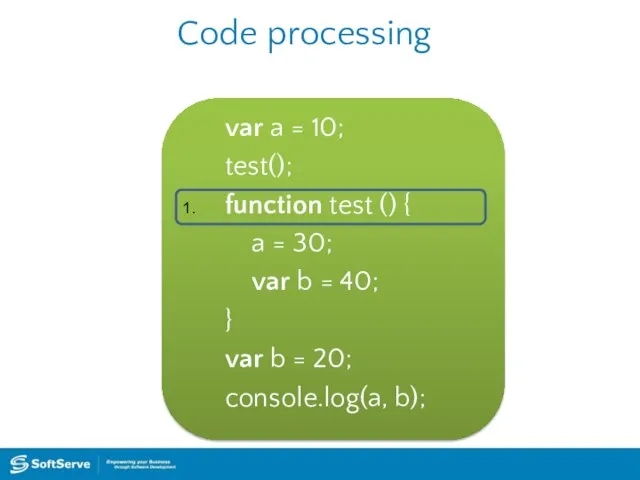
- 20. Code processing var a = 10; test(); function test () { a = 30; var b
- 21. Code processing var a = 10; test(); function test () { a = 30; var b
- 22. Code processing var a = 10; test(); function test () { a = 30; var b
- 23. Code processing var a = 10; test(); function test () { a = 30; var b
- 24. Function Declaration and Expression function name () { body; } [1] var name = function ()
- 25. Additional Facts About Functions Functions in JavaScript are Objects. As a result, functions are accessible by
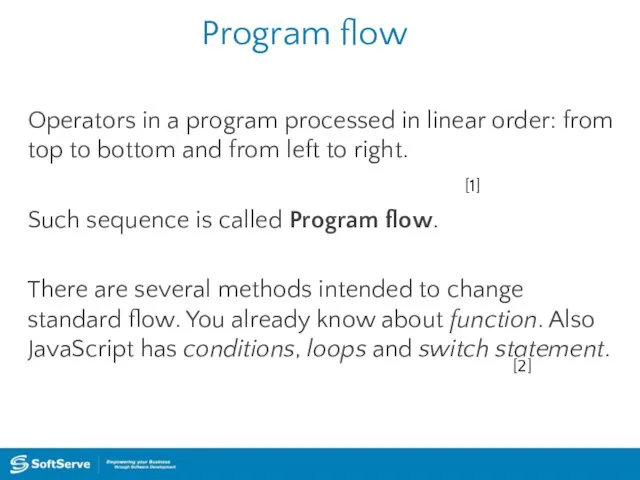
- 26. Program flow Operators in a program processed in linear order: from top to bottom and from
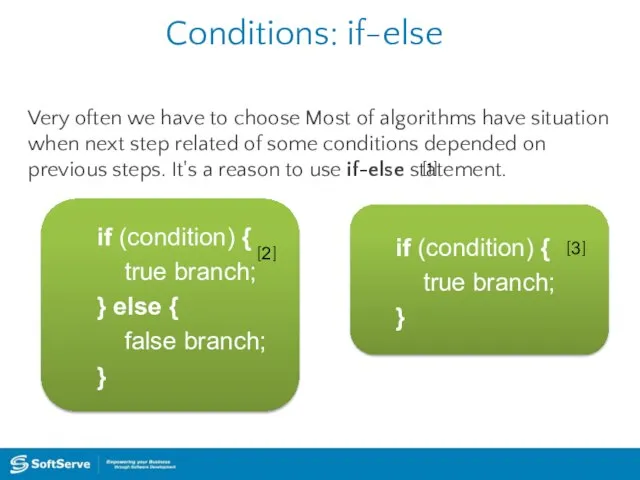
- 27. Conditions: if-else Very often we have to choose Most of algorithms have situation when next step
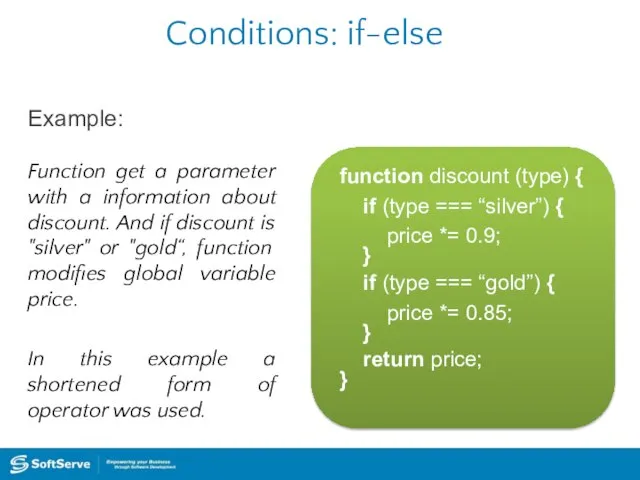
- 28. Conditions: if-else Example: function discount (type) { if (type === “silver”) { price *= 0.9; }
- 29. Conditions: ?: Sometimes if-else too bulky. If we need to initialize a variable modifying it by
- 30. Conditions: ?: function discount (type) { if (type === “silver”) { price *= 0.9; } if
- 31. Loops: for Loops are used when algorithm requires repeating of statements. First of them: for -
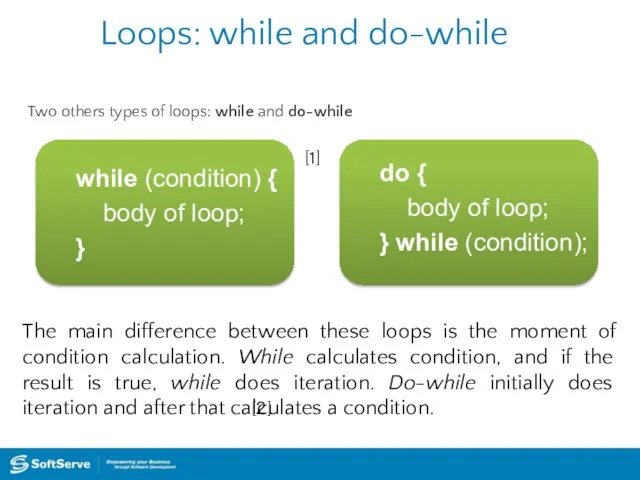
- 32. Loops: while and do-while Two others types of loops: while and do-while while (condition) { body
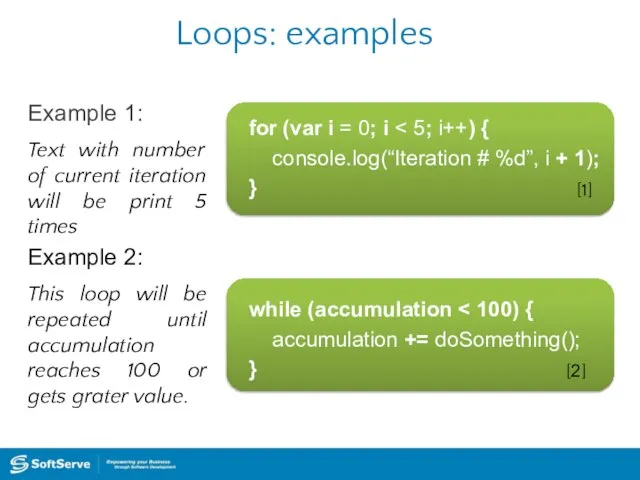
- 33. Loops: examples Example 1: for (var i = 0; i console.log(“Iteration # %d”, i + 1);
- 34. Loops: break and continue There are two keywords for loops control : break – aborts loop
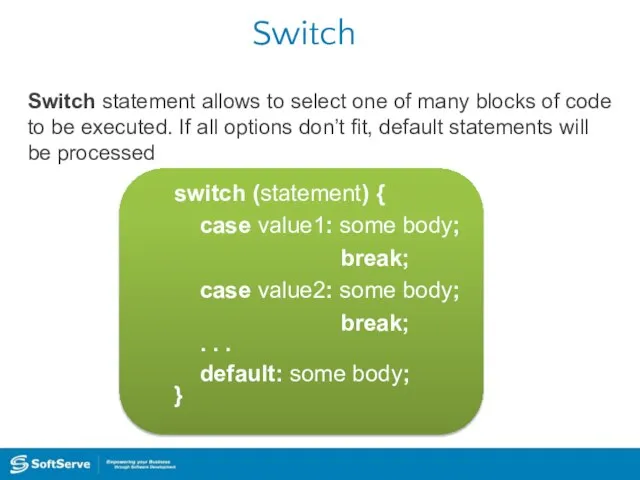
- 35. Switch Switch statement allows to select one of many blocks of code to be executed. If
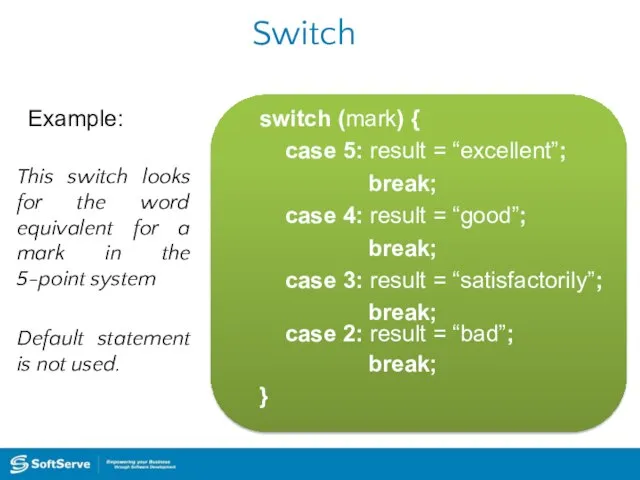
- 36. Switch Example: This switch looks for the word equivalent for a mark in the 5-point system
- 37. Practice Task
- 39. Скачать презентацию






![Functions In mathematics: In classical programming [3] Function is a relation](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/528420/slide-13.jpg)




![Function Declaration and Expression function name () { body; } [1]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/528420/slide-23.jpg)






 Изменение размера массива. Очередь с приоритетом. Бинарная пирамида. Пирамидальная сортировка
Изменение размера массива. Очередь с приоритетом. Бинарная пирамида. Пирамидальная сортировка Создание проекта для графики
Создание проекта для графики Кабинет информатики
Кабинет информатики Интерфейсы и абстрактные классы. (Лекция 2)
Интерфейсы и абстрактные классы. (Лекция 2) Основные правила ввода текста в текстовом процессоре WORD МОУ СОШ № 35 г. Нижний Новгород Учителя информатики: Л.Л. Зинченко, В.Н. Ме
Основные правила ввода текста в текстовом процессоре WORD МОУ СОШ № 35 г. Нижний Новгород Учителя информатики: Л.Л. Зинченко, В.Н. Ме Я – РОССИЯНИН! 20-летию Конституции Российской Федерации
Я – РОССИЯНИН! 20-летию Конституции Российской Федерации Программирование. Работа с символами
Программирование. Работа с символами Лекция 2. Растровая графика
Лекция 2. Растровая графика Склад персонального комп'ютера
Склад персонального комп'ютера Создание слайдов с триггерами. Применение
Создание слайдов с триггерами. Применение Microsoft Excel для создания информационных объектов Выполнил: студент гр. МиИ-5Б Иванов Леонид Юрьевич Руководитель: Софронова Натал
Microsoft Excel для создания информационных объектов Выполнил: студент гр. МиИ-5Б Иванов Леонид Юрьевич Руководитель: Софронова Натал Реализация проекта Память объединяет нас
Реализация проекта Память объединяет нас Какие бывают программисты
Какие бывают программисты Технические аспекты использования интернета
Технические аспекты использования интернета Система учета потребления коммунальных ресурсов
Система учета потребления коммунальных ресурсов Програма Lazarus
Програма Lazarus Microsoft Office Еxcel
Microsoft Office Еxcel 9 класс II
9 класс II Типовые ошибки, допускаемые заявителями при подаче заявления для присвоения, подтверждения или снятия квалификационных категорий
Типовые ошибки, допускаемые заявителями при подаче заявления для присвоения, подтверждения или снятия квалификационных категорий Основная позиция пальцев на клавиатуре
Основная позиция пальцев на клавиатуре  Достижение целевого показателя
Достижение целевого показателя Установка и настройка VPN подключения
Установка и настройка VPN подключения Что такое ООП и с чем его едят
Что такое ООП и с чем его едят Lesson 4 guideline. Жизненный цикл бага
Lesson 4 guideline. Жизненный цикл бага Перспективы развития информационно-коммуникационных технологий
Перспективы развития информационно-коммуникационных технологий №2 Организация сети с использованием коммутатора
№2 Организация сети с использованием коммутатора Модели данных
Модели данных Masyvo rūšiavimas
Masyvo rūšiavimas