Содержание
- 2. The War of 1812
- 3. Election of 1808 James Madison (Republican) Charles Pinckney (Federalist)
- 4. War Hawks Supported war with Britain Henry Clay (KY) John Calhoun (SC)
- 5. Why Did Southerners and Westerners Support War? British trade restrictions hurt farmers Westerners blamed British for
- 6. Moving West Kentucky Tennessee Northwest Territory
- 7. Native American Resistance Little Turtle – chief of the Miami people Washington sent General Anthony Wayne
- 8. Treaty of Greenville August 1795 Indians gave up land in Ohio, Indiana, parts of Illinois and
- 9. Tecumseh Shawnee leader Believed Native Americans needed to unite to protect their lands
- 10. William Henry Harrison Governor of Indiana territory Won at the Battle of Tippecanoe Indian leaders fled
- 11. Declaration of War June 1812 President Madison asked Congress to declare war
- 12. Quote, Madison “Thousands of American citizens, under the safeguard of public law and of their national
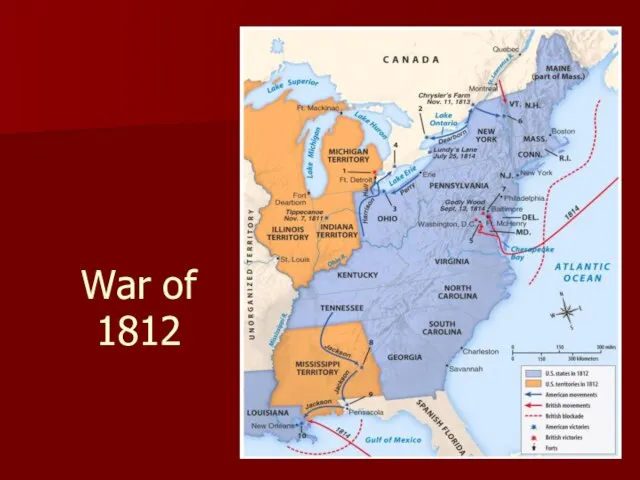
- 13. Invasion of Canada Attacked from Detroit, Niagara Falls, Hudson River Valley All failed
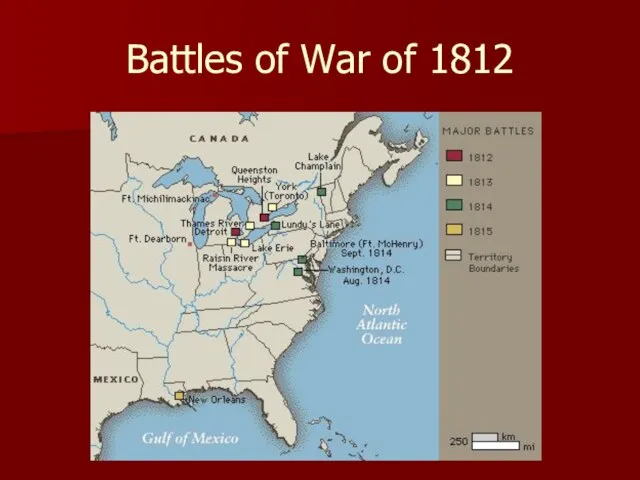
- 14. Battles of War of 1812
- 15. Oliver Hazard Perry Leader of Lake Erie Fleet Defeated the British Control for U.S. of Great
- 16. Washington D.C. August 1814 British fleet entered the city
- 17. Washington D.C. Madison and other leaders fled British set fire to the White House and the
- 18. Fort McHenry British marched on Baltimore Attacked Fort McHenry Not successful
- 19. Francis Scott Key He wrote The Star-Spangled Banner while watching this battle
- 20. Battle of Lake Champlain September 1814 U.S. Victory
- 21. Battle of New Orleans January 1815 British landed at New Orleans Victory for U.S. forces under
- 22. War of 1812
- 23. Treaty of Ghent Dec. 1814 Ended the War of 1812 England must honor U.S. boundaries
- 25. Скачать презентацию




















 Франция Бурбонов и Орлеанов - от революции 1830 г. к новому политическому кризису
Франция Бурбонов и Орлеанов - от революции 1830 г. к новому политическому кризису Гражданская война в России 1917 – 1922 гг
Гражданская война в России 1917 – 1922 гг Найди своего героя
Найди своего героя История военной песни. Смуглянка
История военной песни. Смуглянка Культура России в конце XIX - начале XX вв
Культура России в конце XIX - начале XX вв Türkleri̇n i̇slâmi̇yet’i̇ kabulü
Türkleri̇n i̇slâmi̇yet’i̇ kabulü Сталингра́дская би́тва. Пихтовская сельская библиотека
Сталингра́дская би́тва. Пихтовская сельская библиотека Сквозь опаленное войной детство
Сквозь опаленное войной детство О чём рассказывают гербы и эмблемы
О чём рассказывают гербы и эмблемы Памятники Петру I в Санкт-Петербурге
Памятники Петру I в Санкт-Петербурге Новая экономическая политика ДО
Новая экономическая политика ДО Развитие советской культуры 1945-1990 гг
Развитие советской культуры 1945-1990 гг Походы шведов на Русь в XII-XIII веках
Походы шведов на Русь в XII-XIII веках Моя прабабушка – Главатских Юлия Владимировна
Моя прабабушка – Главатских Юлия Владимировна Средневековые храмы и монастыри Ленинградской области.
Средневековые храмы и монастыри Ленинградской области.  Сыны Отечества - защитники Земли
Сыны Отечества - защитники Земли Битва при Гавгамелах. Немного из истории
Битва при Гавгамелах. Немного из истории Противоречивые 1990 годы в России: некоторые оценки и суждения с позиций современности ( по материалам СМИ и Интернет)
Противоречивые 1990 годы в России: некоторые оценки и суждения с позиций современности ( по материалам СМИ и Интернет)  Мемориал 253 жизни и одна судьба
Мемориал 253 жизни и одна судьба Eesti asi. Barclay de Tolly
Eesti asi. Barclay de Tolly Зависимость Руси от Орды и её последствия
Зависимость Руси от Орды и её последствия British slang of 19 century
British slang of 19 century Библейские сказания Презентацию подговила ученица 5 «Г» класса Грибова София
Библейские сказания Презентацию подговила ученица 5 «Г» класса Грибова София СТРАНЫ ЕВРОПЫ И СЕВЕРНОЙ АМЕРИКИ В КОН xix НАЧЛЕ XXВВ. СТРАНЫ ЕВРОПЫ И СЕВЕРНОЙ АМЕРИКИ В КОН xix НАЧЛЕ XXВВ. 1. ЧЕРТЫ НОВОЙ ИНДУСТРИА
СТРАНЫ ЕВРОПЫ И СЕВЕРНОЙ АМЕРИКИ В КОН xix НАЧЛЕ XXВВ. СТРАНЫ ЕВРОПЫ И СЕВЕРНОЙ АМЕРИКИ В КОН xix НАЧЛЕ XXВВ. 1. ЧЕРТЫ НОВОЙ ИНДУСТРИА Развлечения во времена Петра 1
Развлечения во времена Петра 1 Завершение войны в Европе
Завершение войны в Европе Кронштадт и Шлиссельбургская крепость
Кронштадт и Шлиссельбургская крепость Военные реформы Петра I
Военные реформы Петра I