Содержание
- 2. CONTENTS: The executive branch of the power. The head of the state. Qualifications of candidates and
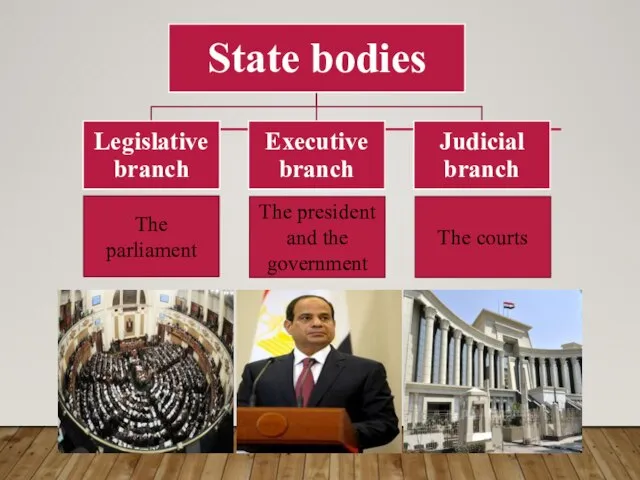
- 3. The parliament The president and the government The courts
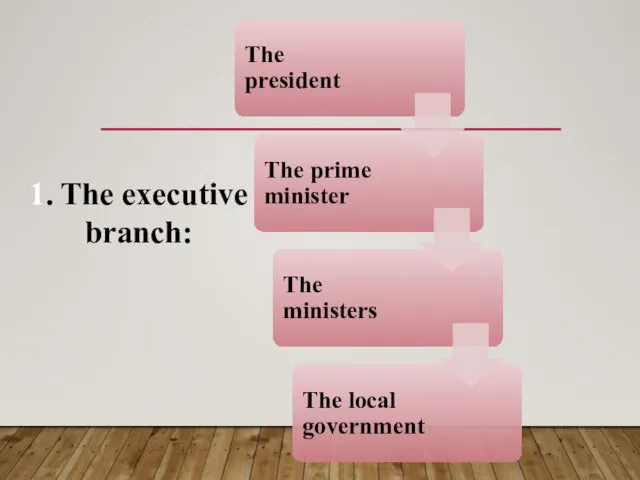
- 4. 1. The executive branch:
- 5. THE EXECUTIVE BRANCH: The executive branch is the state body exercising authority and holding responsibility for
- 6. THE HEAD OF THE STATE: The President is the head of state and the executive branch
- 7. He must be an Egyptian citizen and to be born to Egyptian parents (never having dual
- 8. He rules for a period of 4 years. The president can be re-elected for second term
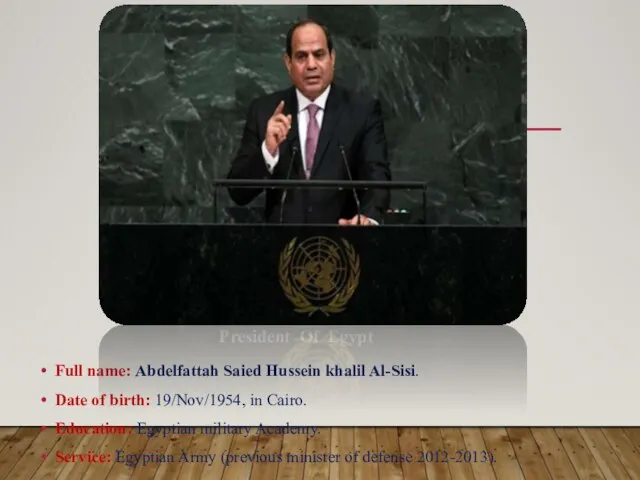
- 9. Full name: Abdelfattah Saied Hussein khalil Al-Sisi. Date of birth: 19/Nov/1954, in Cairo. Education: Egyptian military
- 10. Appoints the Prime Minister to form the government and can also dismiss the government with the
- 11. Resignation: the president can submit his resignation to the parliament to end his term and the
- 12. The president appoints the prime minister and orders him to form the council of ministers, then
- 13. The president, prime minister and the government
- 14. Ministry of defense. Ministry of education. Ministry of interior. Ministry of foreign affairs. Ministry of finance.
- 15. Developing and submitting the state budget to the parliament to be discussed. Managing the national property.
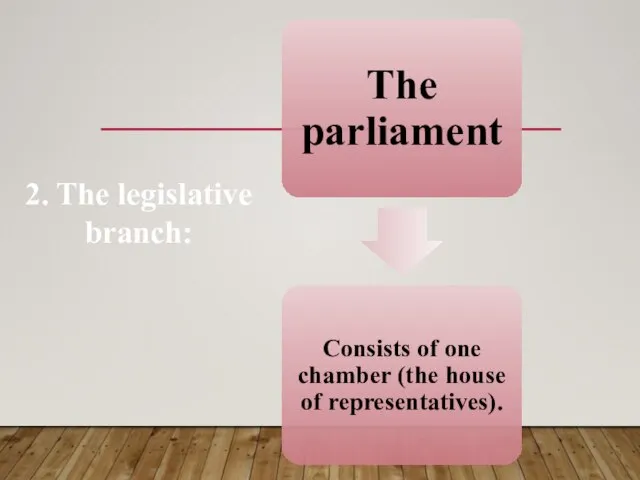
- 16. 2. The legislative branch:
- 17. The house of representatives
- 18. THE EGYPTIAN PARLIAMENT: The Parliament of Egypt is currently a unicameral legislature. The Parliament is located
- 19. QUALIFICATIONS FOR THE CANDIDATES: He must be an Egyptian citizen To be at least 25 years
- 20. FUNCTIONS OF THE PARLIAMENT: The parliament develops and enacts laws. Approves the general policy of the
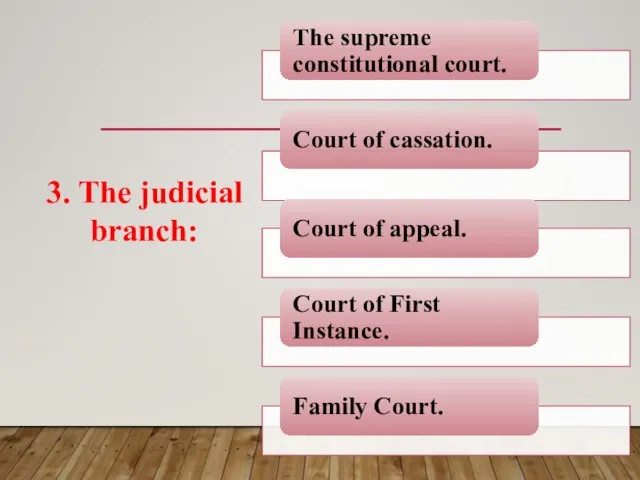
- 21. 3. The judicial branch:
- 22. THE SUPREME CONSTITUTIONAL COURT: The Supreme Constitutional Court is the highest judicial power in the country,
- 23. The supreme constitutional court in Cairo
- 24. COURT OF CASSATION: The Court of Cassation, the only one in its category, was established in
- 25. COURT OF APPEAL: Courts of Appeal, have the competence to consider rulings by the courts of
- 26. COURT OF FIRST INSTANCE: These courts of first instance have the competence to consider lawsuits filed
- 28. Скачать презентацию




















 Граждане (физические лица) как субъекты гражданских правоотношений. Тема 3
Граждане (физические лица) как субъекты гражданских правоотношений. Тема 3 Право в системе социальных норм
Право в системе социальных норм Миграционный центр около д. Сахарово
Миграционный центр около д. Сахарово Алиментные обязательства членов семьи. Усыновление (удочерение)
Алиментные обязательства членов семьи. Усыновление (удочерение) Международный уголовный суд
Международный уголовный суд Общие вопросы трудового законодательства
Общие вопросы трудового законодательства Основи конституційного права України
Основи конституційного права України Трудовой договор
Трудовой договор Українська символіка
Українська символіка Покупка имущества на торгах по банкротству
Покупка имущества на торгах по банкротству Иркутская область, субъект Российской Федерации
Иркутская область, субъект Российской Федерации Преступления на территории г. Москвы
Преступления на территории г. Москвы Административное право России
Административное право России Основы правового регулирования трудовых отношений
Основы правового регулирования трудовых отношений Реестр государственных служащих. Комплектование аппарата государства государственными служащими
Реестр государственных служащих. Комплектование аппарата государства государственными служащими Фонд Международный стандарт. Юридическая помощь и правовое просвещение жителей города при создании ТСЖ
Фонд Международный стандарт. Юридическая помощь и правовое просвещение жителей города при создании ТСЖ Правовые основы семейного устройства детей-сирот и детей, оставшихся без попечения родителей
Правовые основы семейного устройства детей-сирот и детей, оставшихся без попечения родителей Семья в современном обществе. Законодательство о семье
Семья в современном обществе. Законодательство о семье Организация использования земель особо охраняемых природных территорий
Организация использования земель особо охраняемых природных территорий Порядок технологического присоединения жилых помещений нуждающихся граждан к газораспределительной сети
Порядок технологического присоединения жилых помещений нуждающихся граждан к газораспределительной сети Методы криминалистического исследования волокнистых материалов и изделий из них
Методы криминалистического исследования волокнистых материалов и изделий из них Государство и власть
Государство и власть Система электронного делопроизводства и документооборота
Система электронного делопроизводства и документооборота Знай и люби свой край
Знай и люби свой край Судебное разбирательство в арбитражном процессе
Судебное разбирательство в арбитражном процессе Правоохранительные органы
Правоохранительные органы Capital punishment. For and against
Capital punishment. For and against Хищение. Общие характеристики
Хищение. Общие характеристики