Содержание
- 3. Introduction World Health Organization is established in 7th April 1948. It is a specialized, non-political, health
- 4. Vision “The attainment by all people the highest level of health”
- 5. Mission “To lead strategic collaborative efforts among Member States and other partners to promote equity in
- 6. Organizational Structure Secretariat Executive Board World Health Assembly Regions (6) Member Countries (193)
- 7. World Health Assembly It is the Supreme governing body of the organization. It meets annually generally
- 8. Executive Board The board composed of at least 18 members. Now there are 34 members. At
- 9. Secretariat Secretariat is Headed by the Director General who is the chief of technical and administrative
- 10. Divisions of Secretariat Epidemiological surveillance and health situation and trend assessment Communicable Disease Vector biology and
- 11. Divisions of Secretariat Mental health Strengthening of health services Family health Non communicable disease Health manpower
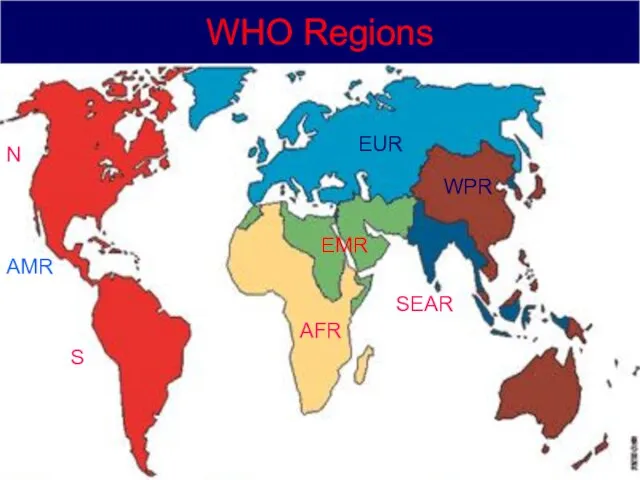
- 12. WHO Regions Regions Headquarters South East Asia New Delhi (India) Africa Brazzaville (Congo) American Washington DC
- 13. WHO Regions AMR AFR EMR SEAR EUR WPR N S WHO Regions
- 14. Member States 193 Member states among which 191 Members and 2 Associate members; Niue and the
- 15. Main Working Areas Prevention and control of specific disease Development of comprehensive health services Family health
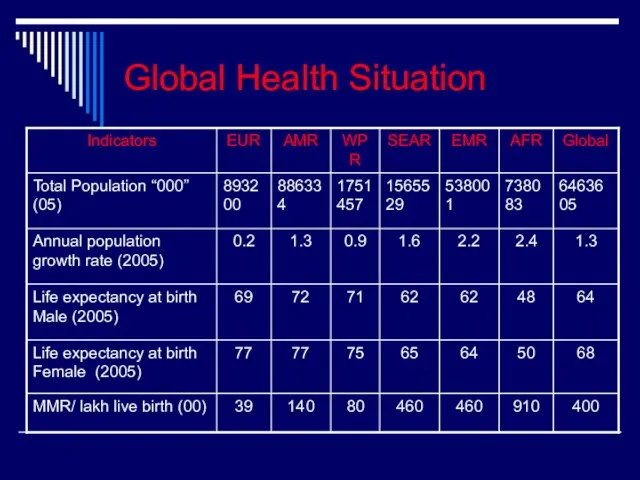
- 16. Global Health Situation
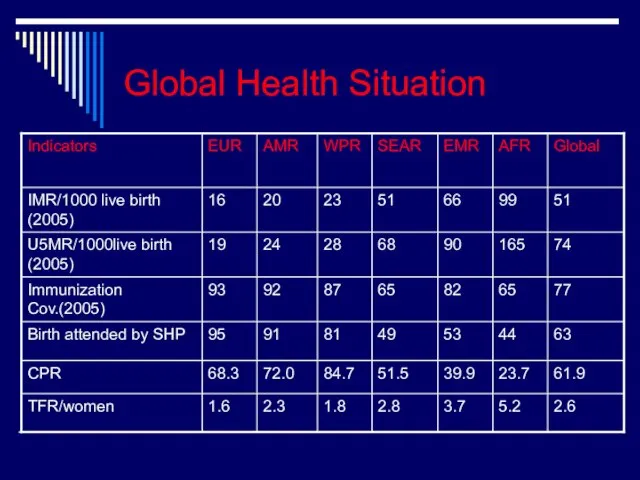
- 17. Global Health Situation
- 18. WHO Priorities Providing support to countries in moving to universal coverage with effective public health interventions;
- 19. Role in Public Health Providing leadership on matters critical to health and engaging in partnerships where
- 20. Role in Public Health Articulating ethical and evidence-based policy options; Providing technical support, catalyzing change, and
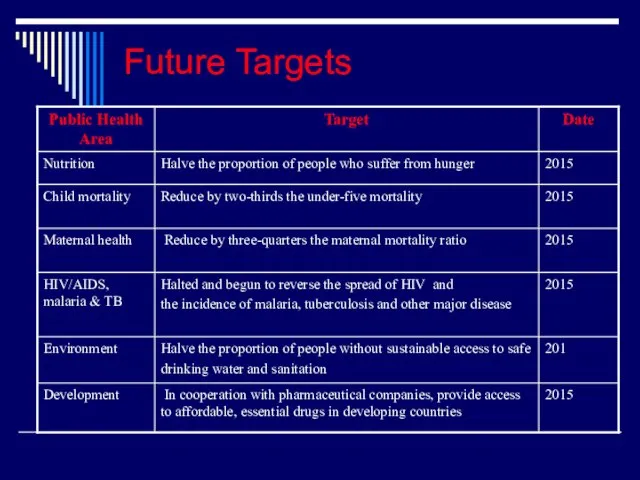
- 21. Future Targets
- 22. Future Targets
- 23. Future Targets
- 24. Major Achievements Small Pox Eradication Alma Ata Conference: Concept of PHC Global strategy for Health for
- 25. Comparative Advantages Neutral Organization to all member state. Nearly universal membership. Global presence and Networking. No
- 26. Major Challenges Investing in health to reduce poverty. Building individual and global health security. Promoting universal
- 27. Statement of Director General “I want my leadership to be judged by the impact of our
- 28. Conclusion “Although WHO has both opportunities and challenges; Its contribution is great to increase the quality
- 29. Suggestion Please. Any Question ???
- 31. Скачать презентацию
























 Самые дорогие отели мира
Самые дорогие отели мира Марина
Марина Введение
Введение Документооборот СЦ , взаимодействие региональной бухгалтерии и СЦ
Документооборот СЦ , взаимодействие региональной бухгалтерии и СЦ Отчет за 2020 год КРОО Родной очаг
Отчет за 2020 год КРОО Родной очаг Введение в строительное дело
Введение в строительное дело Жүрек толғанысы. Фотоальбом
Жүрек толғанысы. Фотоальбом Анализ бюджета Первого канала
Анализ бюджета Первого канала Агропромышленный комплекс (АПК)
Агропромышленный комплекс (АПК) ЕКІНЩІЛІК ГИПОТИРЕОЗ
ЕКІНЩІЛІК ГИПОТИРЕОЗ Мусульманские праздники
Мусульманские праздники Блокировка действия дистанционных защит при выходе параметров нагрузочного режима за допустимые значения
Блокировка действия дистанционных защит при выходе параметров нагрузочного режима за допустимые значения Простые и сложные предложения
Простые и сложные предложения Циклы обмена. Лекция 7
Циклы обмена. Лекция 7 КВП 1.1. Основи метрології і СІ (1)
КВП 1.1. Основи метрології і СІ (1) Ледовый дворец
Ледовый дворец Цех производства ферментированных продуктов
Цех производства ферментированных продуктов Приспособление для соединения с трубами на устье фонтанирующей скважины
Приспособление для соединения с трубами на устье фонтанирующей скважины Добровольческий отряд Вымпел
Добровольческий отряд Вымпел Страна секреты речи
Страна секреты речи Электротехника и электроника. Резонанс напряжений и резонанс токов в электрических цепях
Электротехника и электроника. Резонанс напряжений и резонанс токов в электрических цепях Презентация Чебурашка
Презентация Чебурашка Основы здорового питания
Основы здорового питания Урман
Урман Общие сведения о нефти и газе. Роль и значение буровых работ
Общие сведения о нефти и газе. Роль и значение буровых работ Редактирование растровых и векторных изображений
Редактирование растровых и векторных изображений Транспорт будущего
Транспорт будущего Определение содержания органических кислот в апельсиновом соке Добрый
Определение содержания органических кислот в апельсиновом соке Добрый