Содержание
- 2. * The Professional competences For: Specialists and managers – Apply the best persuading arguments Present information
- 3. * Results of the course The student should : Get practical skills in Search information Make
- 4. * Course’s content The topics include 3 parts: Present information Writing essay Making presentations French logic
- 5. * Teaching and Studying methods The interactive mode of colloquium group discussions role playing case studies
- 6. * Let start !
- 7. Methodology 2015 oct 30 Nadezhda N. Pokrovskaia PhD in Economics ; Doctoral degree in Sociology nnnnp@nnp@europe.com
- 8. * The purpose of the ESSAY SKILLS DEVELOPMENT COURSE is three-fold: 1 - Introduce the proper
- 9. * The purpose of the ESSAY SKILLS DEVELOPMENT COURSE is three-fold:: 2 – Focus on the
- 10. * The purpose of the ESSAY SKILLS DEVELOPMENT COURSE is three-fold: 3 - Develop formal academic
- 11. * Write an Essay 3 minutes Tell us something important A research topic on your choice
- 12. * The following topics will be covered within the lesson: Writing under time pressure The essay:
- 13. * Essays’ common mistakes The most common drawbacks: Spelling Contractions and slang Using “I” Lack of
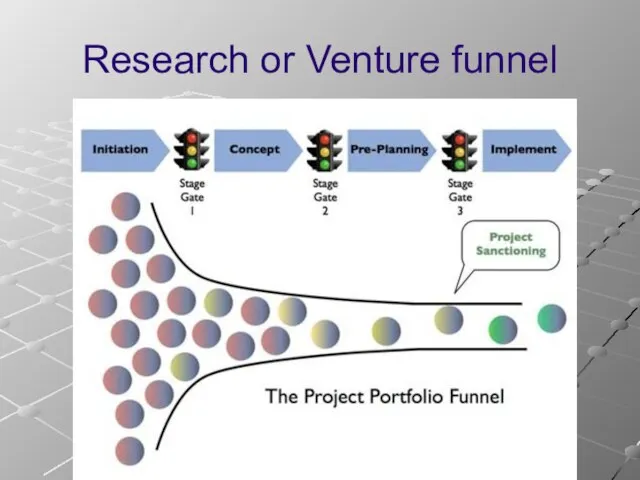
- 14. Research or Venture funnel
- 15. Essay Spiral
- 17. Tools – Step 1 Basic Key Phrase Research Search Engines’ Keyword Suggestion Tools : GoogleSearch Engines’
- 18. Tools – Step 2 Lateral Web Data Filters Search Engine Volume Predictors: Google TrendsSearch Engine Volume
- 19. Tools – Step 3 Search Intent and Semantic Web Search Intent Indicator Tools: Google SetsSearch Intent
- 20. Tools – Step 4 & 5 4: Social Web Filters Freshness & Buzz Filters News: Google
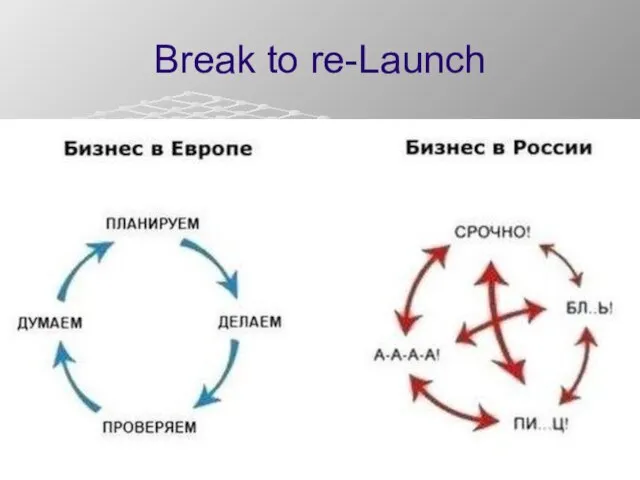
- 21. Break to re-Launch
- 22. Essay Exam
- 23. * Taking an Essay Exam – why? The purpose for writing a research paper ? to
- 24. * Taking an Essay Exam For successful in-class essays: Take into consideration your purpose, audience and
- 25. * PREPARING FOR THE EXAM: Preparation Tips Study connections between ideas when you’re studying, try to
- 26. * PREPARING FOR THE EXAM: Preparation Tips Prepare practice questions Try to prepare for questions that
- 27. * PREPARING FOR THE EXAM: Preparation Tips Always take notes throughout the semester Ask the instructor
- 28. * PREPARING FOR THE EXAM: Preparation Tips if the professor stresses certain information, there is a
- 29. * PREPARING FOR THE EXAM: Preparation Tips Analyze your essay questions from the past to see
- 30. * TAKING THE EXAM While you’re taking the exam, remember that it’s not simply what you
- 31. * Plan your time Take a few minutes to plan your time. Determine how many minutes
- 32. * Plan your time You will want to devote most of your time to the questions
- 33. * Plan your time If you are given the entire exam at once and can determine
- 34. * Plan your time As you read, make tentative choices of the questions you will answer
- 35. * Plan your time Remember that the easiest-looking question is not always as easy as it
- 36. * Read the questions thoroughly Take a few minutes before writing your essay to read the
- 37. * Read the questions thoroughly Read the questions carefully, and mark and circle the key words,
- 38. * If you see one of these terms, try to organize your essay to respond to
- 39. * Analyze the questions Decide what you are being asked to do. Try looking closely at
- 40. * Analyze the questions Focus on what you do know about the question, not on what
- 41. * Plan your answer Jot down the main points you intend to make as you think
- 42. * Structure Your Essay: For any type of essay, always take a minute or two to
- 43. * Structure Your Essay: Always state your thesis in the last sentence of your first paragraph.
- 44. * Structure Your Essay: When drafting your essay, do not worry about spelling and grammatical mechanics.
- 45. * Structure Your Essay: Avoid repetitiveness in the essay. Check that the information that you have
- 46. * Structure Your Essay: Structure your paragraphs clearly. Use headings, numbering, and other technical formats to
- 47. * Structure Your Essay: If the essay is not very clear, then you might want to
- 48. * Write out your essay, using good writing techniques As was said earlier, essay exams are
- 49. * CORRECT ESSAY STRUCTURE Essay Components
- 50. * The Thesis Statement / Introduction Paragraph This is the most important part of any well-written
- 51. * The thesis statement is the leader of your essay, because every other word written afterward
- 52. * Supporting Paragraphs: Everything written after the thesis statement is there to support it. The ideas
- 53. * First paragraph normally, the first paragraph of the essay body contains the strongest argument of
- 54. * Second paragraph The second paragraph contains correspondingly the second strongest argument of the essay. The
- 55. * Third paragraph The third paragraph opens the weakest argument to the reader. The topic sentence
- 56. * Hooks Introductory hook – At the start of the introduction, use a catchy sentence to
- 57. * Reverse hook – this is ideally placed on the first two sentences of the first
- 58. * Conclusion / Summary Paragraph This is the last paragraph in your essay. Here you will
- 59. * Conclusion / Summary Paragraph Do not repeat your thesis statement word for word, however. Restate
- 60. * Essay Types The ability to write effectively is one of the critical skills Typically this
- 61. * The Definition Essay The main function of the definition essay is to explain, or to
- 62. * The Persuasive Essay If you have to persuade your reader about something, your essay becomes
- 63. * The Argumentative Essay The art of argumentation is not an easy skill to acquire. Many
- 64. * The Cause and Effect Essay The cause and effect essay includes some elements of writing
- 65. * The Comparison and Contrast Essays The main purpose and function of compare and contrast essays
- 66. * Conclusion Essay is a way to talk about important things Next meeting – your own
- 67. * Time and place 3 weeks – 3 meetings: Friday 30 Oct Playing lecture Friday 7
- 68. * Assessment The whole score for this course is maximum 20 points and includes 2 parts:
- 69. * Presentation (8 points) Presentation topics At your choice Formal requirements : individually Power Point Presentation
- 70. * Examination (12 points) Written exam lasts 1 hour 30 minutes (1,5 hour) The exam includes:
- 71. * Some common rules Time be late ?? Attention mobile phone are to be switched off
- 73. Скачать презентацию



































































 Презентация на тему "Наша счастливая многодетная семья" скачать
Презентация на тему "Наша счастливая многодетная семья" скачать  Презентация "Фитофтороз томатов" - скачать презентации по Экологии
Презентация "Фитофтороз томатов" - скачать презентации по Экологии ИХ ИМЕНАМИ НАЗВАНЫ УЛИЦЫ СТАВРОПОЛЯ Страницы истории Ставрополья в истории России Информационно-образовательный комплекс по и
ИХ ИМЕНАМИ НАЗВАНЫ УЛИЦЫ СТАВРОПОЛЯ Страницы истории Ставрополья в истории России Информационно-образовательный комплекс по и Модуль « Основы мировых религиозных культур» Святые места мировых религиозных культур
Модуль « Основы мировых религиозных культур» Святые места мировых религиозных культур Исследовательский проект на тему:»Что я знаю о своем попугае?»
Исследовательский проект на тему:»Что я знаю о своем попугае?» Демографическая ситуация в России
Демографическая ситуация в России Возродим сад для потомков. К 600-летию прихода Святого преподобного Варнавы Ветлужского на Красную гору и Варнавинскую пустынь
Возродим сад для потомков. К 600-летию прихода Святого преподобного Варнавы Ветлужского на Красную гору и Варнавинскую пустынь ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОЕ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОЕ БЮДЖЕТНОЕ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ ВЫСШЕГО ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВНИЯ ОМСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ
ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОЕ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОЕ БЮДЖЕТНОЕ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ ВЫСШЕГО ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВНИЯ ОМСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ Презентация на тему "О трудном подростке замолвите слово" скачать
Презентация на тему "О трудном подростке замолвите слово" скачать  Игра «Умники и Умницы». Интеллектуальная игра для учащихся 9-11 классов (2 часа) Автор: учитель истории и обществознания МОУ «Буд
Игра «Умники и Умницы». Интеллектуальная игра для учащихся 9-11 классов (2 часа) Автор: учитель истории и обществознания МОУ «Буд Презентация на тему "Прболемы, которые подросток может решить сам" скачать
Презентация на тему "Прболемы, которые подросток может решить сам" скачать  Методы социометрии
Методы социометрии  Оружие казаков
Оружие казаков Как защититься от загрязненной воды? Подготовила: Рогачёва Елизавета ученица 3 «б» класса школы № 570 Невского района г. Санкт-Пет
Как защититься от загрязненной воды? Подготовила: Рогачёва Елизавета ученица 3 «б» класса школы № 570 Невского района г. Санкт-Пет Исследовательская работа по экологии «Болота и их роль в экологической системе планеты». Выполнил: ученик 4 «А» класса МОУ СОШ
Исследовательская работа по экологии «Болота и их роль в экологической системе планеты». Выполнил: ученик 4 «А» класса МОУ СОШ Презентация "Безопасность на воде"
Презентация "Безопасность на воде" 1 сентября 1997 года
1 сентября 1997 года Влияние окружающей среды на человека - презентация к уроку Окружающий мир_
Влияние окружающей среды на человека - презентация к уроку Окружающий мир_ Социологическая концепция М. Вебера
Социологическая концепция М. Вебера Свадебные традиции народов России
Свадебные традиции народов России Монумент Славы в Новосибирске
Монумент Славы в Новосибирске Управление процессом PR 1. Основные принципы управления и этапы разрешения ПР- проблем управления. 2.Первый этап: определение пр
Управление процессом PR 1. Основные принципы управления и этапы разрешения ПР- проблем управления. 2.Первый этап: определение пр Естественное и социальное в человеке
Естественное и социальное в человеке Окружающий мир 4-б класс Тема: Тундра.
Окружающий мир 4-б класс Тема: Тундра.  Вода в природе и её значение
Вода в природе и её значение Общество и общественные отношения Обществознание, 10 кл
Общество и общественные отношения Обществознание, 10 кл Этнонациональные отношения
Этнонациональные отношения Добровольческое объединение Искра
Добровольческое объединение Искра