Содержание
- 2. Goals Recognize the importance of data, their issues, and their life cycle. Describe the sources of
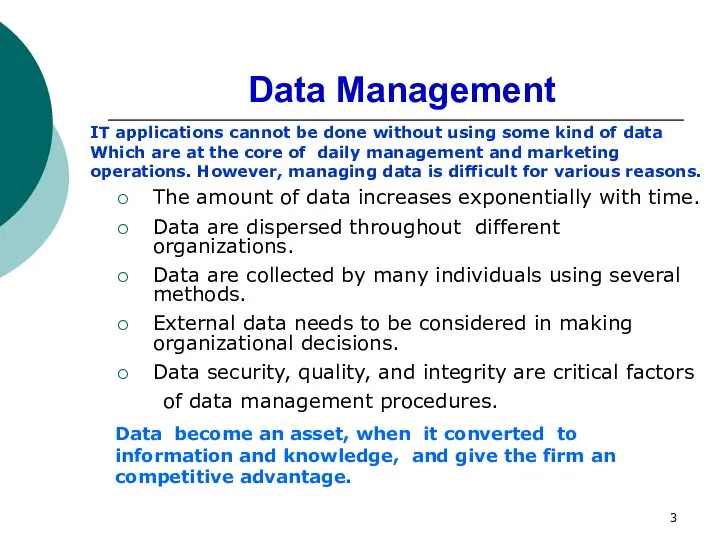
- 3. Data Мanagement The amount of data increases exponentially with time. Data are dispersed throughout different organizations.
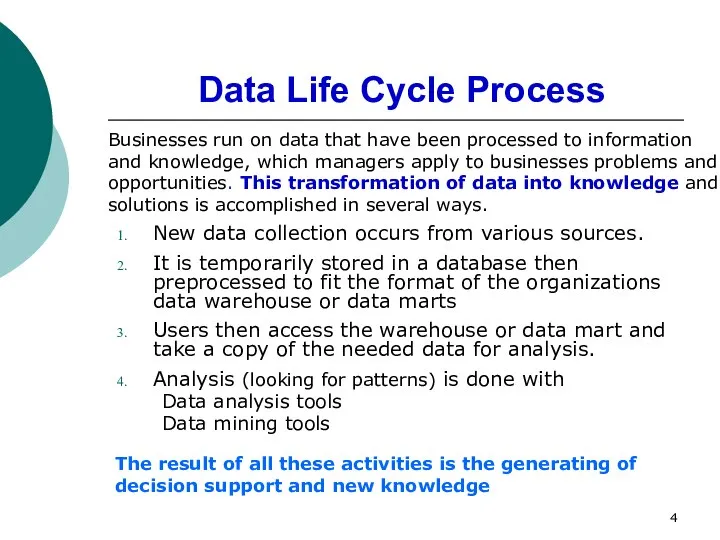
- 4. Data Life Cycle Process New data collection occurs from various sources. It is temporarily stored in
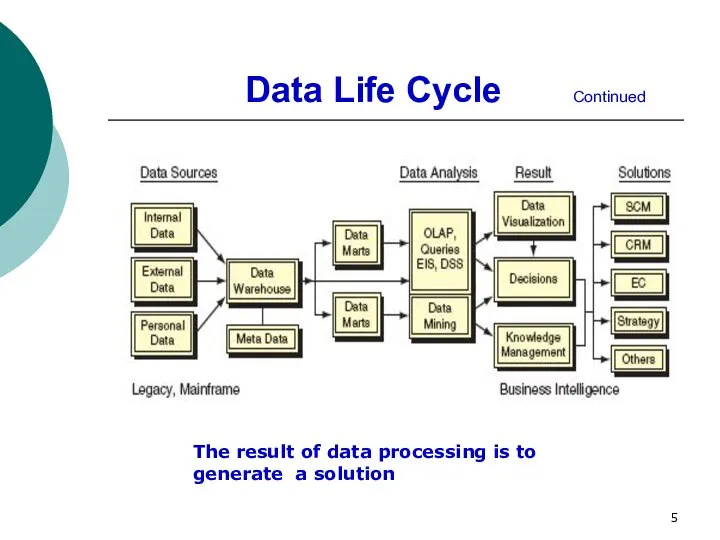
- 5. Data Life Cycle Continued The result of data processing is to generate a solution
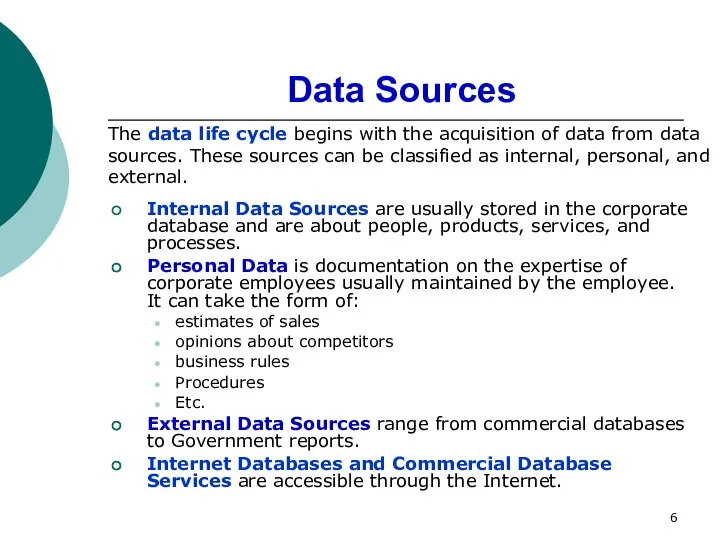
- 6. Data Sources Internal Data Sources are usually stored in the corporate database and are about people,
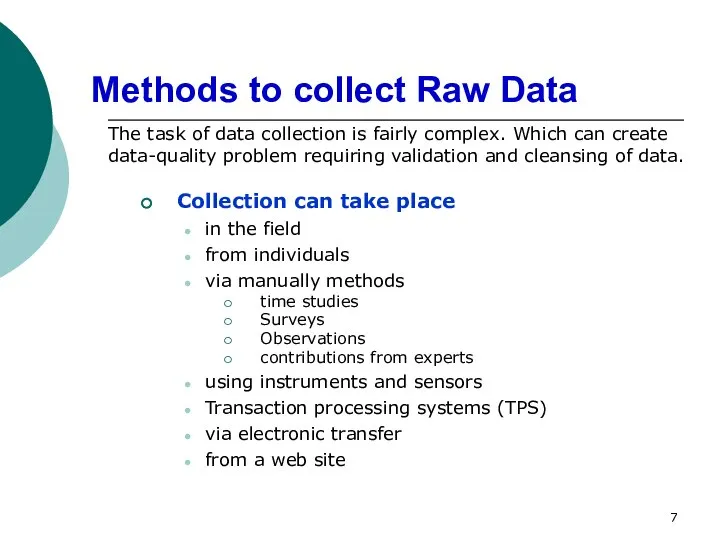
- 7. Methods to collect Raw Data Collection can take place in the field from individuals via manually
- 8. Methods for managing data collection A Data Flow Manager consists of a decision support system a
- 9. Data Quality and Integrity Internal DQ: Accuracy, objectivity, believability, and reputation. Accessibility DQ: Accessibility and access
- 10. \ Document Management Maintaining paper documents, requires that: Everyone have the current version An update schedule
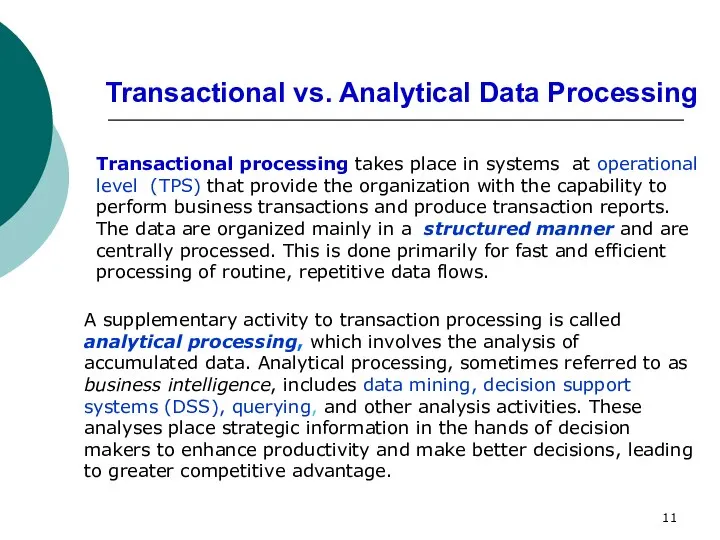
- 11. Transactional vs. Analytical Data Processing Transactional processing takes place in systems at operational level (TPS) that
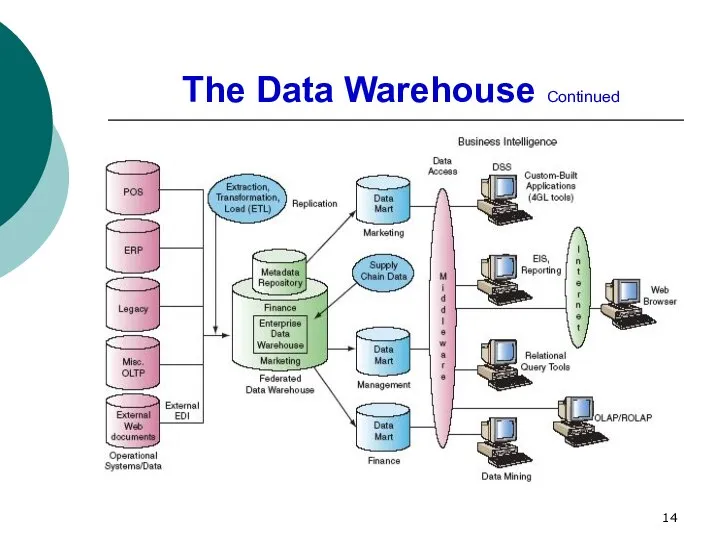
- 12. The Data Warehouse Benefits of a data warehouse are: The ability to reach data quickly, since
- 13. The Data Warehouse Continued Characteristics of data warehousing: Time variant. The data are kept for many
- 14. The Data Warehouse Continued
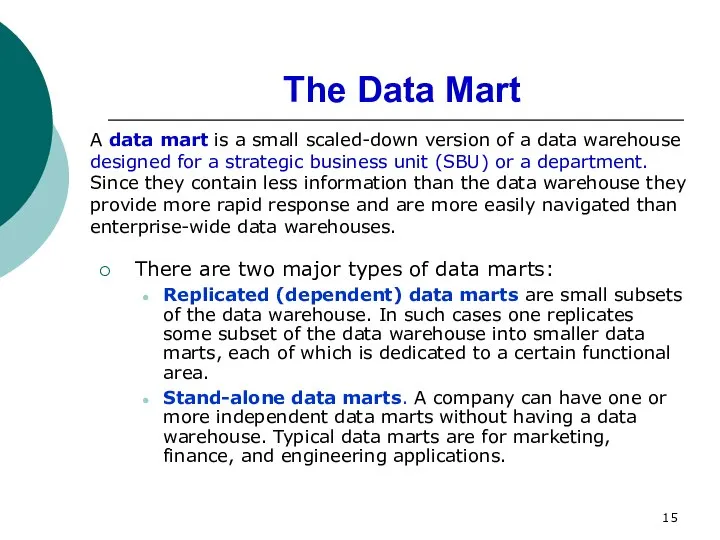
- 15. The Data Mart There are two major types of data marts: Replicated (dependent) data marts are
- 16. The Data Cube One intersection might be the quantities of a product sold by specific retail
- 17. Operational Data Stores It is typically used for short-term decisions that require time sensitive data analysis
- 18. Business Intelligence Business intelligence includes: outputs such as financial modeling and budgeting resource allocation coupons and
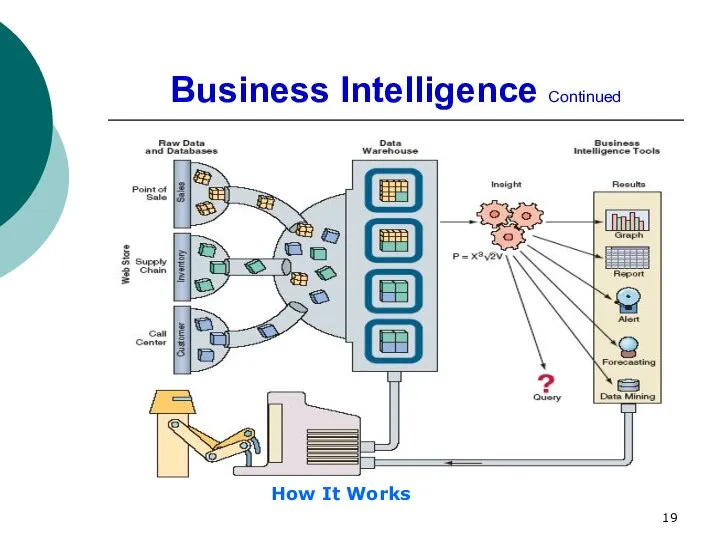
- 19. Business Intelligence Continued How It Works
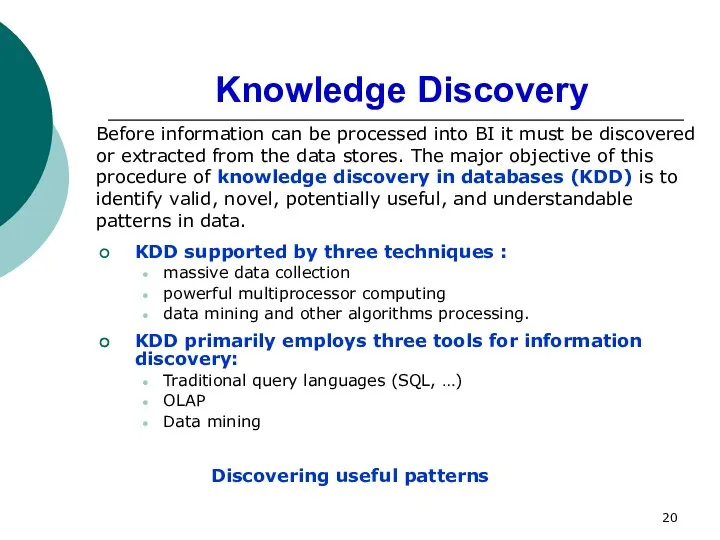
- 20. Knowledge Discovery KDD supported by three techniques : massive data collection powerful multiprocessor computing data mining
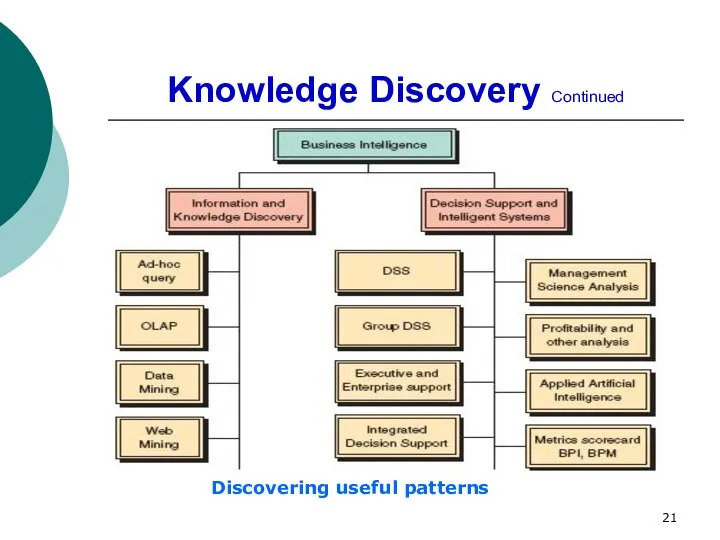
- 21. Knowledge Discovery Continued Discovering useful patterns
- 22. Queries User requests are stated in a query language and the results are subsets of the
- 23. Online Analytical Processing ROLAP (Relational OLAP) is an OLAP database implemented on top of an existing
- 24. Data Mining Data mining technology can generate new business opportunities by providing: Automated prediction of trends
- 25. Data Mining Techniques Case-based reasoning. uses historical cases to recognize patterns Neural computing is a machine
- 26. Data Mining Tasks Classification. Infers the defining characteristics of a certain group. Clustering. Identifies groups of
- 27. Data Visualization Multidimensional visualization means that modern data and information may have several dimensions. Dimensions: Products
- 28. Data Visualization Continued Measures: Money Sales volume Head count Inventory profit Actual versus forecasted results. Time:
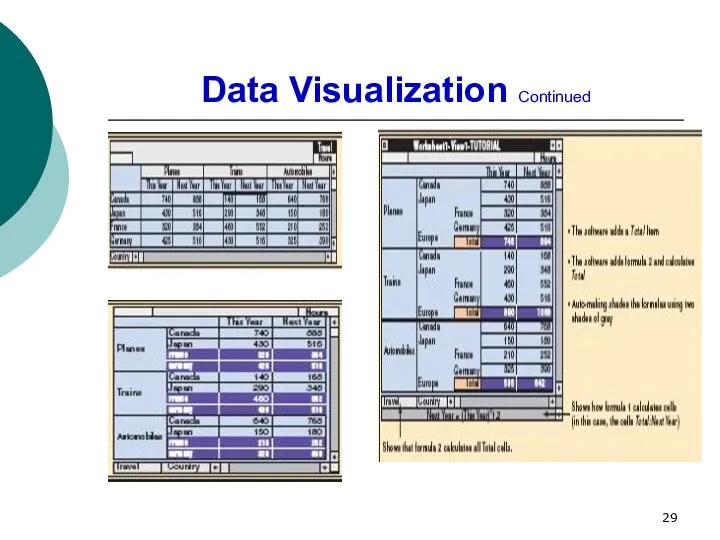
- 29. Data Visualization Continued
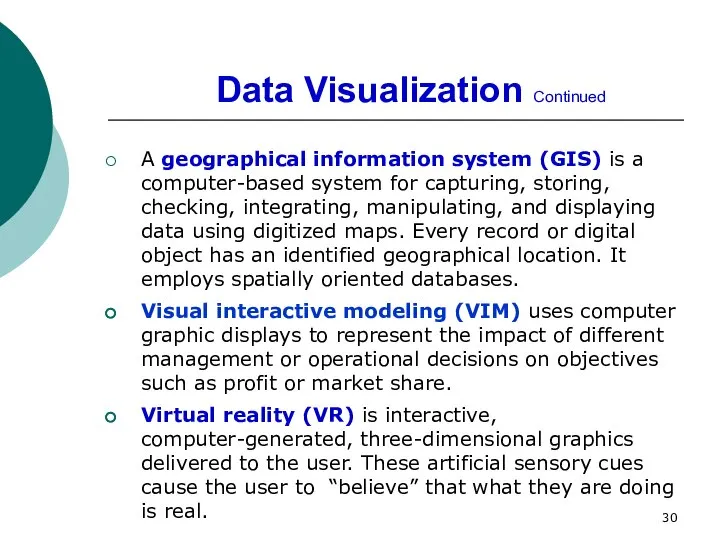
- 30. Data Visualization Continued A geographical information system (GIS) is a computer-based system for capturing, storing, checking,
- 31. Specialized Databases Marketing transaction database (MTD) combines many of the characteristics of the current databases and
- 32. Web-based Data Management Systems Enterprise BI suites and Corporate Portals integrate query, reporting, OLAP, and other
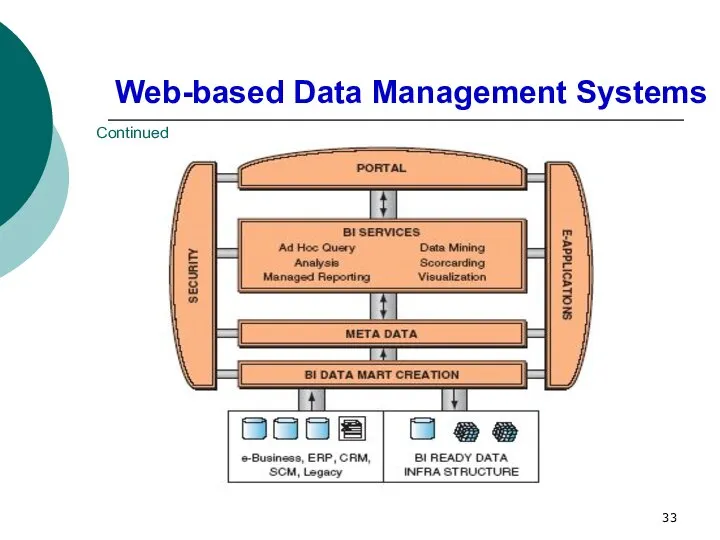
- 33. Web-based Data Management Systems Continued
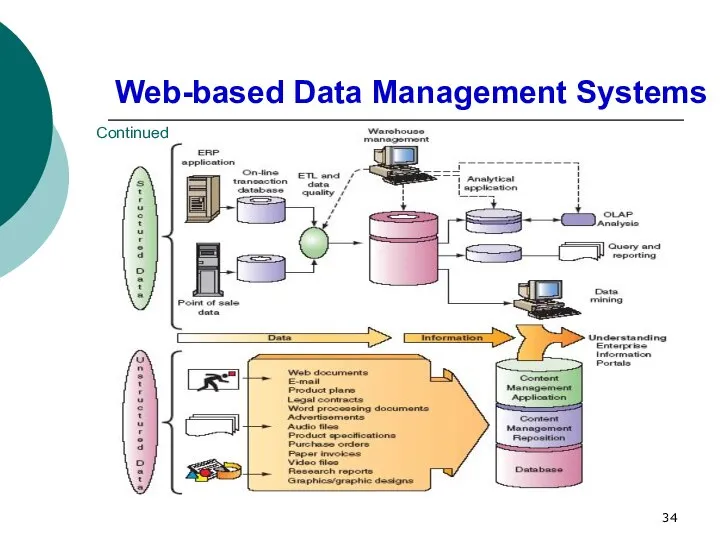
- 34. Web-based Data Management Systems Continued
- 36. Скачать презентацию

















 Информационные технологии в системах управления гостиничным бизнесом
Информационные технологии в системах управления гостиничным бизнесом Педсовет «Планирование работы школы на 2011-2012 учебный год» 30.08.2011
Педсовет «Планирование работы школы на 2011-2012 учебный год» 30.08.2011 Разграничение... Знакомство с синонимами
Разграничение... Знакомство с синонимами Модульное программирование
Модульное программирование  Презентация на тему "Коронарное кровообращение и его регуляция." - скачать презентации по Медицине
Презентация на тему "Коронарное кровообращение и его регуляция." - скачать презентации по Медицине Наноэлектроника. Программы по нанотехнологиям
Наноэлектроника. Программы по нанотехнологиям Хладотранспорт
Хладотранспорт Заюшкина избушка - презентация для начальной школы
Заюшкина избушка - презентация для начальной школы Производственный контур в Microsoft Business Solutions
Производственный контур в Microsoft Business Solutions  Антонио Гауди - гениальный архитектор, великий модернист
Антонио Гауди - гениальный архитектор, великий модернист Теория международных отношений: эволюция развития
Теория международных отношений: эволюция развития Какой-то непонятный проект «Полярный день. Медиагород»
Какой-то непонятный проект «Полярный день. Медиагород» Наследие Древнего Востока. Здесь раскрываются тайны Древнего Востока
Наследие Древнего Востока. Здесь раскрываются тайны Древнего Востока Презентация стационарная система автоматической балансировки
Презентация стационарная система автоматической балансировки Тензоры диэлектрической и магнитной проницаемости вещества
Тензоры диэлектрической и магнитной проницаемости вещества Агния Барто Стихотворения
Агния Барто Стихотворения  Подготовка к ЕГЭ Задание А12
Подготовка к ЕГЭ Задание А12 Презентация "Мегалиты. Дольмены, менгиры, кромлехи" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Мегалиты. Дольмены, менгиры, кромлехи" - скачать презентации по МХК Расчетно-графическая работа по курсу: "Производственная база строительства"
Расчетно-графическая работа по курсу: "Производственная база строительства" Профилактика заболеваний пародонта
Профилактика заболеваний пародонта Влияние международных отношений на политическую карту мира
Влияние международных отношений на политическую карту мира Программирование передачи информации между компьютерами по сети. Клиент-серверные приложения
Программирование передачи информации между компьютерами по сети. Клиент-серверные приложения Анемии гемобластозы
Анемии гемобластозы  Алексей Викторович Щусев
Алексей Викторович Щусев Экспрессионизм в Германии и Австрии (1). Мост и Синий Всадник
Экспрессионизм в Германии и Австрии (1). Мост и Синий Всадник Конструктивная основа многоэтажного здания
Конструктивная основа многоэтажного здания ГМО МЕТОДИСТОВ УДОД г. ВОЛЖСКА ПРОГРАММА РАЗВИТИЯ ОУ По материалам методического пособия для руководителей образовательных уч
ГМО МЕТОДИСТОВ УДОД г. ВОЛЖСКА ПРОГРАММА РАЗВИТИЯ ОУ По материалам методического пособия для руководителей образовательных уч ГЕРОНТОСТОМАТОЛОГИЯ
ГЕРОНТОСТОМАТОЛОГИЯ