Содержание
- 2. Slide Today’s Agenda Regulatory requirements/business requirements Recommendations from the FDA Design Spreadsheet for Part 11/GxP compliance
- 3. Slide Regulations/Guidelines GxPs Systems should be suitable for intended use 21 CFR Part 11 – E-Signatures/Records
- 4. Slide Common Requirements Strict access control to the systems and data Record handling and maintenance Authenticity
- 5. Slide FDA Part 11 Validation Guidance Spreadsheet Calculations and Macro Programs used in GxP environments should
- 6. Slide FDA Warning Letters No procedures are established to validate for its intended purpose the Microsoft
- 7. Slide FDA Warning Letters Failure to validate computer software for its intended use according to an
- 8. Slide FDA Warning Letters "Your laboratory records did not include a record of all calculations performed
- 9. Slide Warning Letter Failure to use fully validated computer spreadsheets to calculate analytical results for in-process
- 10. Slide Verification of Corrective Actions These tests include the entry of the following types of data:
- 11. Slide Verification of Corrective Actions The package contains a list of the tests conducted and the
- 12. Slide Verification of Corrective Actions The firm now saves the spreadsheets in read-only form to compact
- 13. Slide European Medicines Agency GMP-Q&A Q: Which type of accuracy checks (Annex 11 p 6) are
- 14. Slide European Medicines Agency GMP-Q&A Q: Are there any specific considerations for the validation of spreadsheets?
- 15. Slide Compliance Problems with Spreadsheets Easy access to programs Everybody (not trained on GxP validation and
- 16. Slide What to do for GxP/Part 11 Compliance ? Use other programs e.g., perform calculations in
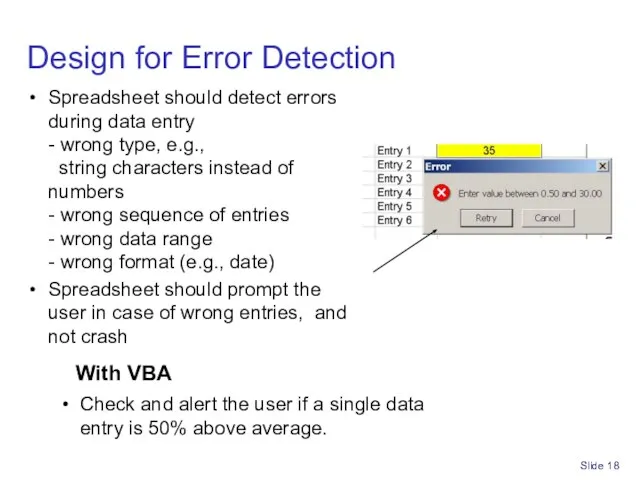
- 17. Slide Design Spreadsheets for Part 11/GxP Follow documented procedures Design for error detection Design with integrity
- 18. Slide With VBA Check and alert the user if a single data entry is 50% above
- 19. Slide Design for Integrity and Authenticity Protect all cells not used for data entry Protect use
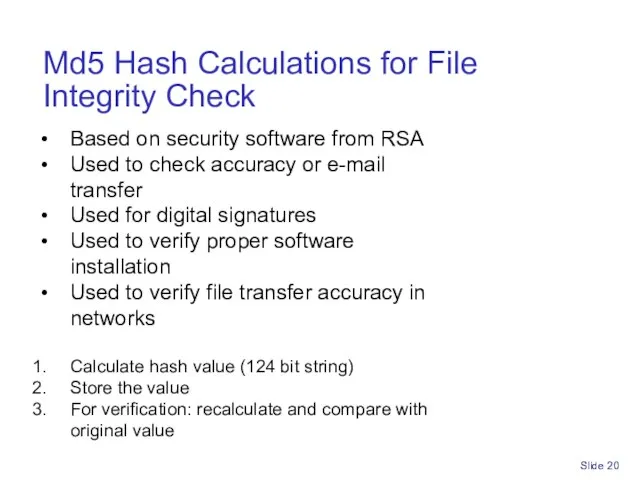
- 20. Slide Md5 Hash Calculations for File Integrity Check Based on security software from RSA Used to
- 21. Slide Design for Security Develop, implement and test procedures for limited system access to authorized users
- 22. Slide What to Validate / What not to Validate Not to Validate Excel software Standard calculations
- 23. Slide What does Validation of Spreadsheets Include? Planning Writing specifications - functional specifications - computer requirements
- 24. Slide Should we Test Standard Excel Functions? Standard functions used in normal operation range don’t need
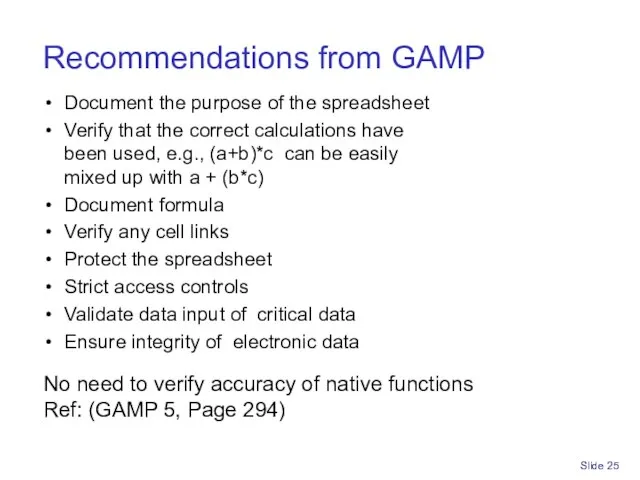
- 25. Slide Recommendations from GAMP Document the purpose of the spreadsheet Verify that the correct calculations have
- 26. Excel Spreadsheet Validation from Beginning to End (1) New spreadsheet proposed Proposal approved Establish validation team
- 27. Excel Spreadsheet Validation from Beginning to End (2) Develop functional specification test plan Distribute test plan
- 28. Slide How to Comply with the Audit Trail Requirement Procedures For low risk systems Print and
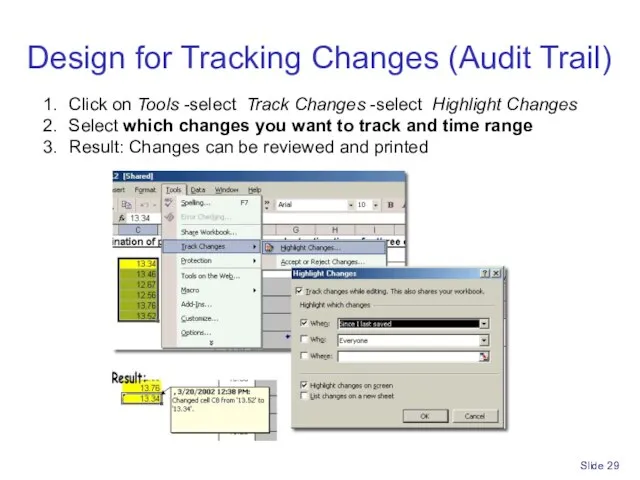
- 29. Slide Design for Tracking Changes (Audit Trail) Click on Tools -select Track Changes -select Highlight Changes
- 30. Slide Multi-User Excel Spreadsheets in FDA Laboratories Source: FDA LIB: Spreadsheet Design and Validation for the
- 31. Slide Test and document correct functioning (input/output, customized formula) Document used formula For direct input of
- 32. Slide Documentation for Part 11 FDA Recommendation: We recommend that each study protocol identifies at which
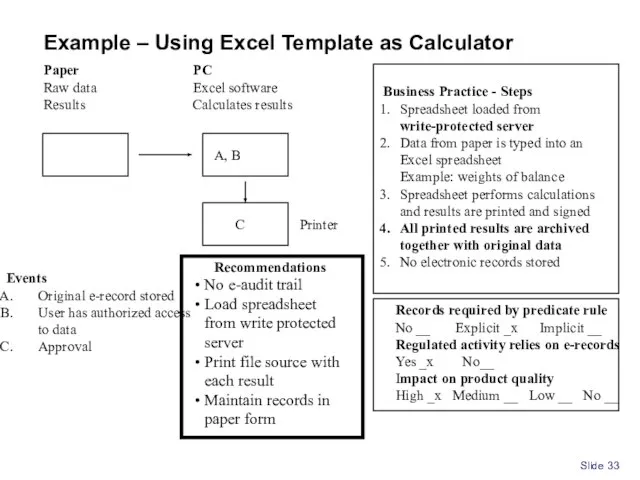
- 33. Slide Paper Raw data Results PC Excel software Calculates results Events Original e-record stored User has
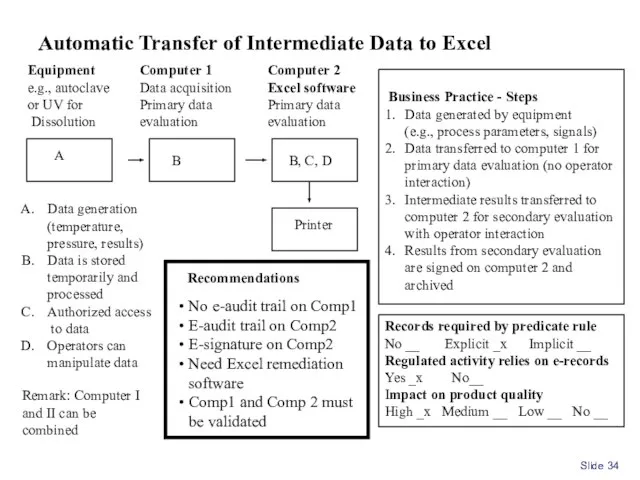
- 34. Slide Equipment e.g., autoclave or UV for Dissolution Computer 1 Data acquisition Primary data evaluation Data
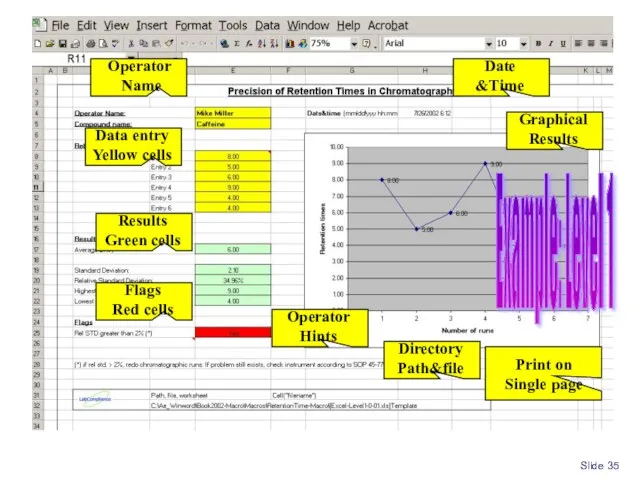
- 35. Slide Example: Level 1
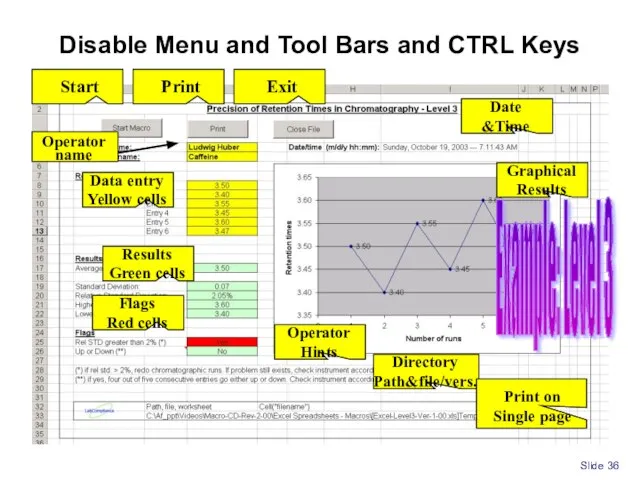
- 36. Slide Disable Menu and Tool Bars and CTRL Keys Example: Level 3
- 37. Slide Minimal Documentation (equally important for new and existing spreadsheets) A description of what the program
- 39. Скачать презентацию




























 ФОРМУЛЫ Учебное пособие по информатике. ©Новоженов С.М., 2007 г.
ФОРМУЛЫ Учебное пособие по информатике. ©Новоженов С.М., 2007 г.  введение в теорию систем
введение в теорию систем Návrh a programování databází (14NDB)
Návrh a programování databází (14NDB) Исключения. Программирование на JAVA
Исключения. Программирование на JAVA Измерение информации. Информационная характеристика источника двоичных сообщений
Измерение информации. Информационная характеристика источника двоичных сообщений Kydas Team. РосПравосудие
Kydas Team. РосПравосудие Компьютерные игры «за» и «против»
Компьютерные игры «за» и «против»  Розробка програмної системи Автобазар
Розробка програмної системи Автобазар Зарубежные информационные ресурсы негуманитарных отраслей науки и практики. (Тема 4)
Зарубежные информационные ресурсы негуманитарных отраслей науки и практики. (Тема 4) Презентация "История ЭВМ" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "История ЭВМ" - скачать презентации по Информатике Создание документов в текстовых редакторах
Создание документов в текстовых редакторах Инкапсуляция
Инкапсуляция Module 1: Introducing Siebel Applications
Module 1: Introducing Siebel Applications Презентация на тему Поисковые системы интернета
Презентация на тему Поисковые системы интернета  Застосування бази даних факультету інформатики
Застосування бази даних факультету інформатики Структуры данных. Система непересекающихся множеств
Структуры данных. Система непересекающихся множеств Словарь. (11 класс)
Словарь. (11 класс) Ақпараттық процеске рұқсатсыз кірісуден сақтану
Ақпараттық процеске рұқсатсыз кірісуден сақтану Производственная практика. ADO.NET и COM при работе с MS ACCESS и MS EXCEL в десктопном приложении
Производственная практика. ADO.NET и COM при работе с MS ACCESS и MS EXCEL в десктопном приложении Информатика и ИКТ (4 класс)
Информатика и ИКТ (4 класс) Система підтримки багатопотокової передачі. Структурна організація
Система підтримки багатопотокової передачі. Структурна організація Module 1: Functions and Organization. Topic 1.1: Why Use Functions?
Module 1: Functions and Organization. Topic 1.1: Why Use Functions? Базы данных - 5
Базы данных - 5 Лабораторная работа №2
Лабораторная работа №2 Презентация на тему Суперкомпьютеры
Презентация на тему Суперкомпьютеры  Передача информации
Передача информации Анализ моделей распространения сигналов в системах OFDM
Анализ моделей распространения сигналов в системах OFDM Компьютерная графика в школе
Компьютерная графика в школе