What does decarbonisation even mean?
DECARBONISATION – process through which the share
of C in the primary
energy is decreased, with the ultimate goal of reaching 0% CO2 emissions –
Vision - ensure the production of energy AND all other related production
processes without using fossil fuels and idealy ensure 0 CO2 emissions
Increase in RES share
Energy efficiency
Reduction of GHG
Energy efficiency and RES;
recycling; waste management
Forestation, food production control
Infrastructure? Funding sources? Biofuels? Hydrogen? Lifestyle? Alimentary habits? New solutions for increased use of technology and the concept of energy efficiency?






 Виды туризма
Виды туризма Журналист? Кто такой?!
Журналист? Кто такой?! Новые стеклообразные материалы и методы их синтеза. Методы осаждения аморфной фазы из растворов
Новые стеклообразные материалы и методы их синтеза. Методы осаждения аморфной фазы из растворов Расчет основных режимов работы районной электрической сети в Ивановской области
Расчет основных режимов работы районной электрической сети в Ивановской области Культура ислама
Культура ислама Настилання підлоги ліноліумом
Настилання підлоги ліноліумом 20140123_agressiya_1_u_detey_kak_sledstvie_uvlecheniya_kompyuternymi_-_kopiya_0
20140123_agressiya_1_u_detey_kak_sledstvie_uvlecheniya_kompyuternymi_-_kopiya_0 Prezentatsia_po_literature (1)
Prezentatsia_po_literature (1) Энергия вокруг нас или как за нее не платить. Новые мировые тенденции 2016 года
Энергия вокруг нас или как за нее не платить. Новые мировые тенденции 2016 года Proekt_po_seti_pekaren_Bushe
Proekt_po_seti_pekaren_Bushe Домострой – энциклопедия ведения домашнего хозяйства
Домострой – энциклопедия ведения домашнего хозяйства Доклад начальника ОК и РЛС УФСИН России по Новгородской области. О результатах работы в учреждениях УИС Новгородской области
Доклад начальника ОК и РЛС УФСИН России по Новгородской области. О результатах работы в учреждениях УИС Новгородской области МБОУ СШ 9 Акция Синий платочек
МБОУ СШ 9 Акция Синий платочек Слайди. Новорічне асорті
Слайди. Новорічне асорті а
а Библейский цикл (древняя книга)
Библейский цикл (древняя книга) Интерактивная игра Загадки о войне
Интерактивная игра Загадки о войне Week 1 Lessons_1_2 (2)
Week 1 Lessons_1_2 (2) 20160507_ssha
20160507_ssha 1
1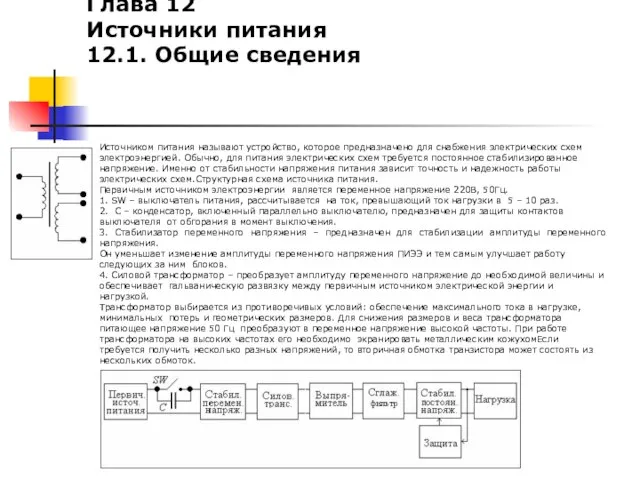 Источники питания. Общие сведения
Источники питания. Общие сведения Основы обогащения полезных ископаемых. Рудоподготовка. Измельчение. Классификация. Промывка
Основы обогащения полезных ископаемых. Рудоподготовка. Измельчение. Классификация. Промывка Презентация Технологические процессы по ТО и Ремонту автомобилей
Презентация Технологические процессы по ТО и Ремонту автомобилей Ленточные конвейеры, виды и назначение
Ленточные конвейеры, виды и назначение Особенности дистанционного обучения по физике
Особенности дистанционного обучения по физике С днём рождения
С днём рождения Do you have an example to follow?
Do you have an example to follow? Этикет принцессы
Этикет принцессы